Multiple choice questions-II from PRADEEP PHYSICS (HINGLISH) PROPERTIES OF BULK MATTER for Class 11
| Class 11 | PHYSICS |
| Chapter | PROPERTIES OF BULK MATTER |
| PRADEEP PHYSICS (HINGLISH) | Multiple choice questions-II |
| Medium | English |
| Academic Year | 2023-2024 |
Question 3
A wire of length L and radius a rigidlyl fixed at one end. On stretching the other end of the wire with a force F, the increase in its length is L, if another wire of same material but of length 2 L and radius 2 a is stretched with a force 2 F, the increase in its length will be View SolutionQuestion 5
An alumminium rod and steel wire of same length and cross-section are attached end to end. Then compound wire is hung fron a rigid support and load is suspended from the free end. Y for steel is (207) times of aluminium. The ratio of increase in length of steel wire to the aluminium wire is View SolutionQuestion 85
A cylindrical metallic rod in thermal contact with two reservation of heat at its two ends conducts an amount of heat Q in time t. The metallic rod is melted and the material is formed into a rod of half the radius of the original rod. What is the amount of heat conducted by the new rod when placed in thermal contact with the two reservation in time t?View SolutionQuestion 105
Two parallel wires A and B of same meterial are fixed to rigid support at the upper ends and subjected to same load at the lower ends. The subjeted to same load at the lower ends. The lengths of the wire are in the ration 4 : 5 and their radii are in the ratio 4 : 3 the increase in the length of wire A is 1 mm. Calculate the increase in the length of wire A is 1mm. Calculate the increase in the length of the wire B.View SolutionQuestion 110
Two wires of equal cross section but one made of steel and the other of copper, are joined end to end. When the combination is kept under tension, the elongations in the two wires are found to be equal. Find the ratio of the lengths of the two wires. Young modulus of steel =2.0×1011Nm−2 and that of copper =1.1×101Nm−2View SolutionQuestion 126
A load of 31.4 kg is suspended from a wire of radius 10−3 m and density 9×103kg/m3 Calculate the change is temperature of the wire if 75% of the work done is converted into heat. The Young's modulus and the specific heat capactiy of the meterial of the wire are 9.8×1010N/m2and490J/kg/K respectively.View SolutionQuestion 130
When the weight on a string is change from 3.0 kg to 5.0 kgs the elengation changes from 0.61 mm to 1.02 mm. How much work is done during this extension of the string ? Find the Young's modulus of meterical of string if it is 1m in length and has a cross-sectional area 0.4×10−4m2.View SolutionQuestion 131
A solid sphere of radius R made of a material of bulk modulus K is surrounded by a liquid in a cylindrical container. A massless pistion of area A floats on the surface of the liquid. When a mass M is placed on the piston to compress the liquid the fractional change in the radius of the sphere, δR/R, is .............View SolutionQuestion 142
The menual of a car instructs the owner to inflate the tyres to pressure of 200 kPa. (a) What is the recommended gauge pressure ? (b) What is the recommended absolute pressure ? (c ) If after the required inflation of the tyres, the car is driven to a mountain peak. where the atmospheric pressrre is 10 % below that at sea level, what will be the tyre gauge read ? Atmospehric pressure =1.01×105Pa.View SolutionQuestion 151
A hydraulic press with the larger piston of diameter 35 cm at a heigth of 1.5 m relative to the smaller piston of diameter 10 cm. The mass on the smaller piston is 20 kg. What is the force exerted on the load placed. On the larger piston ? The density of oil in the press is 750kgm−3View SolutionQuestion 160
A rubber ball of mass 10 gram and volume 15cm3 is dipped in water to a depth of 10m. Assuming density of water uniform throughtout the depth, find (a) the ac celeration of the ball, and (b) the time taken by it to reach the surface if it is relased from rest. (Takeg=980cm/s2)View SolutionQuestion 162
A spring balance reads 10 kg when a bucket of water is suspended from it. What is the reading on the spring balance when (i) an ice cube of mass 1.5 kg is put into the bucket (ii) an iron piece of mass 7.8 kg suspended by another spring is immersed with half its volume inside the water n the bucket. Relative density of iron = 7.8View SolutionQuestion 165
A concrete sphere of radius R has cavity of radius r which is packed with sawdust. The specific gravities of concrete and sawdust are respectively 2.4and0.3 for this sphere to float with its entire volume submerged under water. Ratio of mass of concrete to mass of swadust will be View SolutionQuestion 170
A soap film is formed on a rectangular frame of 7 cm side dipping into a scop solution. The frame hangs from the arm of a balance. An extra weight of 0.4 gram is to be placed in the opposite pan to balance the pull on the frame. Caluclate the surface tension of the soap solution. View SolutionQuestion 177
If a number of litle of droplets of water of surface tension S, all of the same radius r combine to from a single drop of radius R and the energy relased is converted into kinetic energy. Find the velocity acquired by the bigger drop. If the energy relased in converted inot heat, find the rise in temperature.View SolutionQuestion 179
A glass tube of 1mm diameter is dipped vertically into a tube of mercury, with its lower end 3 cmm below the mercury surface. What must be the gauge pressure of air in the tube to blow a hemispherical bubble at its lower and ? Given, density of mercury =13.6g/cc and surface tension of mercury =0.540Nm−1.g=10ms−2.View SolutionQuestion 181
There is an air bubble of radius 2.0 mm in a liquid of surface tension 0.070Nm−1 and density 103kgm−3 The bubble is at a depth of 12.0 cm below the free surface of liquid. By what amount is the pressure inside the bubble is greater then the atmospheric pressure ? Use g=10m/s2.View SolutionQuestion 192
A U-tube of uniform cross section (see figure) is partially filled with a liquid I. Another liquid II which does not mix with liquid I is poured into one side. It is found that the liquid levels of the two sides of the tube are the same, while the level of liquid I has risen by 2cm. If the specific gravity of liquid I is 1.1, the specific gravity of liquid II must be
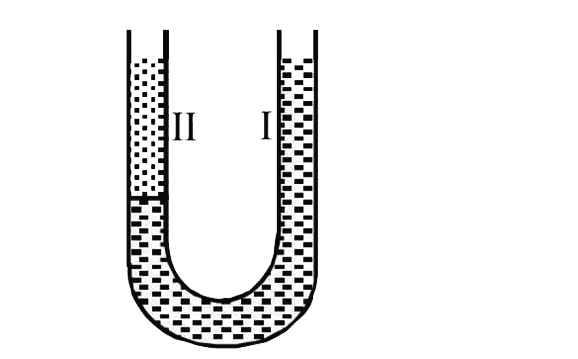 View Solution
View SolutionQuestion 196
If a number of litle of droplets of water of surface tension S, all of the same radius r combine to from a single drop of radius R and the energy relased is converted into kinetic energy. Find the velocity acquired by the bigger drop. If the energy relased in converted inot heat, find the rise in temperature.View SolutionQuestion 199
A flat plate of 20 cm squre moves over another similar plate with a thin layer of 0.4 cm of a liquid between them. If a force of one kg. wt. moves one of the plates uniformly with a velocity with a velcoity of 1ms−1 calculate the strain rate, sheraing stres and coefficient of viscosity.View SolutionQuestion 201
A capillary tube of 1mm diameter and 20 cm long is fitted horizontally to a vessel kept full of alcohol of density 0.8 gm//c.c. The depth of centre of capillary tube below the surface of alcohol is 20 cm. If the visosity of oil is 0.12dynecm−2 s, find the amount of liquid that will flow in 5 minuts. View SolutionQuestion 202
Two capillary tubes of length 15 cm and 5 cm and radii 0.06 cmand 0.02 cm respectively are connected in series. If the pressure difference across the end faces is equal to pressure of 15 cm high water column, then find the pressure difference across the (i) first tube and (ii) second tube.View SolutionQuestion 204
Two tubes A and B of length 80 cm and 40 cm have radii 0.1 mm and 0.2 mm respectively are connected in series end to end. If a liquid passing through tow tubes is entering A at a pressure of 82 cm of mercury and leaving B at a pressure of 76 cm of mercury. Find the pressure at the junction of A and B.View SolutionQuestion 205
