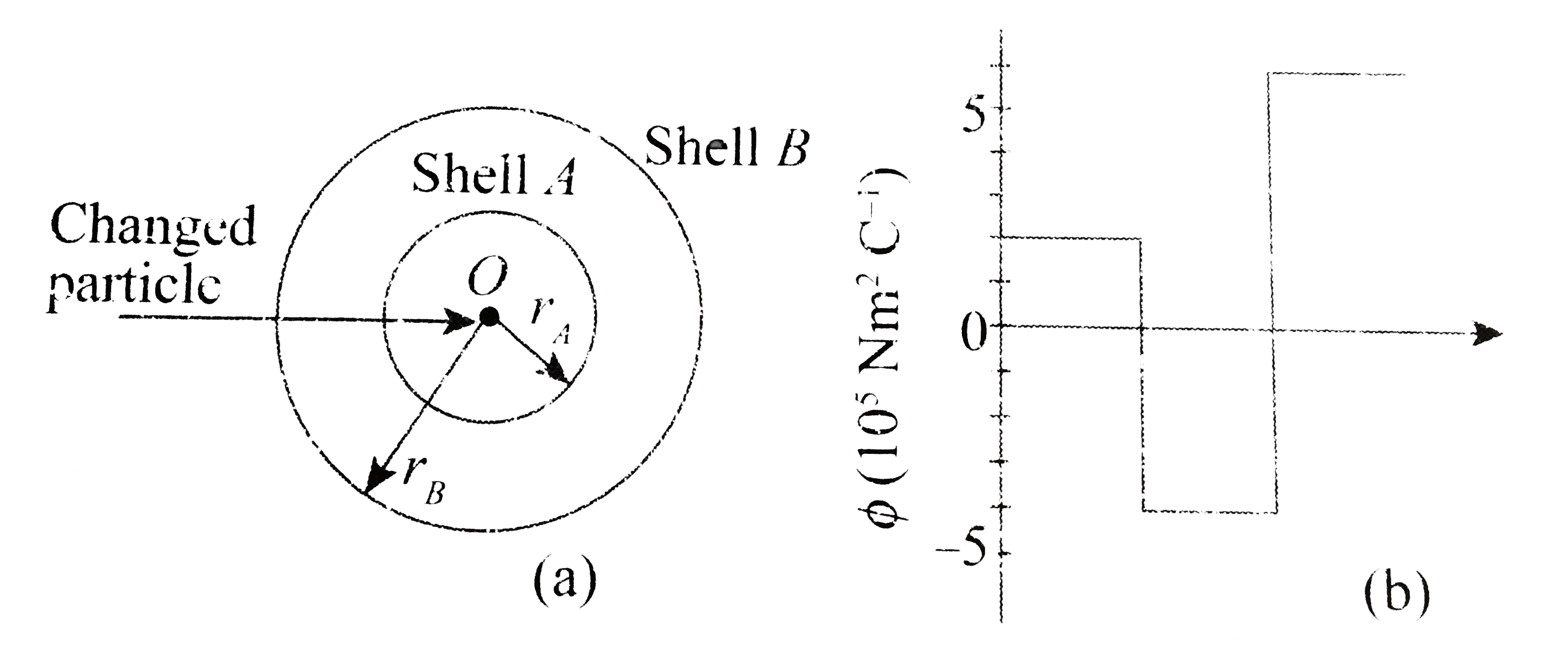
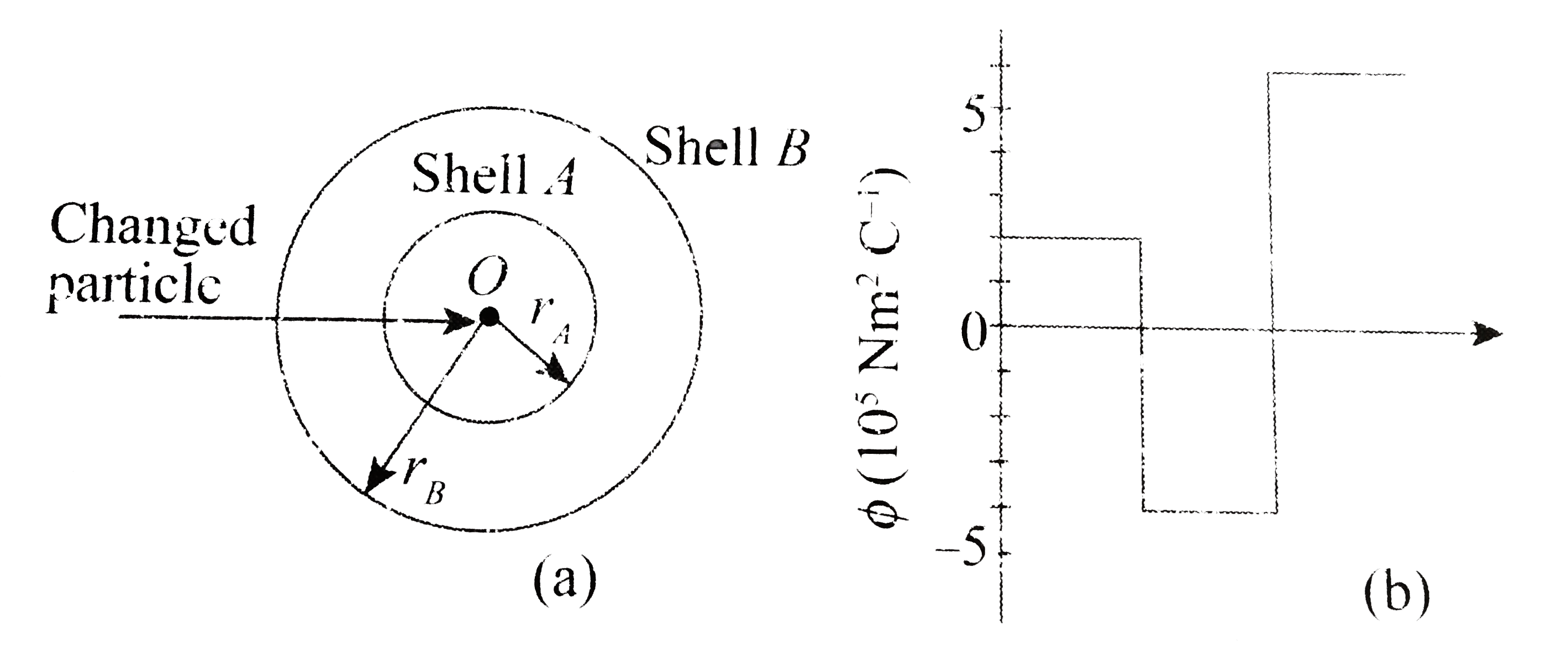
A charged particle is suspended at the center of two thin concentric spherical charged shells, made of nonconducting material. Figure shows cross section of the arrangement. Figure (b) gives the net flux ϕ through a Gaussian sphere centered on the particle, as a function of the radius r of the sphere.
 ,
,
In which range of the values of r is the electric field zero?
0→rA
rA→rB
for r>rB
for no range of r, electric field is zero.
The correct Answer is:D
We see that ϕ remains constant up to r1. So r1<rA. Let q be the charge at centre than
ϕ=qinε0 or 2×105=q8.85×10−12 or q=1.77μC ltBrgt Similarly ϕ=−4×105=q+qAε0 qA=−5.31μC
Where qA is the charge on A. electric field is zero nowhere as ϕ is not zero anywhere.