The level of liquid in a cylindrical vessel is kept constant at 30cm. It has three identical horizontal tubes A, B and C of length 40 cm each coming out at heights 0, 5 and 10 cm respectively. Calculate the length of a single overflow tube of the same radius as that of identical tubes which can replace the three when placed horizontally at the bottom of the cylinder. View SolutionQuestion 224
Each of the two wings of an aeroplane has area 30m2. The speed of the air on the upper and lower surfaces of theon the wing of aeroplane are 90ms−1 and 70ms−1 respectively. If the plane is in level flight at constant speed, find the uplift and the mass of the aeroplane. Given density of air =1.29kgm−3.View SolutionQuestion 226
A hole of area 1mm2 opens near the bottm of a large- water storage tank, and a stream of water shoots from it. If the top of water in the tank is to be kept at 20 m above the point of leak , how much water in litres//s should be added to the reservoir tank to keep this level ? (g=10m/s2).View SolutionQuestion 231
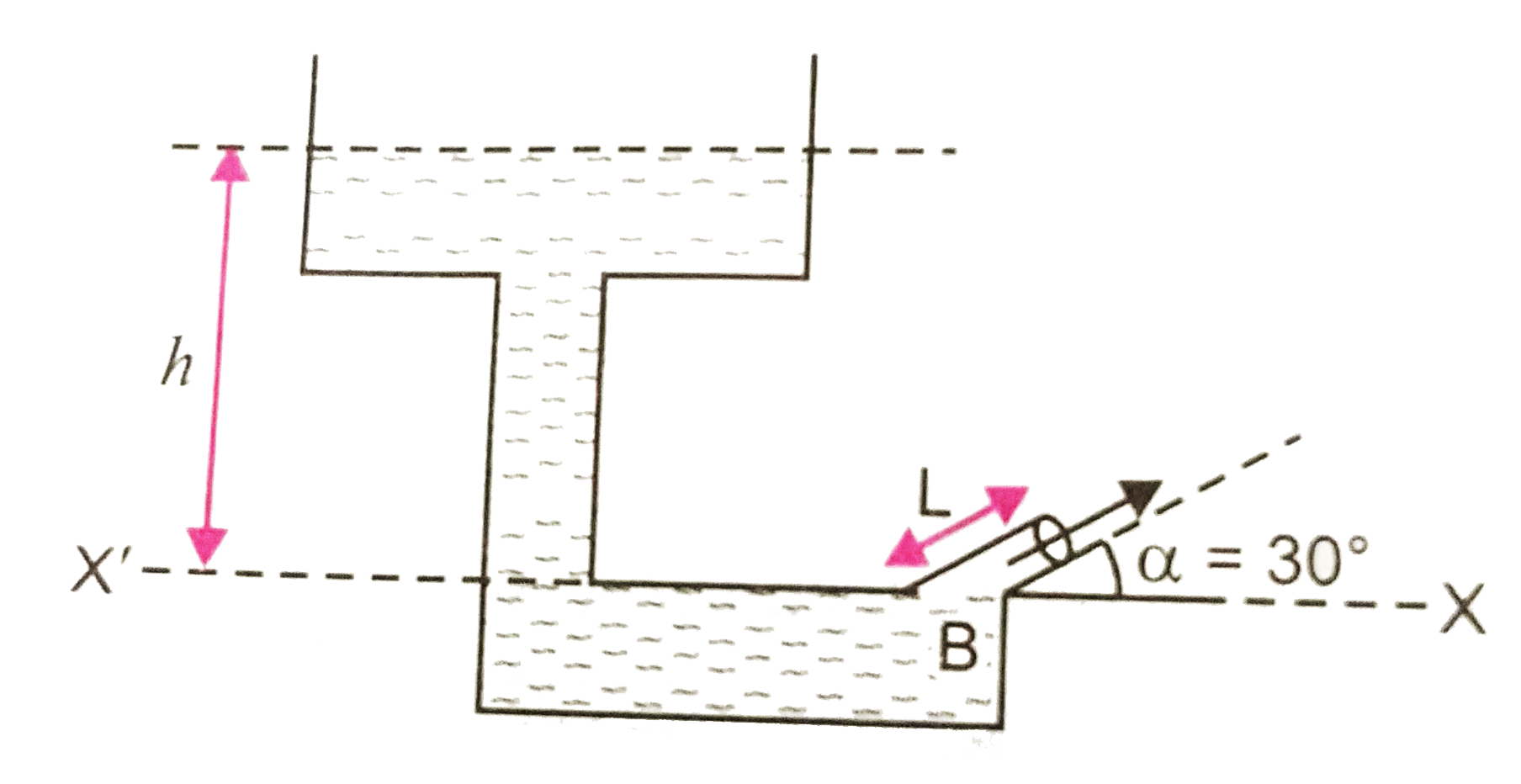
The opening near the bottom of the vessel shown in the figure has an area A. A disc is held against the opening keep the liquid from running out. Let F1 be the net forces on the disc applied by liquid and air in this case. Now the disc is moved away from the opening a short distance. The liquid comes out and strikes the disc in elastically. Let F2 be the force exerted by the liquid in this condition. The F1/F2 is
 View Solution
View SolutionQuestion 234
A large open tank has two holes in the wall. One is a square hole of side L at a depth h from the top and the other is a circular hole of radius r at a depth 4h from the top. Whwn the tank is completely filled with water, the quantity of water flowing out per second from both the holes are the same. What is the value of r?View SolutionQuestion 237
The rate of flow of the liquid through the tube of length l and radius r, connected across a perssure haed h be V. If two tubes of the same length but of radius r and r/2 are connected in series, across the same pressure head h, find the rate of flow of liquid through the combination. If both the tubes are connected inparallel to the same pressure head, then find the rate of flow of liquid through the combination.View SolutionQuestion 238
Water stand at a heigh H in a tank whose sides are vertical. An orifice is made at the depth h on one of the wall Fig. 7(c).25. The emerging stream of water strikes at the distance R from the tank on the floor./ Find the relation for R in term of h, and H. When R is maxmimum, how h and H are related.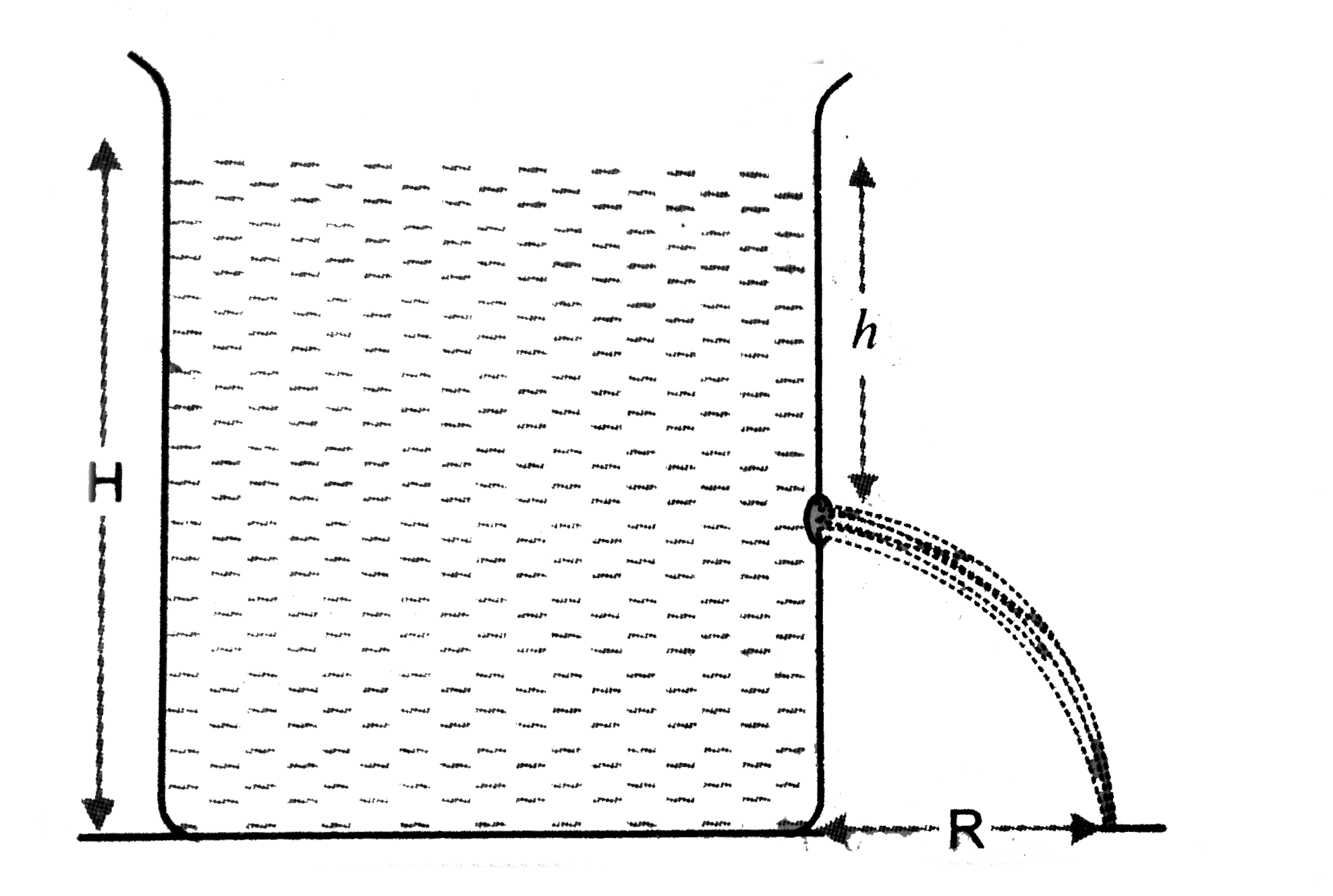 View Solution
View SolutionQuestion 239
There capillaries of length l, 2l and l/2 are connected in series. Their radii are r, r/2 and r/3 respectively. If stream line flow is maintained and the pressure difference across the first capillary tube is P1, find the pressure difference across (i) the second and (ii) the thired capillary tube. View SolutionQuestion 240
Air is streaming past a horizontal air plane wing such that its speed is 120ms−1 over the upper surface and 90ms−1 at the lower surface. If the density of air is 1.3kgm−3m find the difference in pressure between the top and bottom of the wing. If the wing is 10m long and has an average width of 2m, calculate the gross lift of the wing.View SolutionQuestion 250
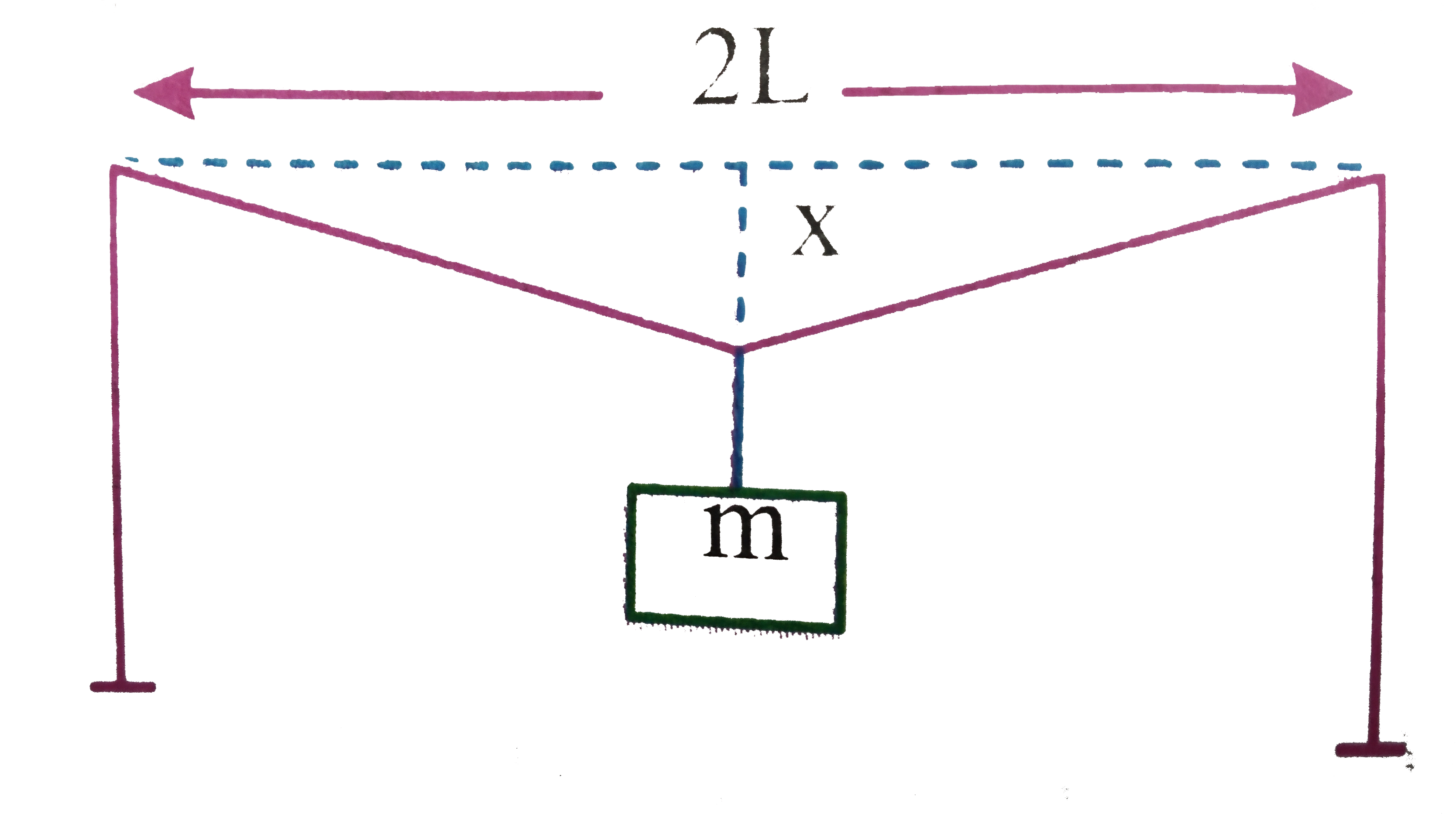
A rail track made of steel having 20m is clamped on a railway line at its two ends as show in Fig. 7(d).17. On a summer day due to rise in temperature by 22∘C, it is deformed as show in Fig. 7(d).17 .Find displacement of the center (x) . Given cofficient of liner expansion of steel is 1.2×10−5.∘C−1.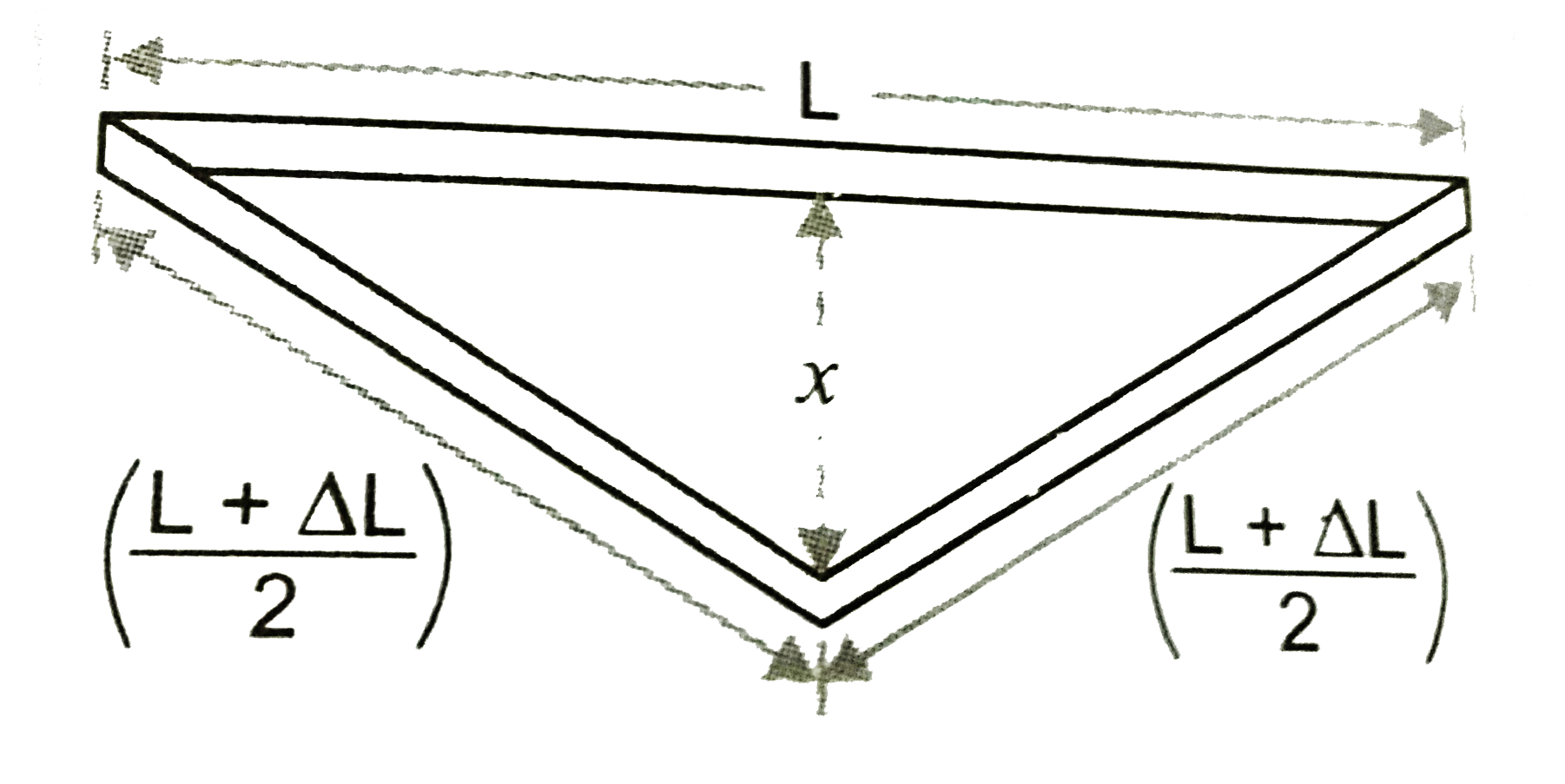 View Solution
View SolutionQuestion 252
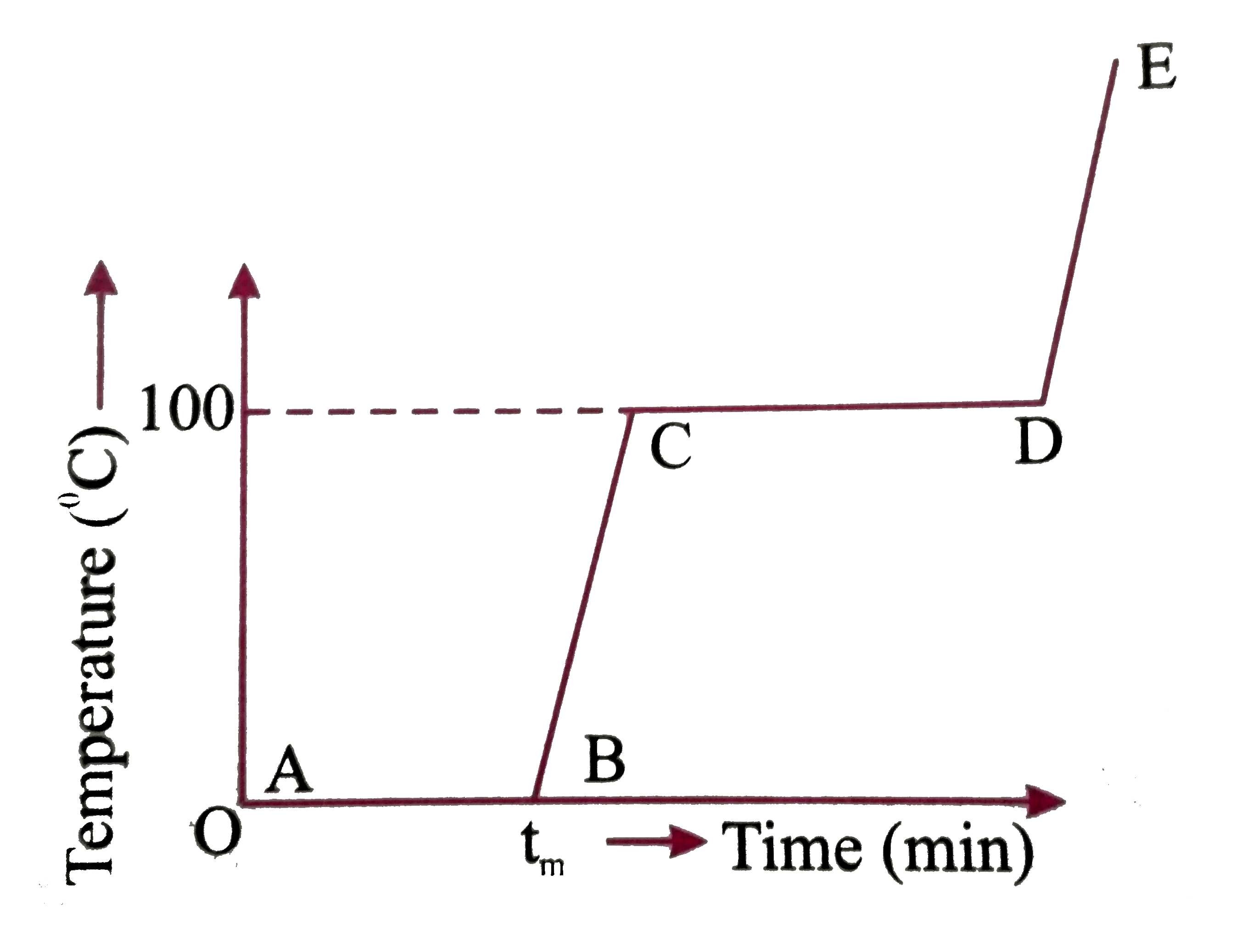
Calcuate the heat required to convert 0.6 kg of ice at - 20∘C, kept in a calorimeter to steam at 100∘C at atmospheric pressure. Given the specific heat capacity of ice=2100jkg−1K−1, specific heat capacity of water =4186jkg−1K−1 latent heat ice =3.35×105jkg−1 and latent heat of steam =2.256×106jkg−1View SolutionQuestion 254
A piece of iron of mass 100g is kept inside a furnace for a long time and then put in a calorimeter of water equivalent 10g containing 240g of water at 20∘C. The mixture attains an equilibrium temperature of 60∘C. Find the temperature of the furnace.
Specific heat capacity of iron =470Jkg−1.∘C−1View SolutionQuestion 256
A 50 g lead bullet (specific heat 0.02) is initially at 30∘C. It is fired vertically upward with a speed of 840ms−1. On returning to the starting level it strikes a cake of ice at 0∘C. How much ice is melted ? Assume that all energy is spent in melting only. Latent heat of ice =336jg−1. View SolutionQuestion 258
A tank of volume 0.2m3 contains helilum gas at a temp. of 300 K and pressure 105N/m2 . Find the amount of heat required to raise the temp. to 500 K. The molar heat capacity of helium at constant volume is 3.0cal/mole−K . Neglect any expansion in the volume of the tank. Take R=8.31j/mole−K.View SolutionQuestion 262
A tank of volume 0.2m3 contains helium gas at a temperature of 300K and pressure 1.0×105Nm−2. Find the amount of heat required to raise the temperature to 400K. The molar heat capacity of helium at constant volume is 3.0calK−1mol−1. Neglect any expansion in the volume of tank.View SolutionQuestion 265
The heat of combustion of ethane gas at 373 k cal per mole. Assume that 50% of heat is lost, how many litres of ethane measured at STP must be convert 50 kg of water at 10∘C to steam at 100∘C ? One mole of gas oc cupies 22.4 litres at STP. Take latent heat of steam =2.25×106jkg−1 .View SolutionQuestion 268
A ball is dropped on a floor from a height of 2.0m. After the collision it rises up to a height of 1.5m. Assume that 40% of the mechanical energy lost goes as thermal energy into the ball.Calculate the rise in the temperature of the ball in the collision. Heat capacity of the ball is 800JK−1View SolutionQuestion 269
A slab of stone of area of 0.36m2 and thickness 0.1m is exposed on the lower surface to steam at 100∘C. A block of ice at 0∘C rests on the upper surface of the slab. In one hour 4.8kg of ice is melted. The thermal conductivity of slab is
(Given latent heat of fusion of ice =3.63×105Jkg−1)View SolutionQuestion 272
An iron boiler is 1 cm thick and has a heating area 2.5m2. The two surface of the boiler are at 230∘C and 100∘C respectively. If the latent heat of the steam is 540kcalkg−1 and thermal conductivity of iron is 1.6×10−2Kcals−1m−1K−1, then how much water will be evaporated into steam per minute ? View SolutionQuestion 276
What is the temperature of the steel-copper junction in the steady state system show in Fig. 7(e).17? Length of steel rod = 15.0 cm, length of the copper rod = 10.0 cm, temperature of the furnace =300∘C, temperature of other end 0∘C. The are of cross-section of the steel rod is twice that of the copper rod. (Thermal conductivity of steel =50.2js−1m−1K−1 and of copper =3895js−1m−1K−1).
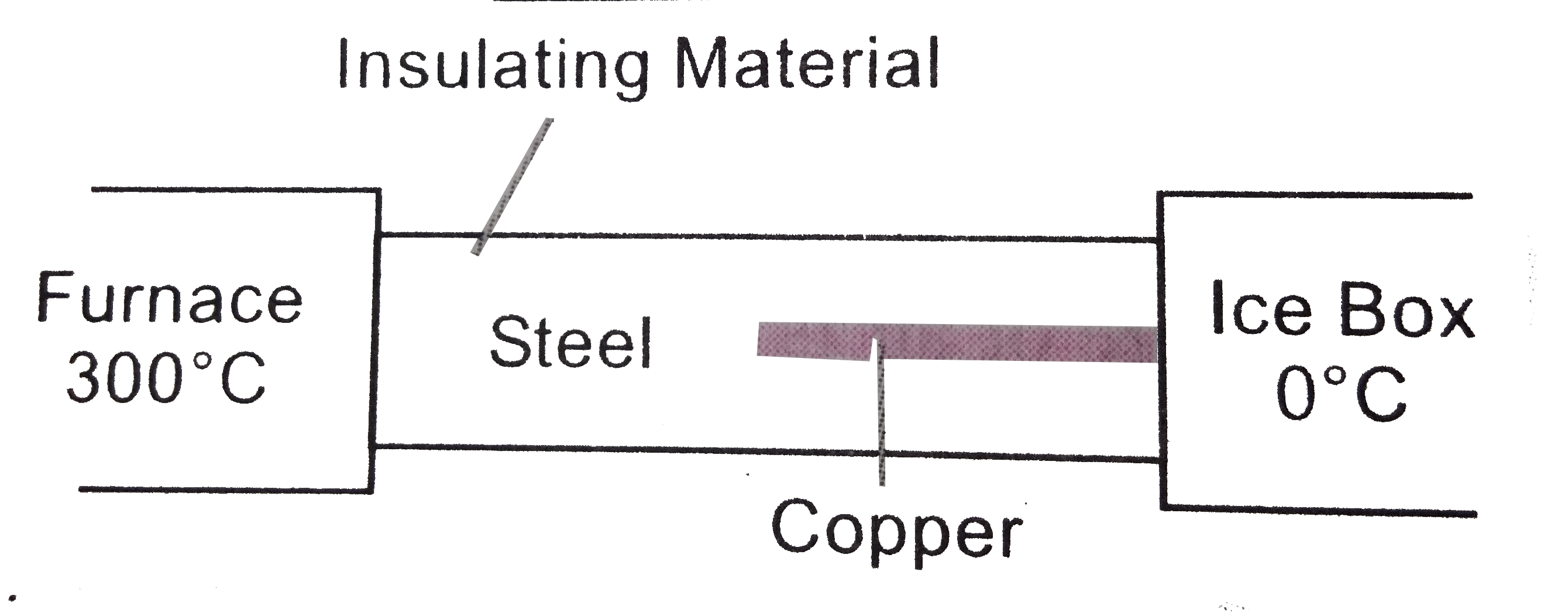 View Solution
View SolutionQuestion 277
A cylinder of radius R made of a material of thermal conductivity K1 is surrounded by cylindrical shell of inner radius R and outer radius 2R made of a material of thermal con-ductivity K2 The two ends of the combined system are maintained at two differnet tem-peratures There is no loss of heat across the cylindrical surface and system is in steady state What is the effective thermal conductivity of the system
 .View Solution
.View SolutionQuestion 279
Two metal cubes A and B of same size are arranged as shown in Figure. The extreme ends of the combination are maintained at the indicated temperatures. The arrangement is thermally insulated. The coefficients of thermal conductivity of A and B are 300W/m∘Cand200W/m∘C, respectively. After steady state is reached the temperature t of the interface will be ......
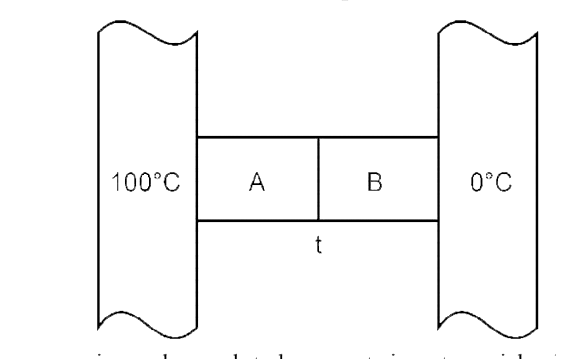 View Solution
View SolutionQuestion 290
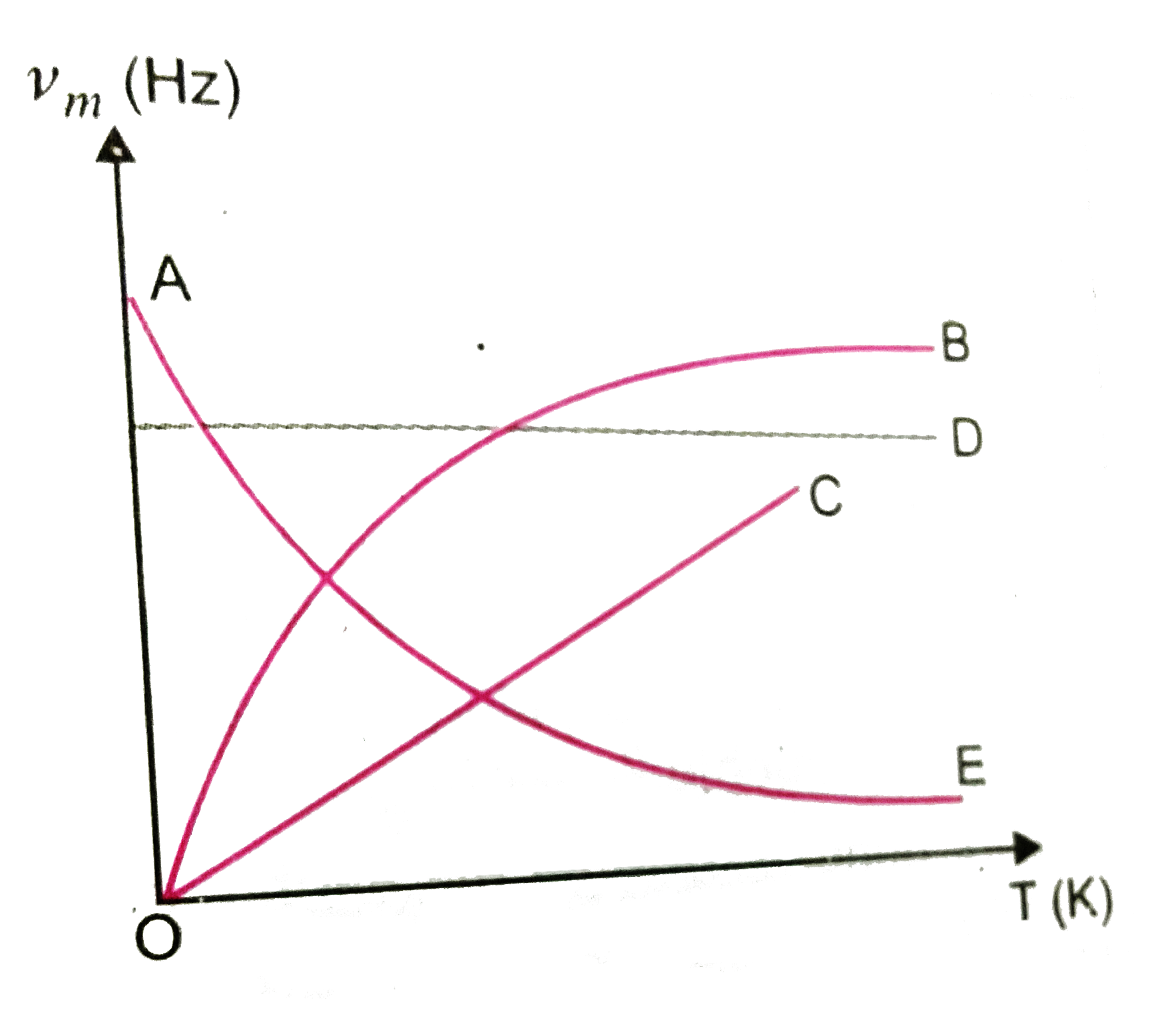
Two bodies A and B have thermal emissivities of 0.01 and 0.81 respectively. The outer surface areas of the two bodies are same. The two bodies emit total radiant power at the same rate. The wavelength λB corresponding to maximum spectral radiancy from B is shifted from the wavelength corresponding to maximum spectral radiancy in the radiation from A by 1.0 μm. If the temperature of A is 5802 K, calculate (a) the temperature of B, (b) wavelength λB. View SolutionQuestion 296
A bar of copper of length 75cm and a bar of steel of length 125cm are joined together end to end. Both are of circular cross section with diameter 2cm. The free ends of the copper and the steel bars are maintained at 100∘C and 0∘C respectively. The curved surface of the bars are thermally insulated. What is the temperature of the copper-steel junction? What is the amount of heat transmitted per unit time across the junction? Thermal conductivity of copper is 386Js−1m−1.∘C−1 and that of steel is 46Js−1m−1.∘C−1View SolutionQuestion 298
Three rods of material X and three rods of material Y are connected as shown in the figure. All the rods are of identical length and cross-sectional area. If the end A is maintained at 60∘C and the junction E at 10∘C. Calculate the temperature of the junction B, C and D. The thermal conductivity of X is 0.92cal/sec−cm∘C and that of Y is 0.46cal/sec−cm−∘C.
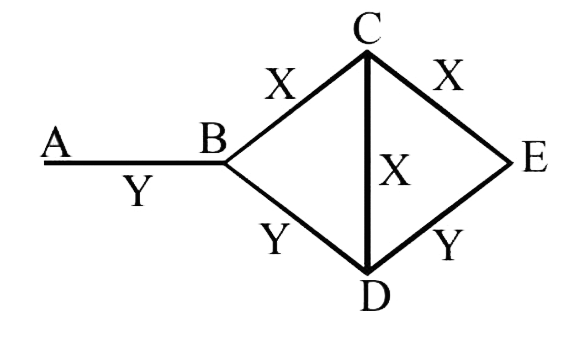 View Solution
View SolutionQuestion 309
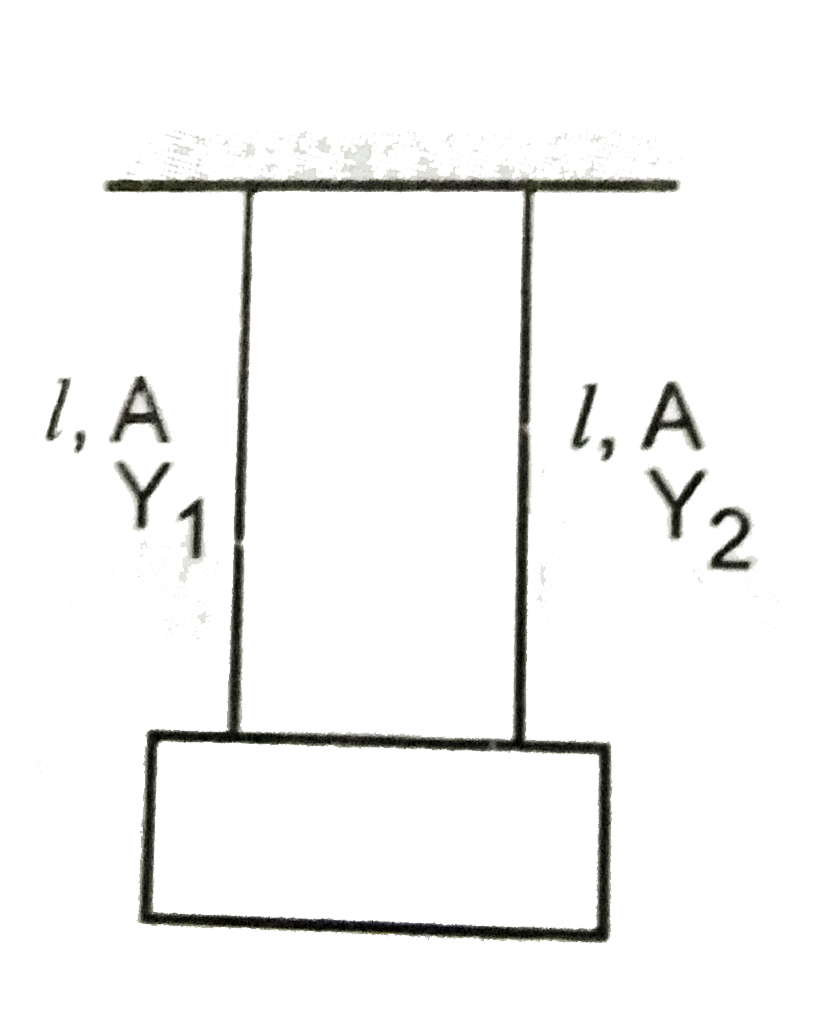
A rod of length 1.05 m having negliaible mass is supported at its ends by two wires of steel (wire A) and aluminium (wire B) of equal lengths as shown in fig. The cross-sectional area of wire A and B are 1mm2 and 2mm2, respectively . At what point along the rod should a mass m be suspended in order to produce (a) equal stresses and (b) equal strains in both steel and aluminium wires. Given,
Ysteel=2×1011Nm−2andY−(aluminium)=7.0×1010N−2
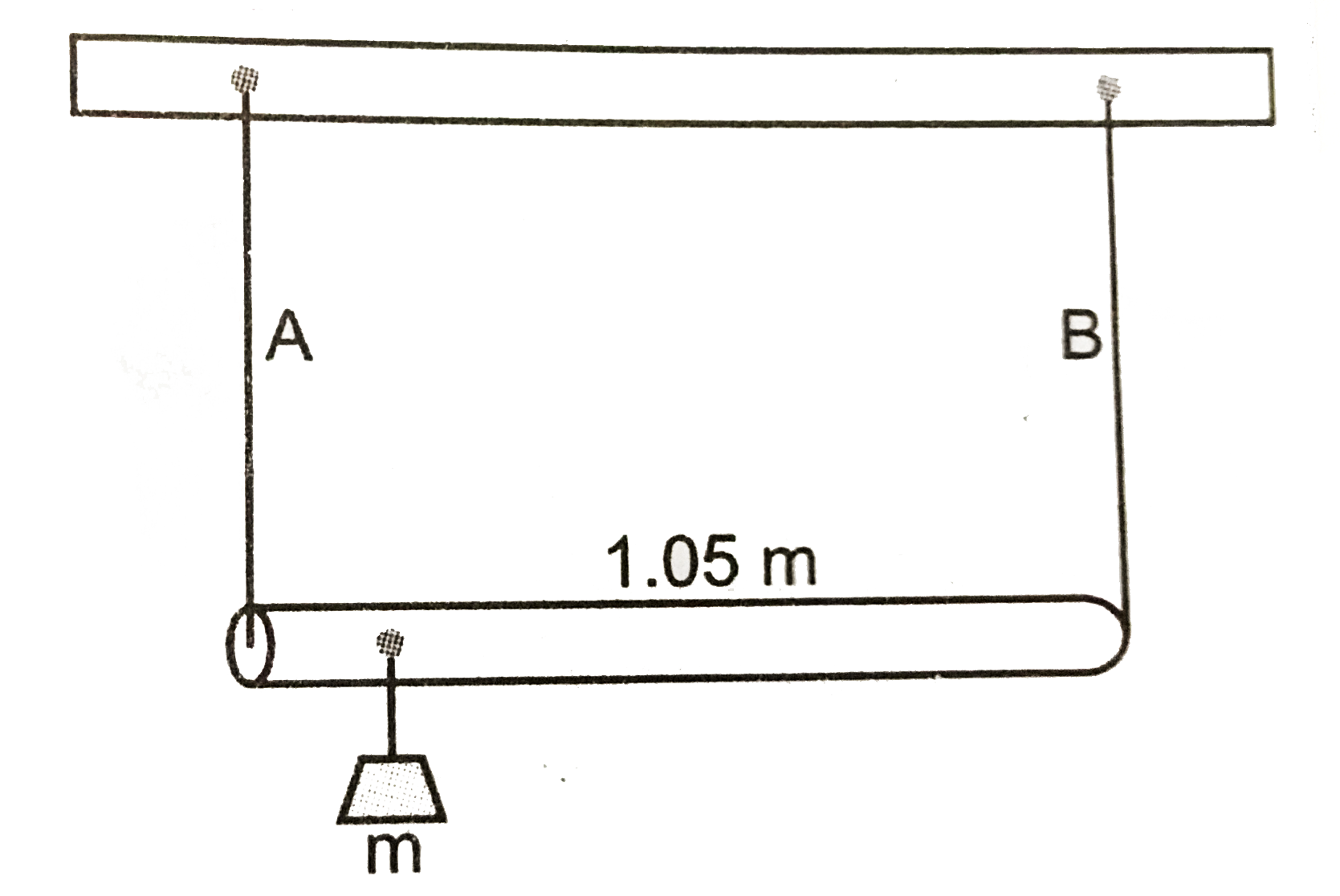 View Solution
View SolutionQuestion 316
The angle of contact at the interface of water glass is 0∘ ethylalcohol-glass is 0∘ mercury glass is 140∘ and methyliodide-glass is 30∘ A glass capillary is put in a through containing one of these four liquids. It is observed that the meniscus is convex. The liquid in the through isView SolutionQuestion 331
Gulab jamuns (assumed to be spherical) are to be heated in on oven They are available in two sizes, one twice bigger (in radius) than the other Pizzas (assumed to discs) are also to be heated ibn oven They are also in two sizes, one twice bigger (in radius) than the other All four are put together to be heated option to oven temperature. Choose the correct option from the following .View SolutionQuestion 335
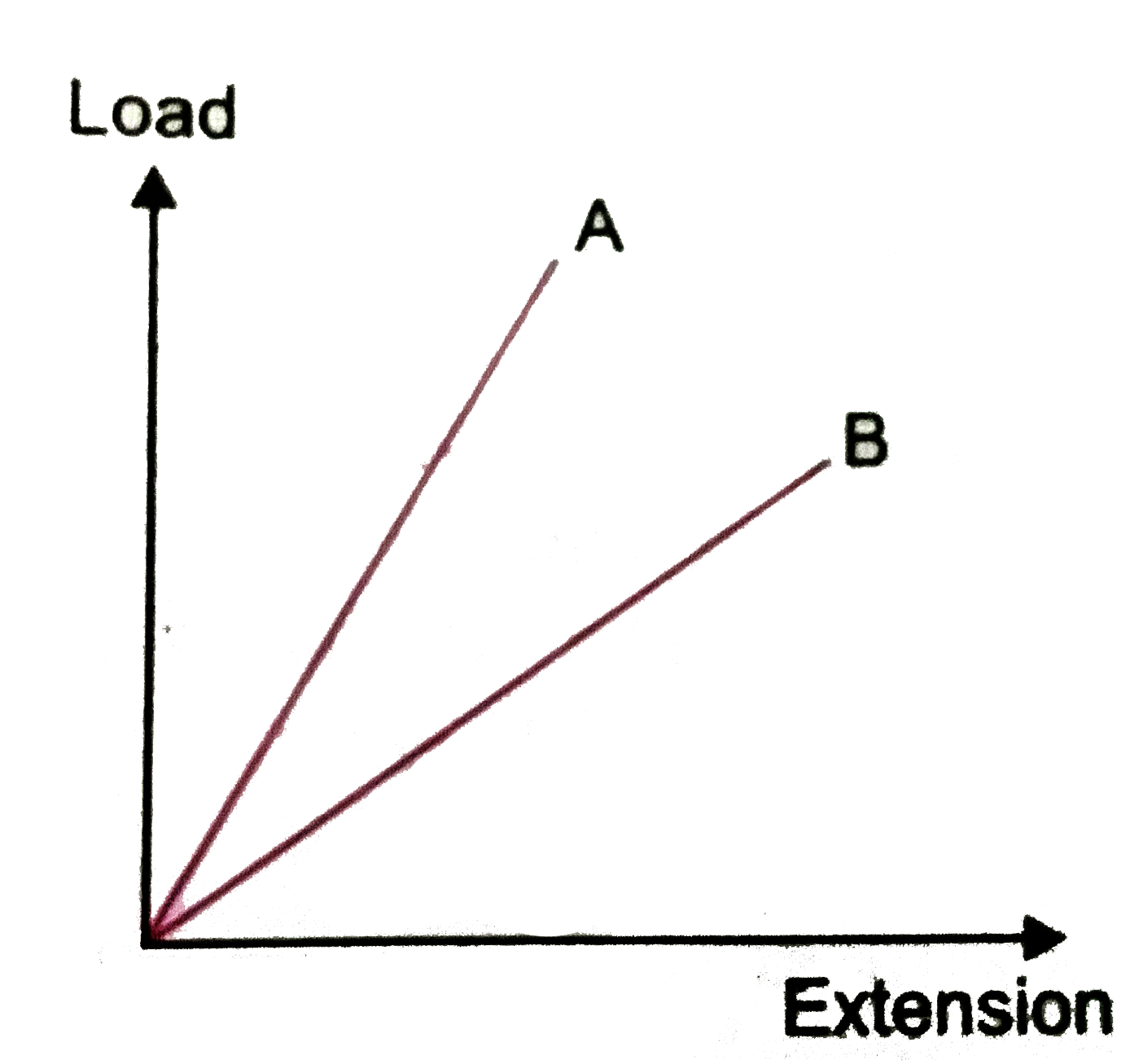
The Young's modulus of steel is twice that of brass. Two wires of the same length and of the same area of cross section, one of steel and another of brass are suspended from the same roof. If we want the lower ends of the wires to be at the same level, then the weight added to the steel and brass wires must be in the ratio of View SolutionQuestion 341
An alumminium rod and steel wire of same length and cross-section are attached end to end. Then compound wire is hung fron a rigid support and load is suspended from the free end. Y for steel is (207) times of aluminium. The ratio of increase in length of steel wire to the aluminium wire is View SolutionQuestion 344
A steel wire of length 20 cm and uniform cross-section 1mm2 is tied rigidly at both the ends. If the temperature of the wire is altered from 40∘C to 20∘C, the change in tension. [Given coefficient of linear expansion of steel is 1.1×105.∘C−1 and Young's modulus for steel is 2.0×1011Nm−2]View SolutionQuestion 345
Two rods of different materials having coefficient of thermal expansion α1,α2 and young's modulii Y1,Y2 respectively are fixed between two rigid massive walls. The rods are heated such that they undergo the same increase in temperature. There is no bending of rods. If α1:α2=2:3, the thermal stresses developed in the two rods are equal provided Y1:Y2 is equal toView SolutionQuestion 347
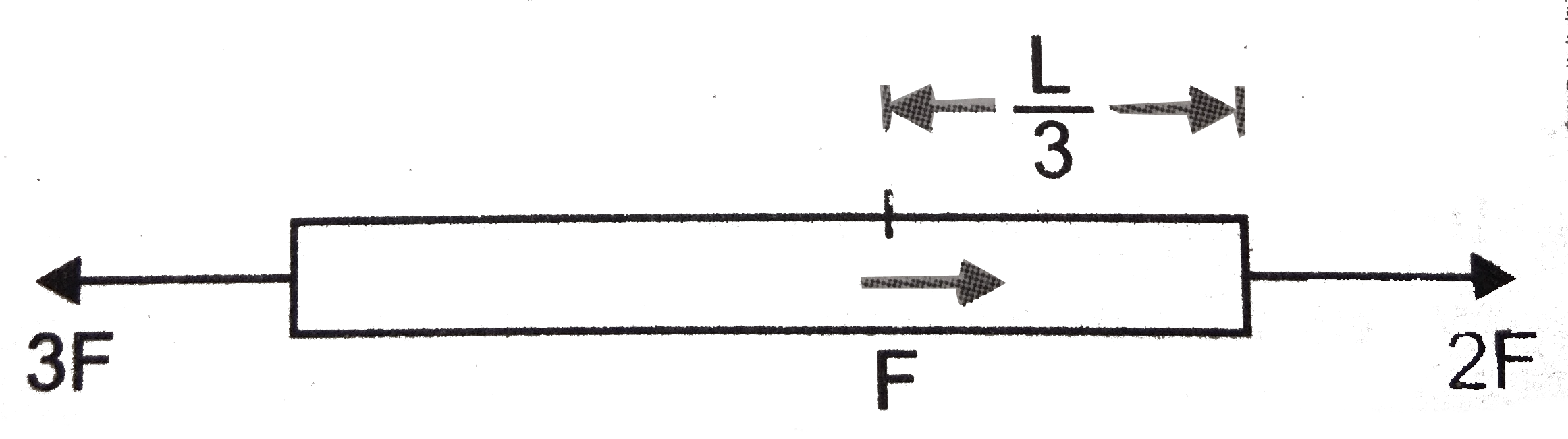
A light rod AC of length 2.00 m is suspended from the ceiling horizontally by means of two vertical wires of equal length tied to its ends. One of the wires is made of steel and is of cross-section 10−3m2 and the other is of brass of cross-section 2×10−3m2. The position of point D from end A along the rod at which a weight may be hung to produce equal stress in both the wires is [Young's modulus of steel is 2×1011Nm2 and for brass is 1×1011Nm−2]
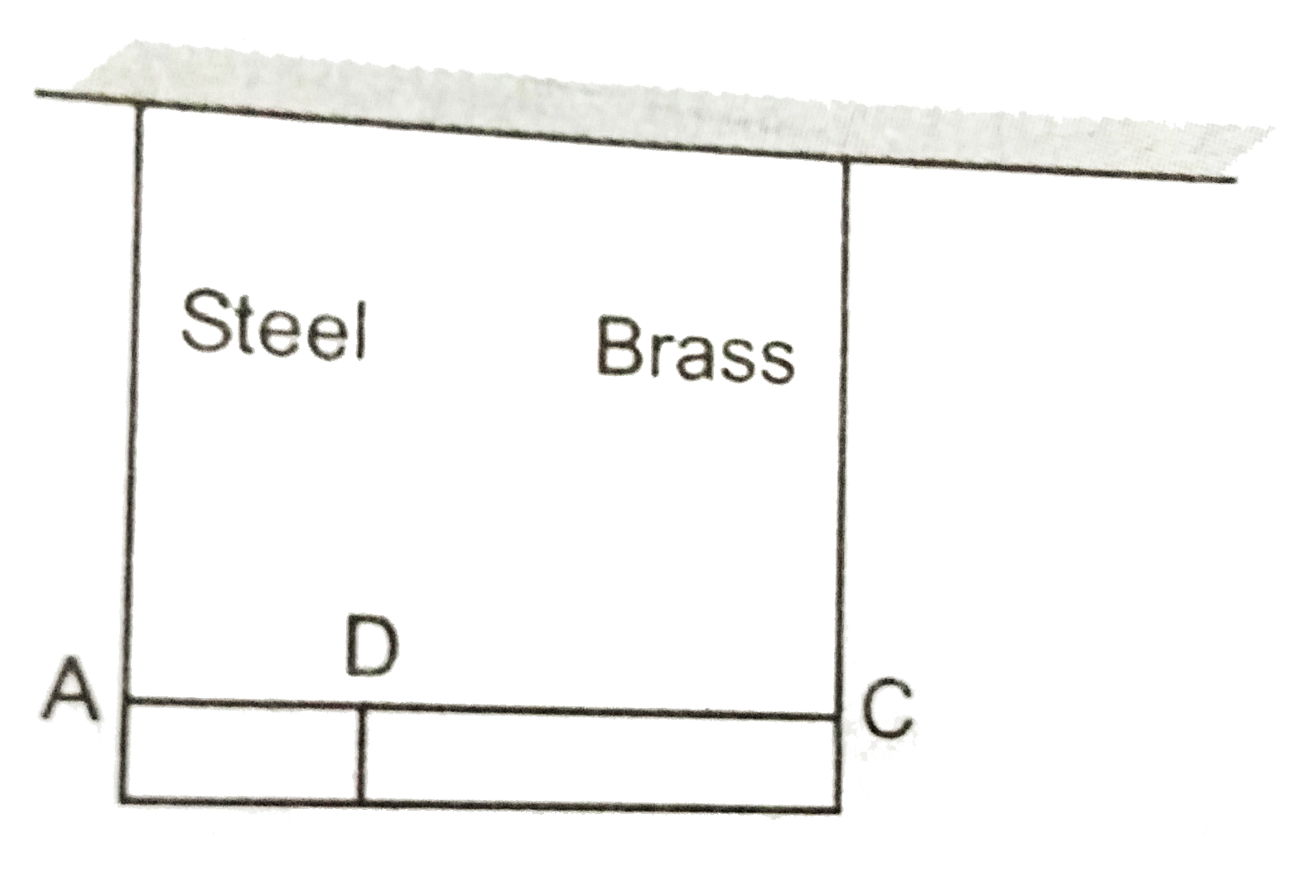 View Solution
View SolutionQuestion 351
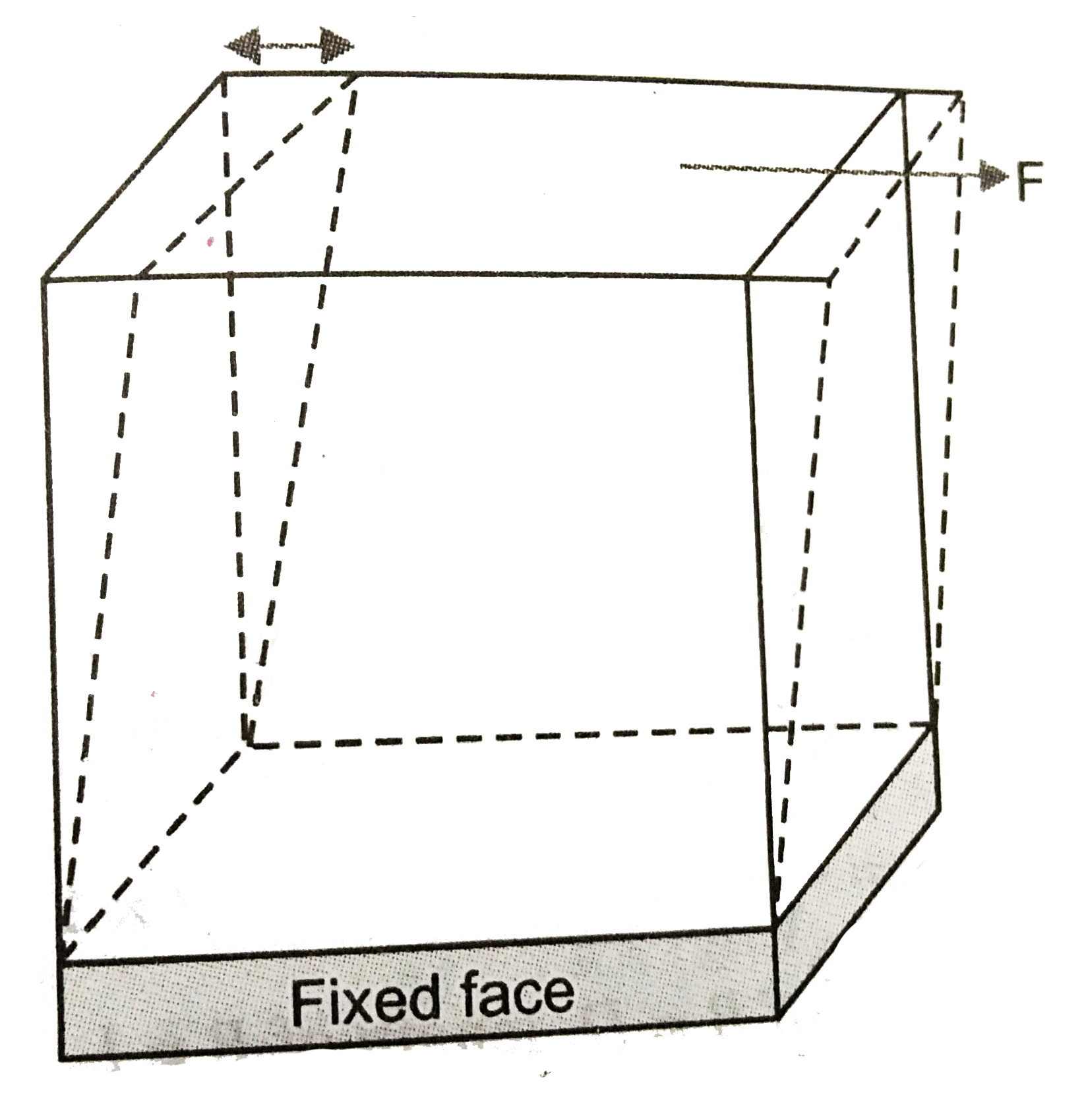
A highly rigid cubical block A of small mass M and side L is fixed rigidly on the other cubical block of same dimensions and of modulus of rigidity η such that the lower face of A completely covers the upper face of B. The lower face of B is rigidly held on a horizontal surface . A small force F is applied perpendicular to one of the side faces of A. After the force is withdrawn , block A executes faces of A. After the force is withdrawn , block A exceutes small oscillations , the time period of which is given byView SolutionQuestion 355
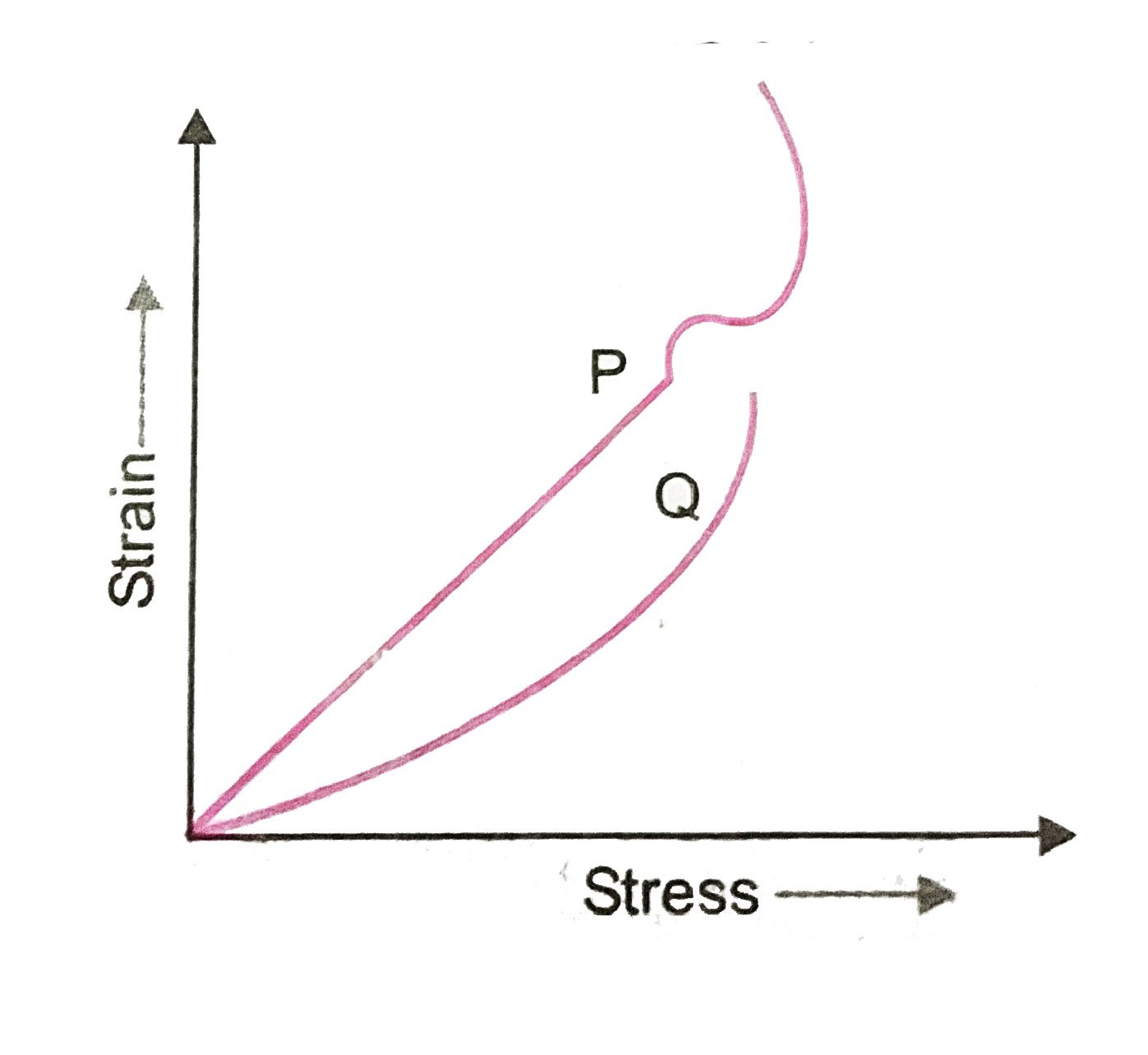
In the determination if Young's modulus ((Y=4MLgπld2 by using searle's method, a wire of length L=2m and diameter d=0.5mm is used. For a load M=2.5kg, an extension l=0.25mm in the length of the wire is observed. Quantites Dandl are measured using a screw gauge and a micrometer, respectively. they have the same pitch of 0.5mm. the number of divisions on their circular scale is 100. the contrubution to the maximum probable error of the Y measurement View SolutionQuestion 361
Water is filled up to a height h in a beaker of radius R as shown in the figure. The density of water is ρ, the surface tension of water is T and the atmospheric pressure is P0. Consider a vertical section ABCD of the water column through a diameter of the beaker. The force on water on one side of this section by water on the other side of this section has magnitude
 View Solution
View SolutionQuestion 362
A U-tube with both ends open to the atmosphere is partially filled with water. Oil, which is immiscible with water. Is poured into one side until it stands at a distance of 10mm above the water level on the other side. Meanwhile the water rises by 65mm from its original level (see diagram). The density of the oil is:
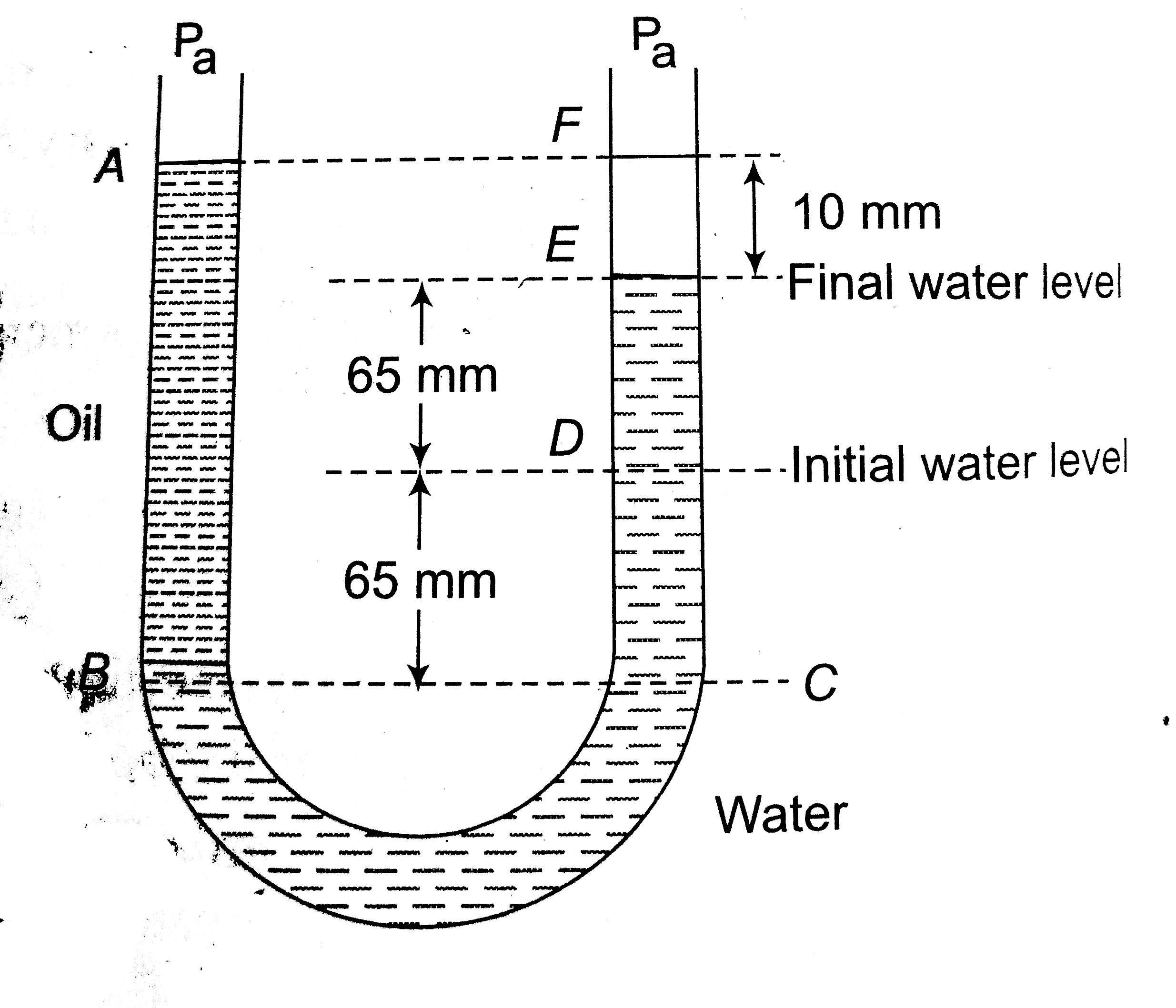 View Solution
View SolutionQuestion 371
A solid uniform ball having volume V and density ρ floats at the interface of two unmixible liquids as shown in Fig. 7(CF).7. The densities of the upper and lower liquids are ρ1 and ρ2 respectively, such that ρ1<ρ<ρ2. What fractio9n of the volume of the ball will be in the lower liquid.
 View Solution
View SolutionQuestion 372
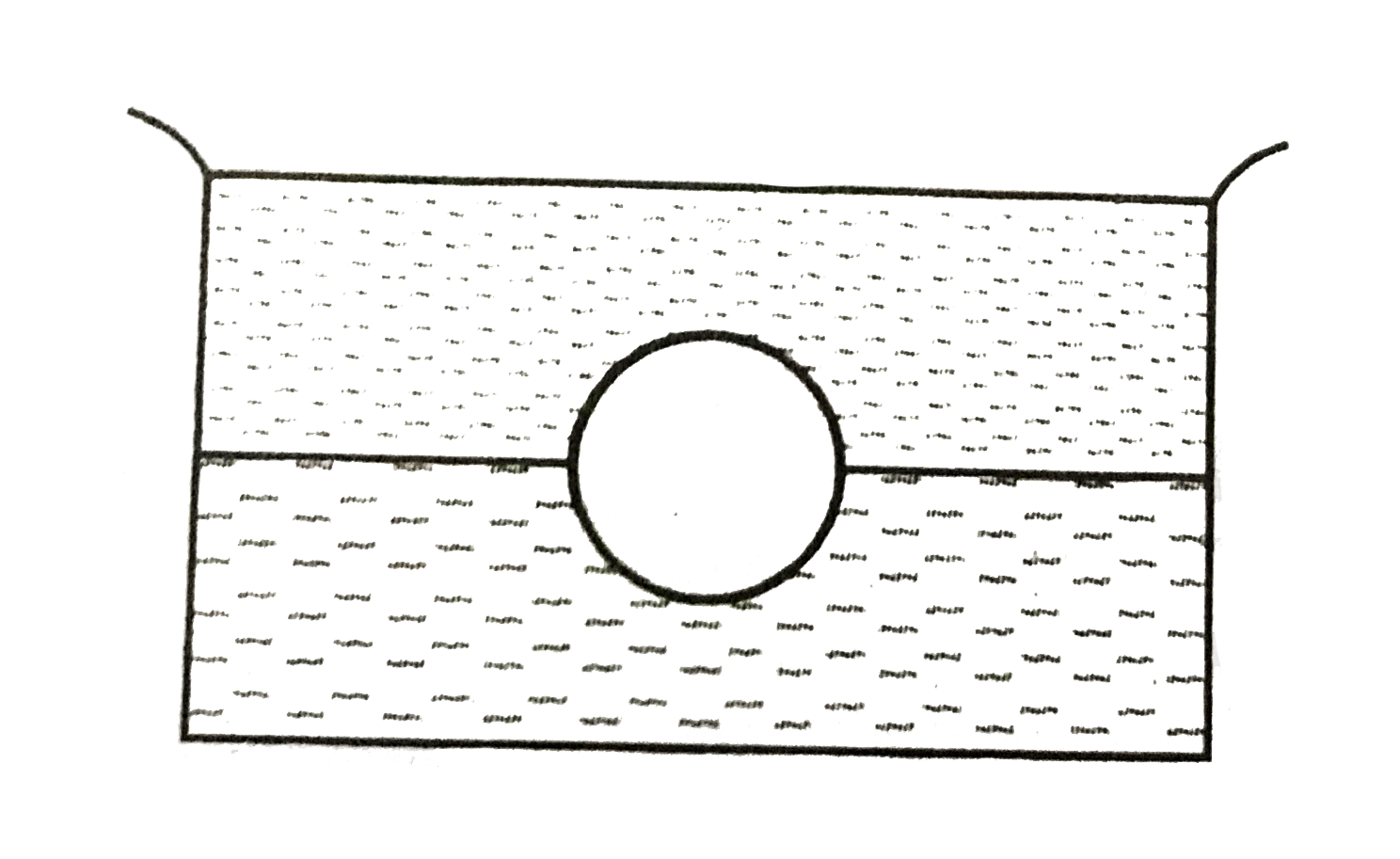
A hemispherical portion of radius R is removed from the bottom of a cylinder of radius R. The volume of the remaining cylinder is V and its mass is M. It suspended by a string in a liquid of density ρ where it stays vertical. The upper surface of cylinder is at a depth h below the liquid surface. The force on the bottom of the cylinder bby the liquid is
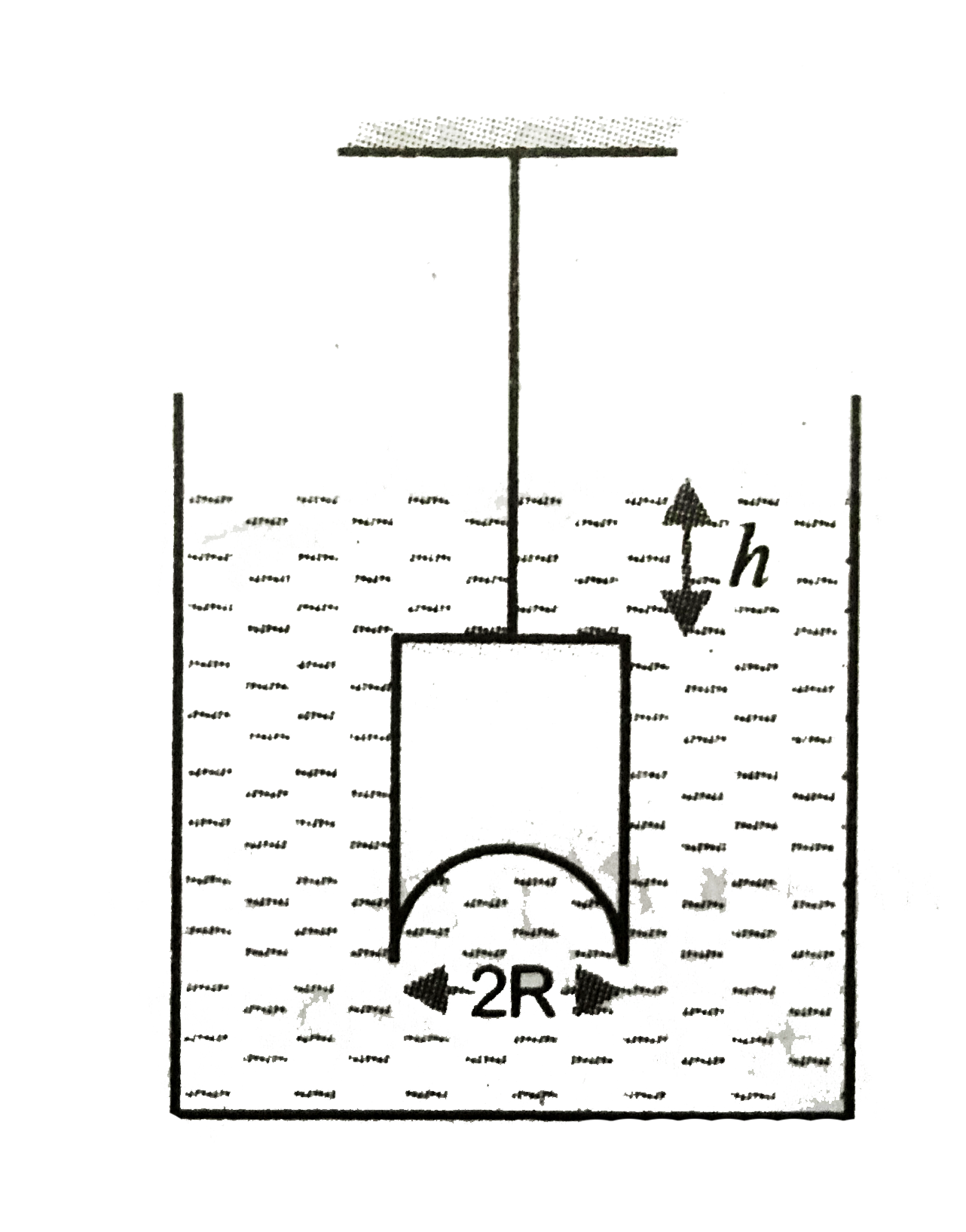 View Solution
View SolutionQuestion 383
A thin uniform cylindrical shell, closed at both ends, is partially filled with water. It is floating vertically in water in half-submerged state. If ρc is the relative density of the material of the shell with respect to water, then the correct statement is that the shell is View SolutionQuestion 384
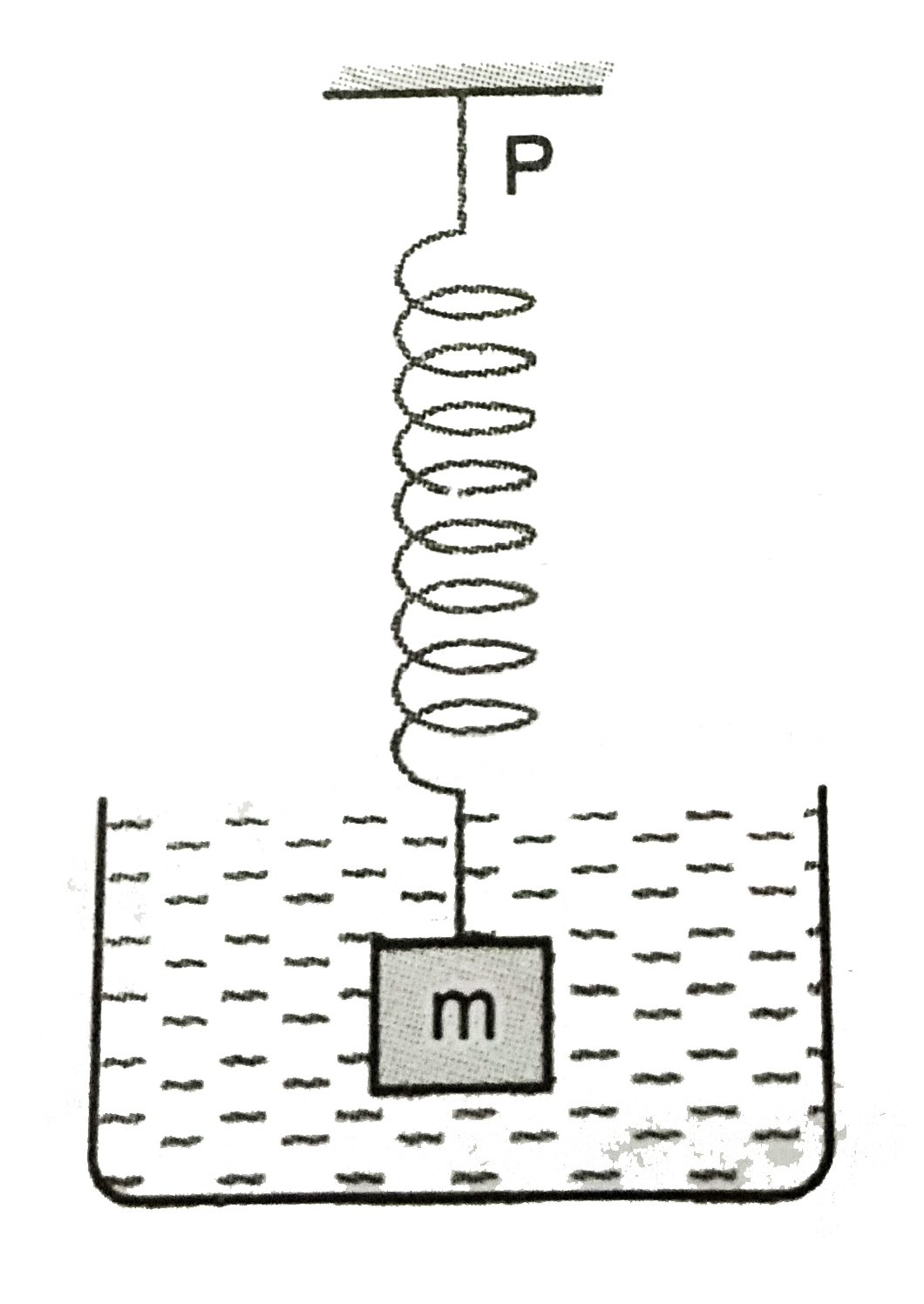
A uniform cylinder of length L and mass M having cross-sectional area A is suspended, with its length vertical, from a fixed point by a massless spring such that it is half submerged in a liquid of density σ at equilibrium position. The extension x0 of the spring when it is in equlibrium is:View SolutionQuestion 385
Two non-mixing liquids of densities ρ and (n>1) are put in a container. The height of each liquid is h. A solid cylinder of length L and density d is put in this container. The cylinder floats with its axis vertical and length pL(p<1) in the denser liquid. The density d is equal to : View SolutionQuestion 395
Assume that a drop of liquid evaporates by decreases in its surface energy, so that its temperature remains unchanged. What should be the minimum radius of the drop for this to be possible? The surface tension is T, density of liquid is ρ and L is its latent heat of vaporization.View SolutionQuestion 396
On heating water, bubbles being formed at the bottom of the vessel detach and rise. Take the bubbles to be spheres of radius R and making a circular contact of radius r with the bottom of the vessel. If r<<R and the surface tension of water is T, value of r just before bubbles detach is: (density of water is ρw)
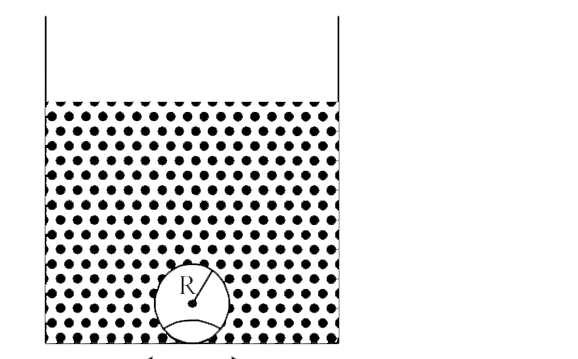 View Solution
View SolutionQuestion 401
A glass capillary tube is of the shape of a truncated cone with an apex angle α so that its two ends have cross sections of different radii. When dipped in water vertically, water rises in it to a high h, where the radius of its cross section is b. If the surface tension of water is S, its density if ρ, and its contact angle with glass is θ, the value of h will be (g is the acceleration due to gravity)
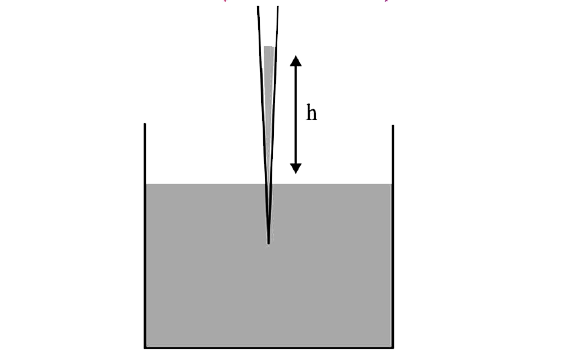 View Solution
View SolutionQuestion 406
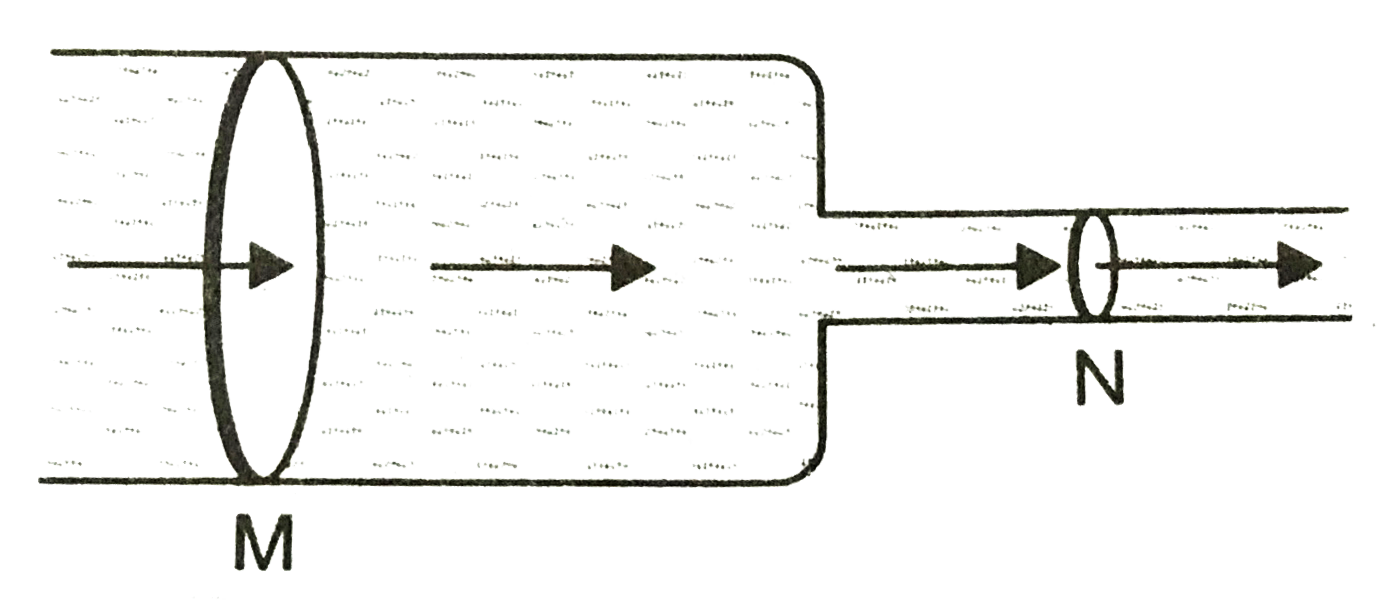
The rate of steady volume flow of water through a capillary tube of length ' l ' and radius ' r ' under a pressure difference of P is V . This tube is connected with another tube of the same length but half the radius in series. Then the rate of steady volume flow through them is (The pressure difference across the combination is P ) View SolutionQuestion 408
Two solild spheres manufactured of the same material freely fall down in the air. One sphere has a dimeter twice as large as the other. The force due to air resistance is proportional to the cross-section area of a moving object and is quadration function of the speed of an object and is quadration function of the speed of an object. In sometime after the beginning of motion in the presence of air resistance, the velocity of each sphere become constant. It is called the terminal velocity vbig/vsmall is View SolutionQuestion 409
A spherical solild of volume V is made of a material of density ρ1. It is falling through a liquid of density ρ2(ρ2<ρ1). Assume that the liquid applies a viscous froce on the ball that is proportional ti the its speed v, i.e., Fviscous=−kv2(k>0). The terminal speed of the ball is View SolutionQuestion 415
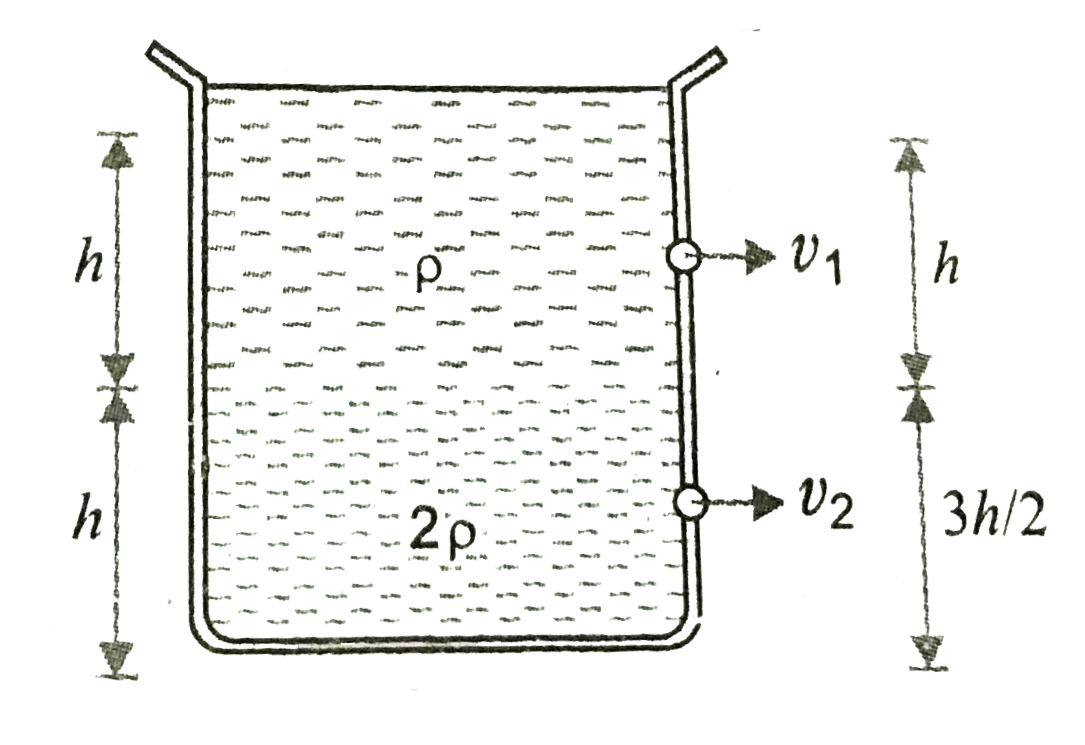
Water flows through a vertical tube of varible cross-section. The area of cross-section at A and B 6 and 3 mm2 respectively. If 12c c of water enters per second through A, find the pressure difference PA−PB.(g=10m/s2). The separation between the cross-section at A and B is 100 cm.
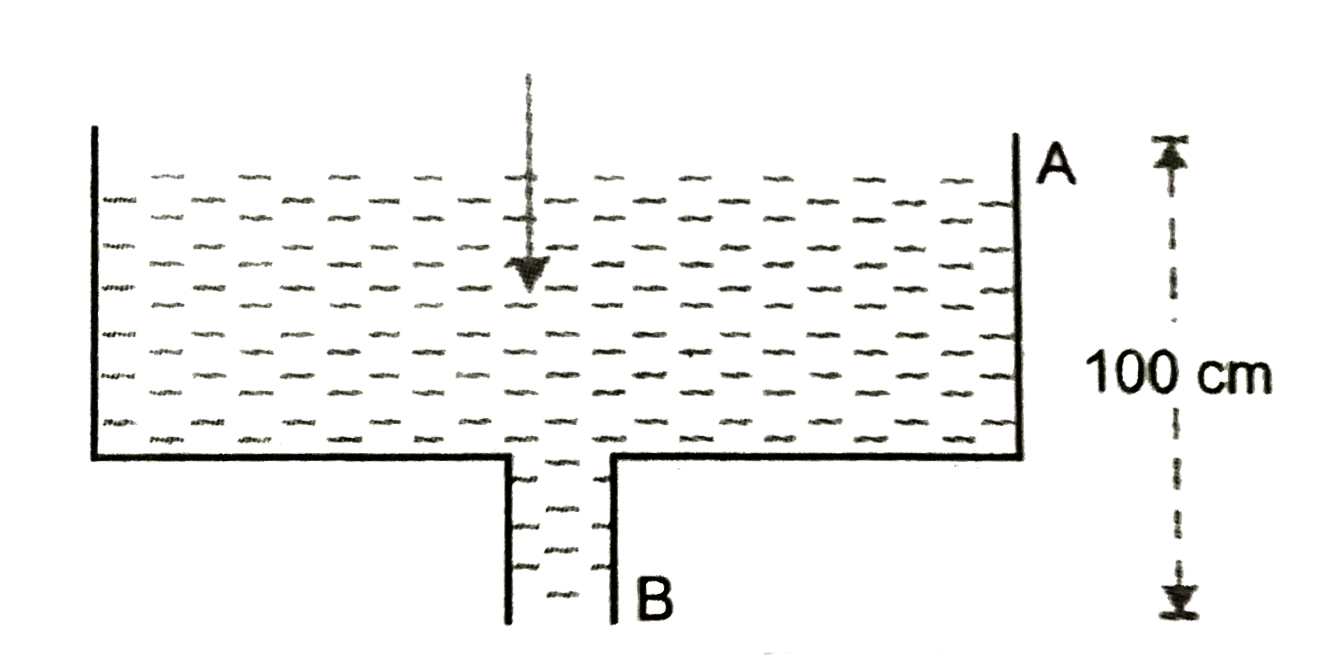 View Solution
View SolutionQuestion 424
Two rods of different materials having coefficient of thermal expansion α1,α2 and young's modulii Y1,Y2 respectively are fixed between two rigid massive walls. The rods are heated such that they undergo the same increase in temperature. There is no bending of rods. If α1:α2=2:3, the thermal stresses developed in the two rods are equal provided Y1:Y2 is equal toView SolutionQuestion 425
An external pressure P is applied on a cube at 0∘C so that it is equally compressed from all sides. K is the bulk modulus of the material of the cube and α is its coefficient of linear expansion. Suppose we want to bring the cube to its original size by heating. The temperature should be raised by View SolutionQuestion 426
A copper ball of mass 100 gm is at a temperature T. It is dropped in a copper calorimeter of mass 100 gm, filled with 170 gm of water at room temperature. Subsequently, the temperature of the system is found to be 75∘C . T is given by : (Given : room temperature = 30∘C, specific heat of copper =0.1cal/gm∘C)View SolutionQuestion 433
A wooden wheel of radius R is made of two semicircular part . The two parts are held together by a ring made of a metal strip of cross sectional area S and length L. L is slightly less than 2πR. To fit the ring on the wheel, it is heated so that its temperature rises by ΔTand it just steps over the wheel. As it cools down to surrounding temperature, it process the semicircle parts together. If the coefficient of linear expansion of the metal is α, and it Young's modulus is Y, the force that one part of the wheel applies on the other part is :
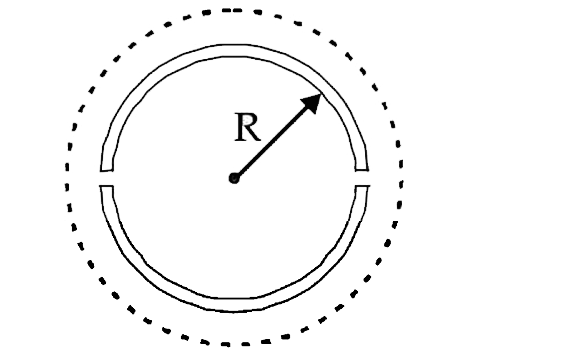 View Solution
View SolutionQuestion 435
The specific heat capacity of a metal at low temperature (T) is given as
Cp(kJK−1kg−1)=32(T400)3
A 100 gram vessel of this metal is to be cooled from 20∘K to 4∘K by a special refrigerator operating at room temperaturte (27∘C) . The amount of work required to cool the vessel is View SolutionQuestion 438
A water cooler of storages capacity 120 liters can cool water at a constant rate of P watts. In a closed circulation system (as shown schematically in the figure), the water from the cooler is used to cool an external device that generates constantly 3kW of heat (thermal load). The temperature of water fed into the device cannot exceed 30∘C and the entire stored 120 liters of water is initially cooled to 10∘C. The entire system is thermally insulated. The minimum value of P ( in watts) for which the device can be operated for 3hours is
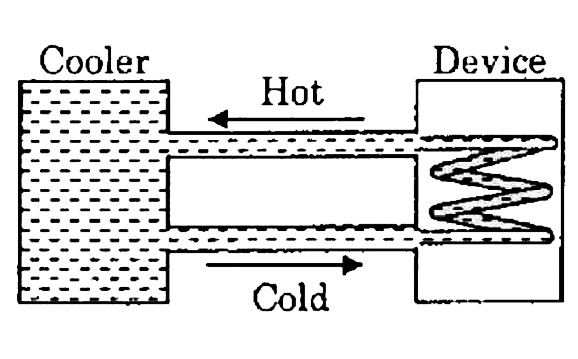
(Specific heat of water is 4.2kJkg−1K−1 and the density of water is 1000kgm−3)View SolutionQuestion 441
A ice box of styrofoam (thermal conductivity = 0.01 J ms−1K−1) is used to keep liquid cool. It has a total wall area, including lid, of 10.8m2 and wall thickness of 2.0 cm. A bottle of water is placed in the box and filled with ice. If the outside temperature is 30∘C, the rate of flow of heat into the box is (in J/s)View SolutionQuestion 447
Two identical rods are connected between two containers. One of them is at 100∘C containing water and another is at 0∘C containing ice. If rods are connected in parallel then the rate of melting of ice is q1g/s . If they are connected in series then teh rate is q2g/s . The ratio q2/q1 is View SolutionQuestion 448
Three rods of identical cross-sectional area and made from the same metal, from the sides of an isosceles triangle ABC right angled at B, as shown in Fig .7(CF).23. The points A and B are maintained at temperature T and √2T respectively in the steady. Assuming that only heat conduction takes place, temperature of point C will be
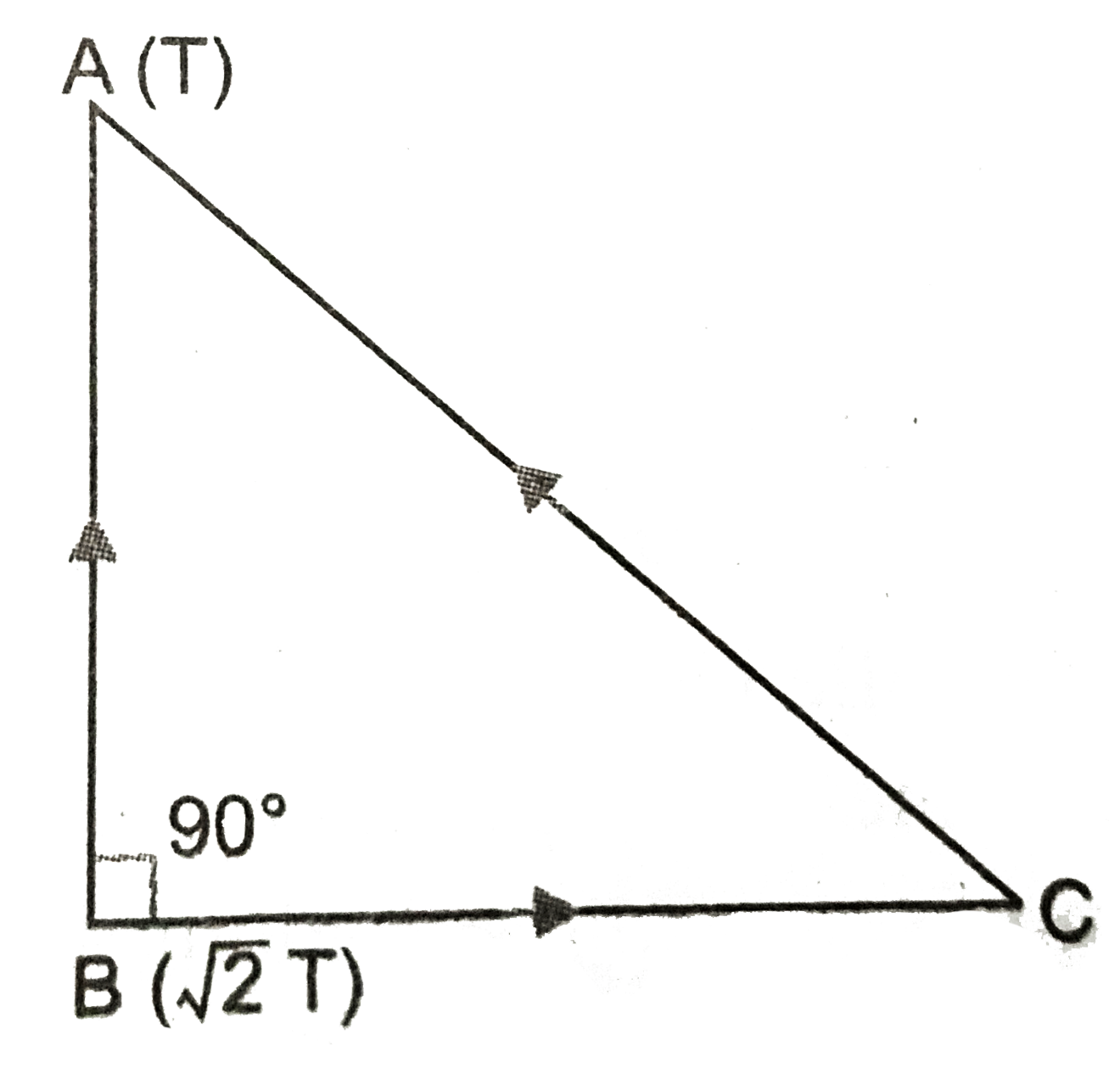 View Solution
View SolutionQuestion 449
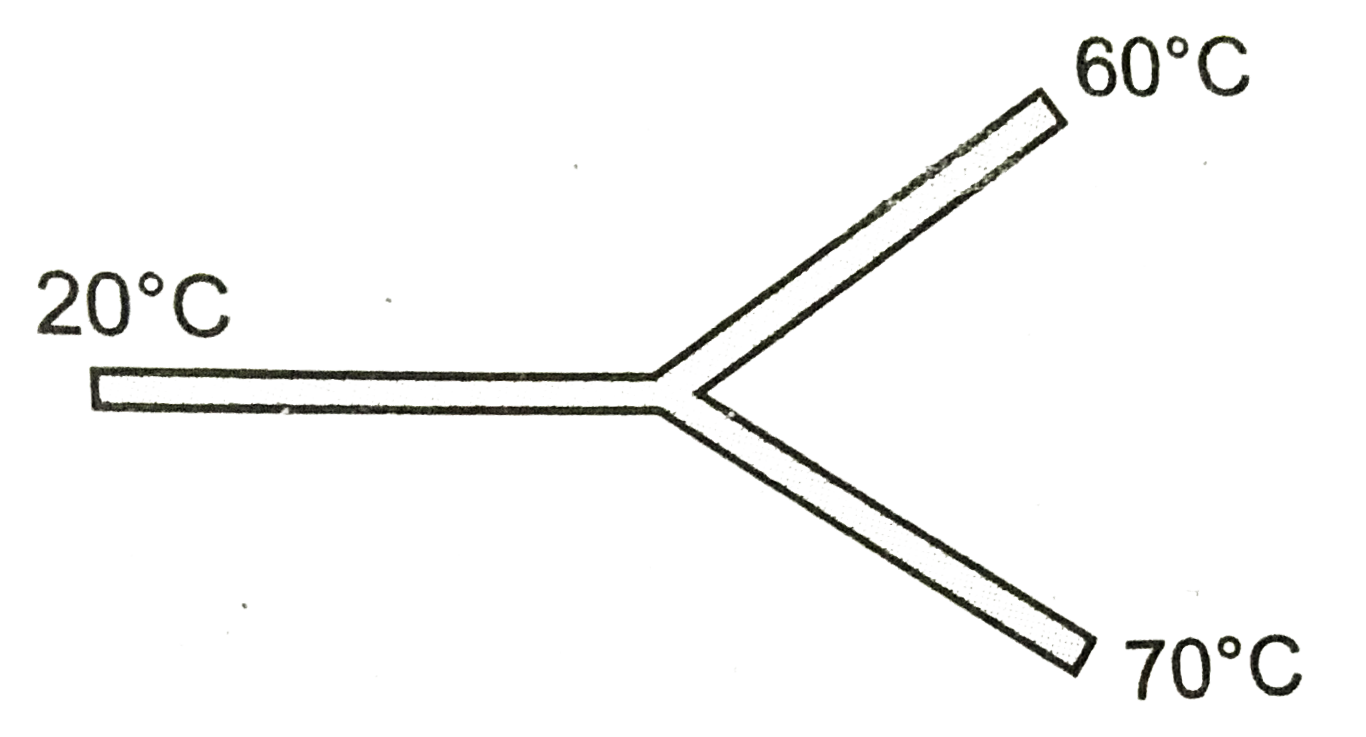
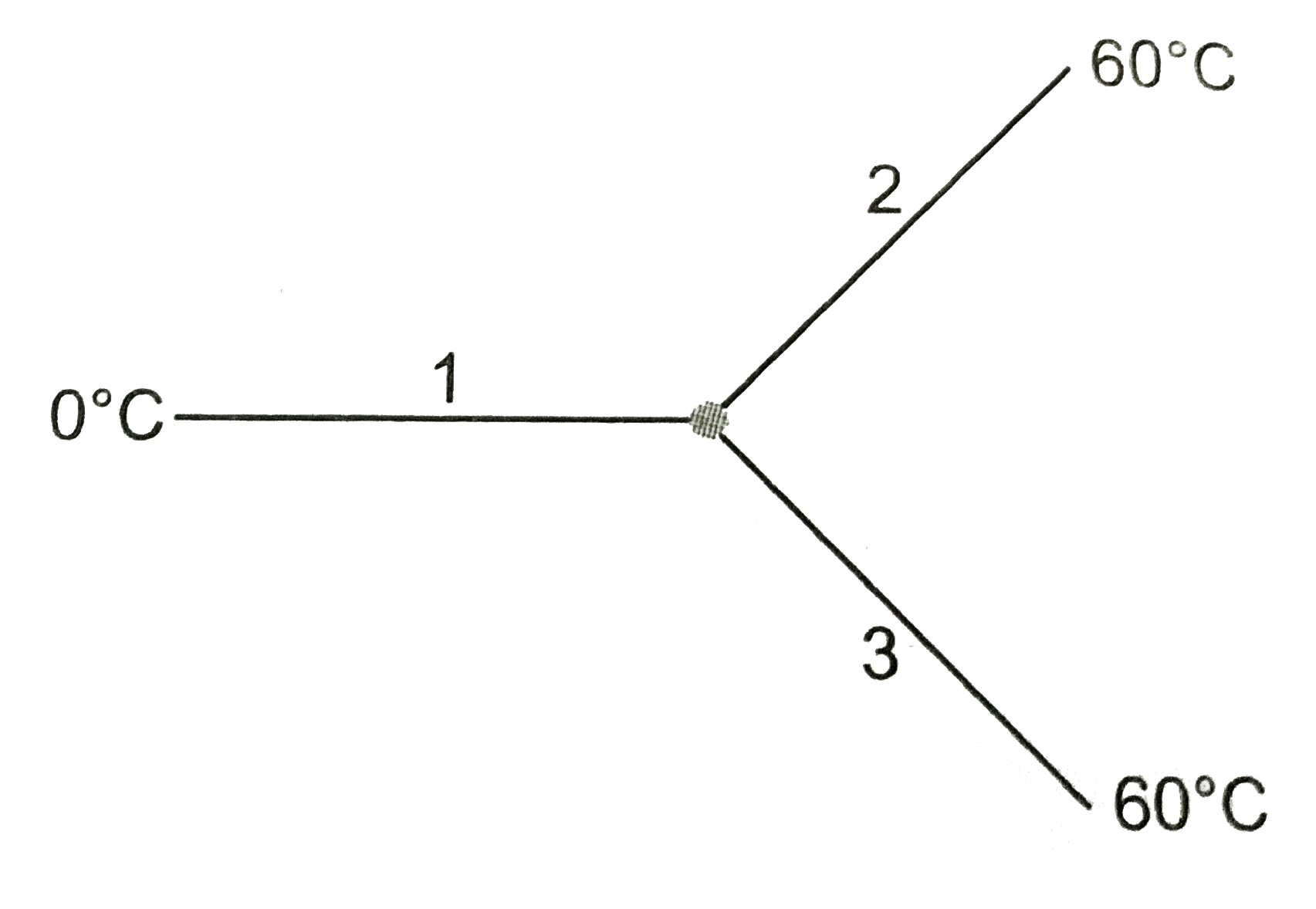
Three rods of copper, brass and steel are welded togeher to from a Y -shaped structure. Area of cross-section of each rod =4cm2. End of copper rod is maintained at 100∘C whereas the ends of brass and steel are at 0∘C . Lengths of copper, brass and steel rods are 46, 13 and 12 cm respectively. The rods are thermally insulated from surroundings except at ends. Thermal conductivities of copper, brass and steel are 0.92,0.26 and 0.12 CGS units respectively. Rate of heat flow through copper rod is View SolutionQuestion 451
The ends Q and R of two thin wires, PQ and RS, are soldered (joined) together. Initially each of the of wire has a length of 1m at 10∘C. Now the end P is maintained at 10∘C, while the ends S is heated and maintained at 400∘C. The system is thermally insultated from its surroundings. If the thermal conductivity of wire PQ is twice that of the wire RS and the coefficient of linear thermal expansion of PQ is 1.2×10−5K−1, the change in length of the wire PQ is View SolutionQuestion 459
Three very large plates of same area are kept parrallel and close to each other. They are considered as ideal black surfaces and have high thermal conductivity. The first and third plates are maintained at temperatures 2T and 3T respectively. The temperature of the middle (i.e., second) plate under steady state condition is View SolutionQuestion 462
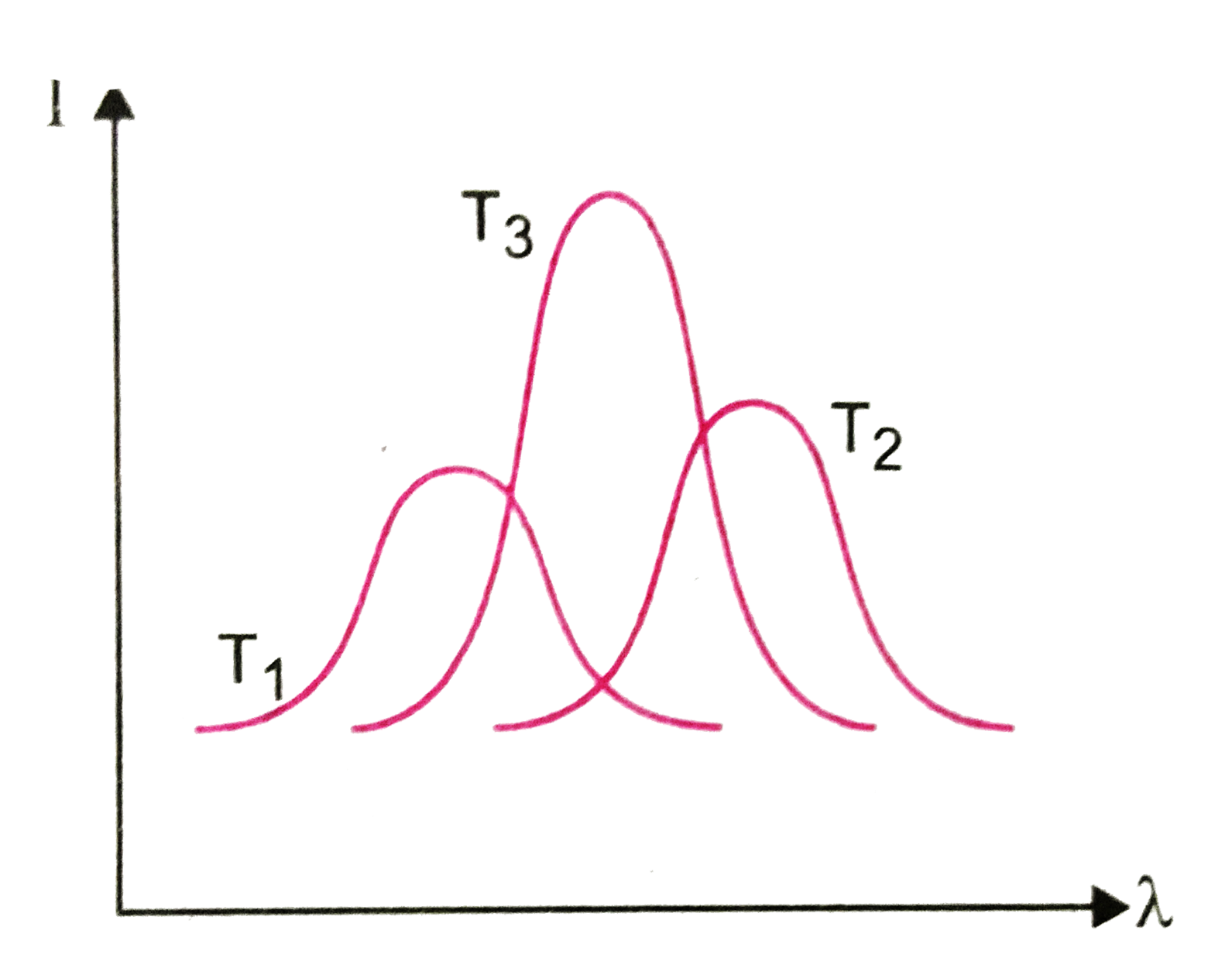
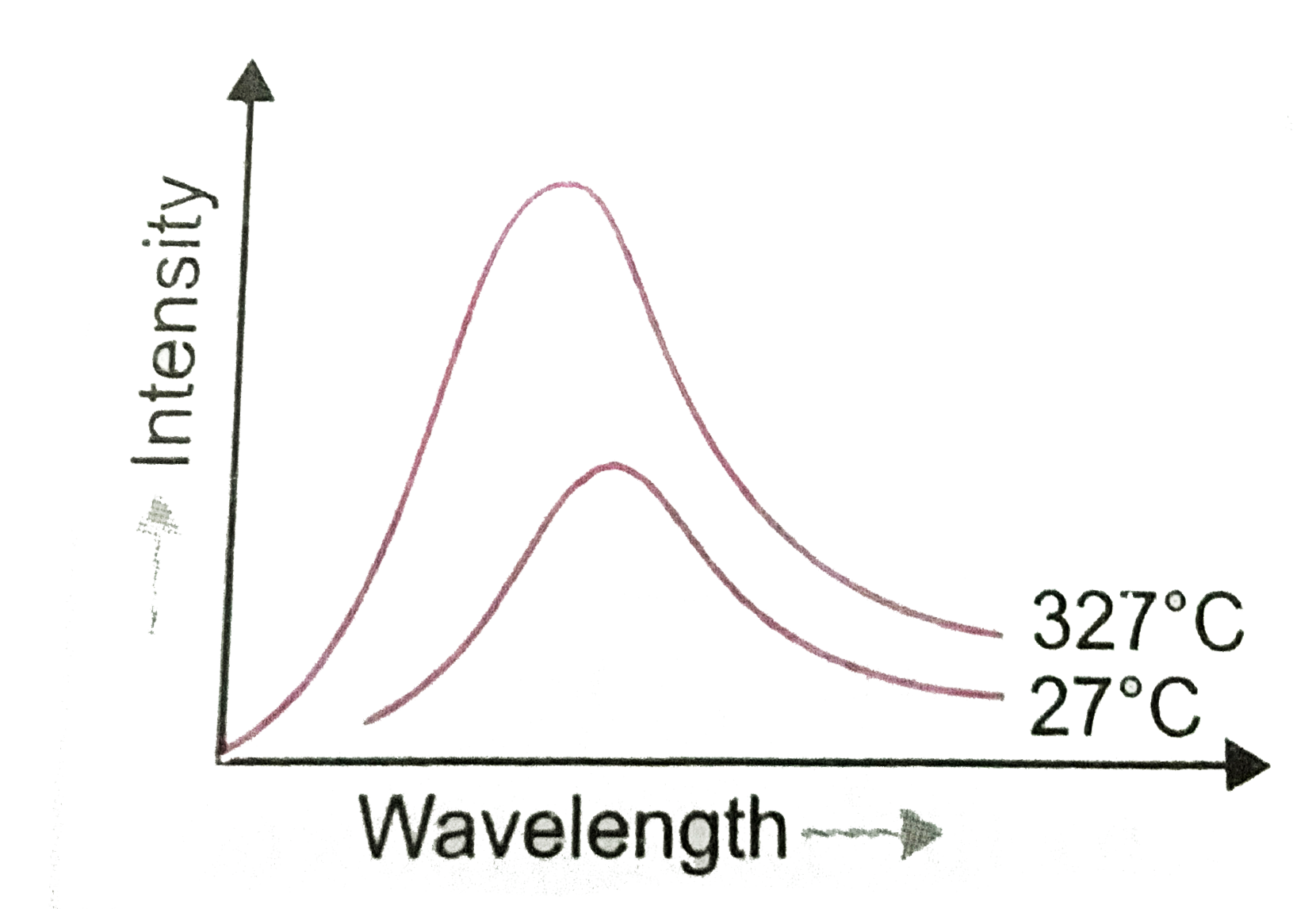
On observing light from three different stars P, Q and R, it was found that intensity of violet colour is maximum in the spectrum of P, the intensity of green colour is maximum in the spectrum of R and the intensity of red colour is maximum in the spectrum of Q. if TP, TQ and TR are respective absolute temperature of P, Q and R. then it can be concluded from the above observation thatView SolutionQuestion 463
The black body spectrum of an object O1 is such that its radiant intensity (i.e. intensity per unit wavelength interval) is maximum at a wavelength of 200 nm. Another object O2 has the maximum radiant intensity at 600 nm. The ratio of power emitted per unit area by source O1 to that of source O2 is View SolutionQuestion 468
Two spheres P and Q of equal radii have densities ρ1 and ρ2, respectively. The spheres are connected by a massless string and placed in liquids L1 and L2 of densities σ1 and σ2 and viscosities η1 and η2, respectively. They float in equilibrium with the sphere P in L1 and sphere Q in L2 and the string being taut(see figure). If sphere P alone in L2 has terminal velocity →Vp and Q alone in L1 has terminal velocity →VQ, then
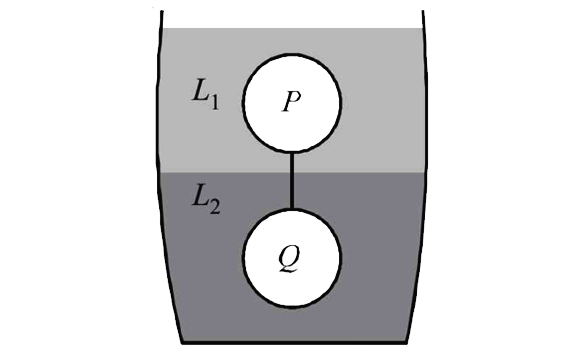 View Solution
View SolutionQuestion 473
A human body has a surface area of approximately 1 m2. The normal body temperature is 10 K above the surrounding room temperature T0. Take the room temperature to be T0=300K. For T0=300K, the value of σT40=460Wm−2 (where σ is the Stefan-Boltzmann constant). Which of the following options is/are correct?View SolutionQuestion 481
Let n number of little droplets of water of surface tension S (dyne/cm), all of the same radius r cm combine to from a single drop of radius R heat, while using cgs system of units answer the following questions.
If the whole energy released is taken by water drop fromed, then rise in temperature in .^(@)C is View SolutionQuestion 482
Let n number of little droplets of water of surface tension S (dyne/cm), all of the same radius r cm combine to from a single drop of radius R heat, while using cgs system of units answer the following questions.
If the radius of the big drop formed is made two times without any change in temperature then the work done is View SolutionQuestion 483
A wooden cylinder of diameter 4 r, height H and density ρ/3 is kept on a hole of diameter 2 r of a tank, filled with water of density ρ as shown in the
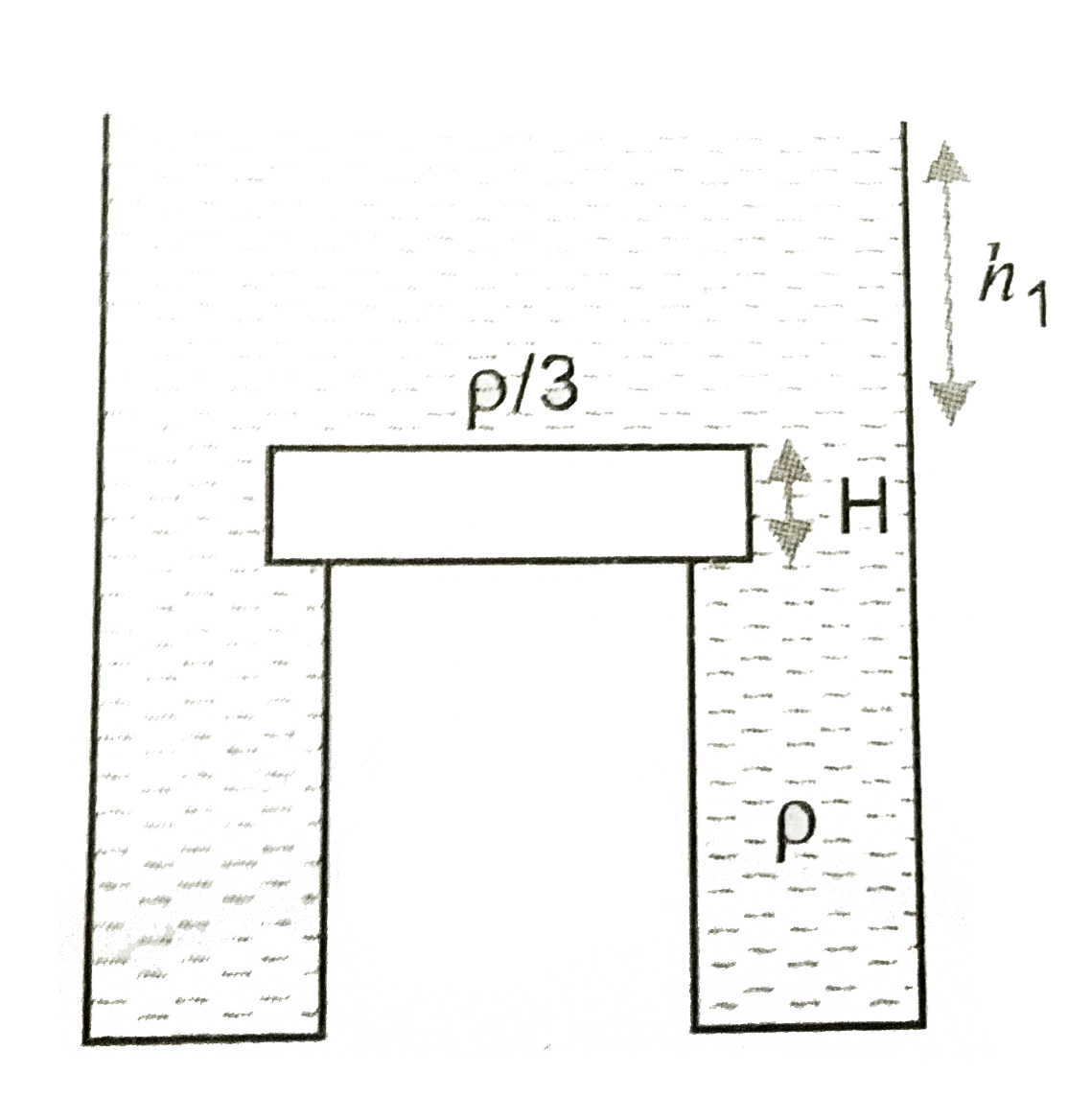
If level of liquid starts decreasing slowly, when the level of liquid is at a height h1 above the cylinder, the block just start moving up. Then the value of h1 is View SolutionQuestion 484
A wooden cylinder of diameter 4 r, height H and density ρ/3 is kept on a hole of diameter 2 r of a tank, filled with water of density ρ as shown in the

The block in the above question is maintained by external means and the level of liquid is lowered. The height h2 when this external force reduces to zero is
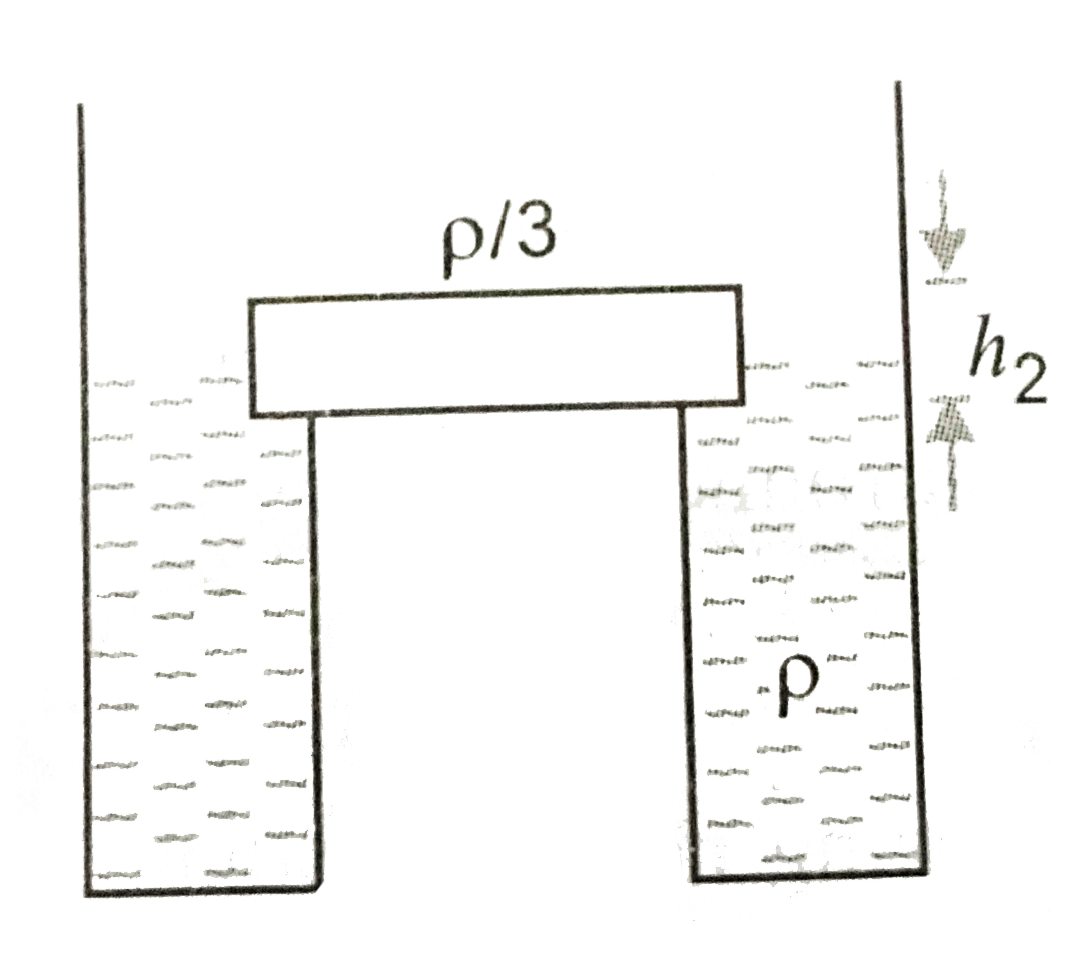 View Solution
View SolutionQuestion 486
During Searle's experiment, zero of the Vernier sacle lies between 3.20×10−2, and 3.25×10−2m of the main scale. The 20th division of the Vernier scale exactly coincides with one of the main scale divisions. When an additional load of 2kg is applied to the wire, the zero of the vernier scale still lies between 3.20×10−2, and 3.25×10−2m of the main scale but now the 45th division of Vernier scale coincide with one of the main scale divisions. the length of the thin metallic wire is 2m and its cross-sectional ares is 8×10−7m2. the least count of the Vernier scale is 1.0×10−5m. the maximum percentage error in the Young's modulus of the wire is View SolutionQuestion 487
When equal volumes of two metals are mixed together the specific gravity of alloy is 4. When equal masses of the same two metals are mixed together the specific gravity of the alloy becomes 3. find specific gravity of each metal?
(specific gravity =density of substancedensity of water)View SolutionQuestion 491
Water flows through a tapering horizontal tube whose radii of cross-section of the ends r1=20cm and r2=10cm. The velocity of water at the points for the radius of cross-section r1 is v1=2ms−1 . The force imparted by the emergiang water at the other end of teh tube is nearly 2×10nN. What is the value of n ?View SolutionQuestion 492
Water flowing steadily through a horizontal pipe of non-unifrom cross-section. If the pressure of water is 4×104N/m2 at a point where cross-section is 0.02m2 and velocity of flow is 2ms−1 . The pressure at a point where cross-section reduces to 0.01m2 is 3.4×10n Pa. What is the value of n ?View SolutionQuestion 493
A piece of ice (heat capacity =2100Jkg−1.∘C−1 and latent heat =3.36×105Jkg−1) of mass m grams is at −5.∘C at atmospheric pressure. It is given 420 J of heat so that the ice starts melting. Finally when the ice . Water mixture is in equilibrium, it is found that 1 gm of ice has melted. Assuming there is no other heat exchange in the process, the value of m in gram is View SolutionQuestion 495
Consider two solid spheres P and Q each of density 8gmcm−3 and diameters 1cm and 0.5cm, respectively. Sphere P is dropped into a liquid of density 0.8gmcm−3 and viscosity η=3 poiseulles. Sphere Q is dropped into a liquid of density 1.6gmcm−3 and viscosity η=2 poiseulles. The ratio of the terminal velocities of P and Q isView SolutionQuestion 496
A metal is heated in a furnace where a sensor is kept above the metal surface to read the power radiated (P) by the metal. The sensor has scale that displays log2,(P/P0), where P0 is constant. When the metal surface is at a temperature of 487∘C, the sensor shows a value 1. Assume that the emissivity of the metallic surface remains constant. What is the value displayed by the sensor when the temperature of the metal surface is raised to 2767∘C?View SolutionQuestion 498
STATEMENT-1: The stream of water flowing at high speed from a garden hose pipe tends to spread like a fountain when held vertically up, but tends to narrow down when held vertically down.
STATEMENT-2: In any steady flow of an incompressible fluid, the volume flow rate of the fluid remains constant.View SolutionQuestion 502
Assertion : A given mass of a gas is subjected to an external pressure of 0.5×1010N/m2 , the bulk modulus of the gas is 0.5×1010N/m2 . The ratio of the density of the gas before and after applying the external pressure is 1:1
Reason : Pressure is inversely proportional to density of gas and bulk modulus is inversely proportional to change in volume View SolutionQuestion 508
Assertion : Water is flowing through a horizontal tube, the static pressure and total pressure at any point are 1.20×105 P and 1.28×105 P . If the density of water is 1000kg/m3 , the velocity of liquid flow is 4 m/s.
Reason : Work done on the liquid by difference in pressure is equal to gain in K.E. of liquid View SolutionQuestion 515
Statement -1 : A tiny shere of mass m and density ρ is dropped in a tall jar of glycerine of density ρ0 . When the sphere acquires terminal velocity v, the magnitude of viscous force is mg(1−ρ0/ρ).
Statement -2 : Viscous force on the body falling in a medium is F=6πηrv , where η is the coeff. of viscosity of medium and r is the radius of bodyView SolutionQuestion 516
In the experiment to determine Young's modulus of the material of a wire under tension
used in the arrangement as shown. The percentage error in the measurement
of length is a in the measurement of the radius of the wire is b and in the
measurement of the change in length of the wire is c. Percentage error in the measurement
of Young's modulus for a given load is
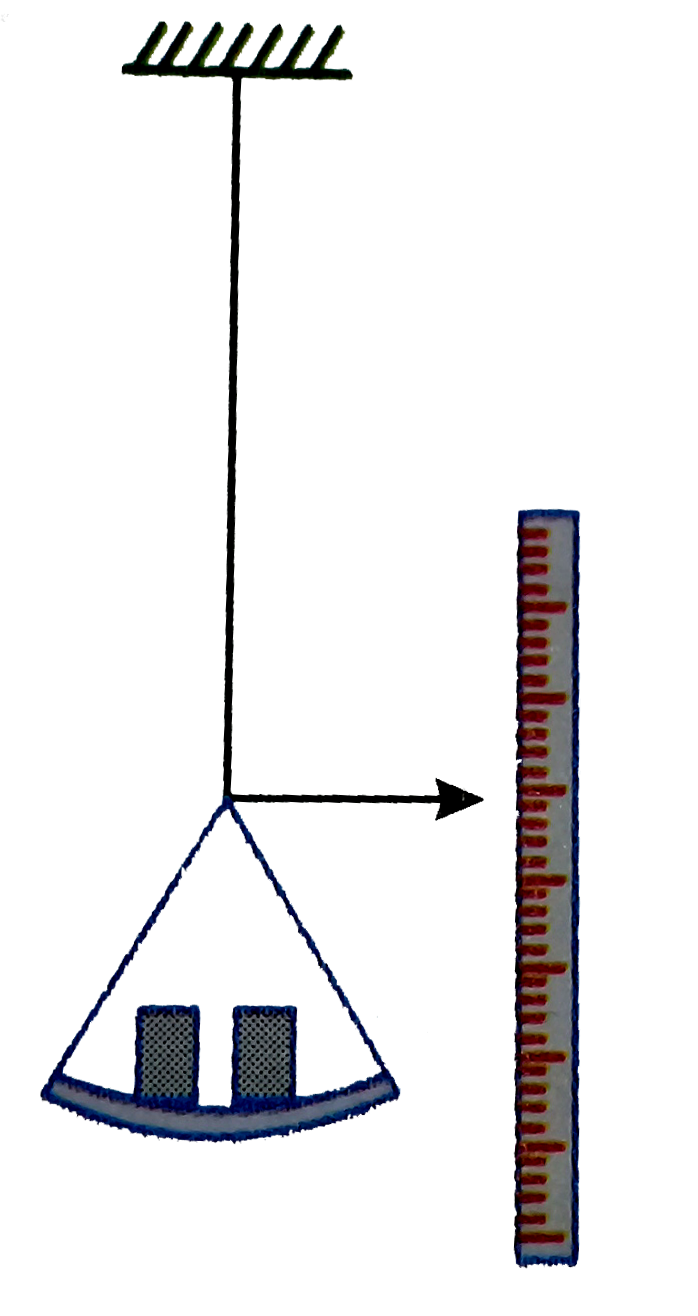 View Solution
View Solution
All Exercises from PRADEEP PHYSICS (HINGLISH) Class 11 PHYSICS PROPERTIES OF BULK MATTER
- ASSERATION - REASON TYPE QUESTION
- FILL IN THE BLANKS A
- FILL IN THE BLANKS B
- FILL IN THE BLANKS C
- FILL IN THE BLANKS D
- FILL IN THE BLANKS E
- INTEGER TYPE QUESTIONS
- MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
- MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS-I
- MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS-II
- PROBLMES FOR PRACTICE
- TEST YOUR GRIP A
- TEST YOUR GRIP B
- TEST YOUR GRIP C
- TEST YOUR GRIP D
- TEST YOUR GRIP E
- ADVANCED PROBLEMS FOR COMPETITIONS
- CONCEPTUAL PROBLEMS
- CURIOSITY QUESTIONS
- HIGHER ORDER THINKING SKELLS
- LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
- NCERT QUESTIONS
- SAMPLE PROBLEM
- SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
- SOLVED EXAMPLES
- VALUE BASED QUESTION
- VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
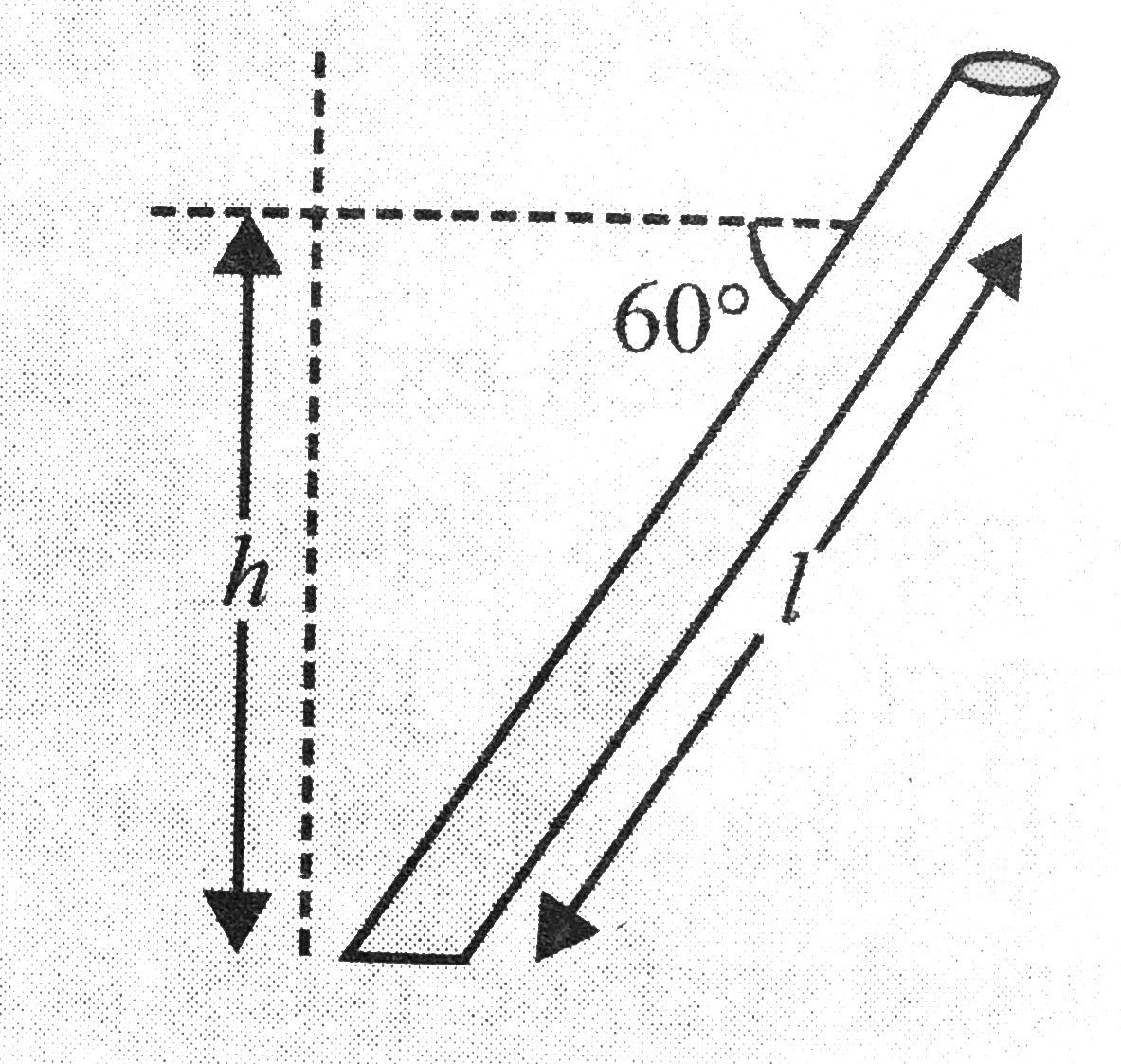

_S01_001_Q01.png)
 .
.