Topper's Solved these Questions
- MISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 3Book:CENGAGE PHYSICSChapter:MISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 3Exercise:Interger Answer type
Explore 20 Videos
- MISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 3Book:CENGAGE PHYSICSChapter:MISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 3Exercise:Fill in the blanks
Explore 10 Videos
- MISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 3Book:CENGAGE PHYSICSChapter:MISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 3Exercise:Assertion and Reason Type
Explore 8 Videos
- MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDSBook:CENGAGE PHYSICSChapter:MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDSExercise:Question Bank
Explore 4 Videos
- MISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 5Book:CENGAGE PHYSICSChapter:MISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 5Exercise:Integer
Explore 12 Videos
Similar Questions
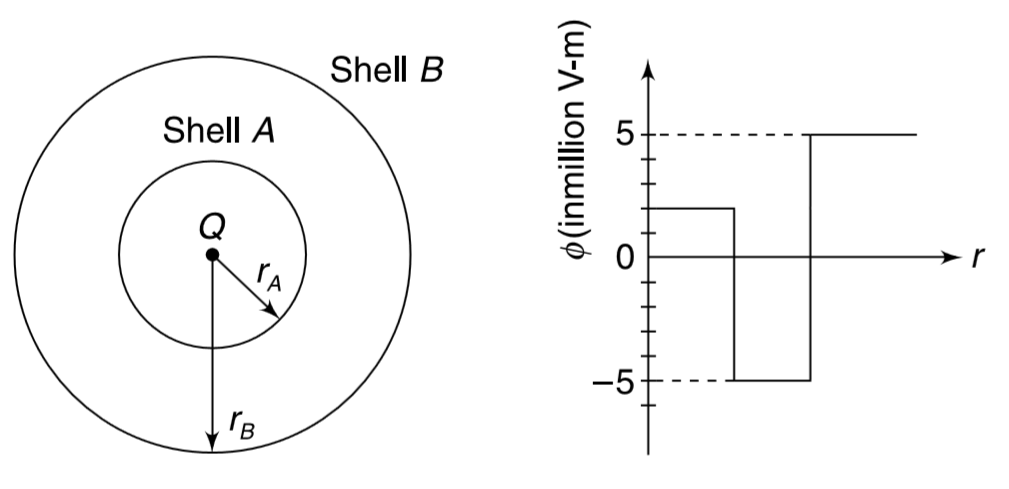
A charged particle is placed at the centre of two thin concentric spherical charged shells, made of non-conducting material. Figure A shows cross-section of the arrangement. Figure B gives the net flux ϕ through a Gaussian sphere centered on the particle, as a function of the radius r of the sphere. (a) Find charge on the central particle and shell A. (b) In which range of the finite values of r, is the electric field zero?
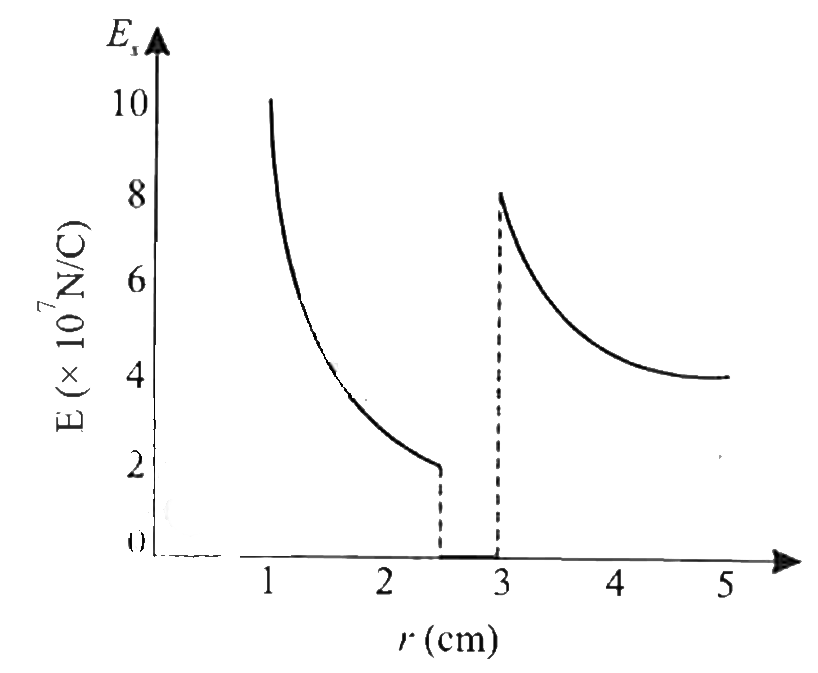
View SolutionA charged particle is held a the centre of a spherical shell. The following figure gives the magnitude E of the electric field versus radial distance r. what is the net charge on the shell ?
View Solution
Knowledge Check
A charged particle is suspended at the centre of two thin concentric spherical charged shells, made of non conducting material. Figure A shows cross section of the arrangement. Figure B gives the net flux ϕ through a Gaussian sphere centered on the particle, as a function of the radius r of the sphere.

In which range of the values of r is the electric field zero ?A0 to rABrA to rBCFor r>rBDFor no range of r, electric field is zero.A charged particle is suspended at the centre of two thin concentric spherical charged shells, made of non conducting material. Figure A shows cross section of the arrangement. Figure B gives the net flux ϕ through a Gaussian sphere centered on the particle, as a function of the radius r of the sphere.
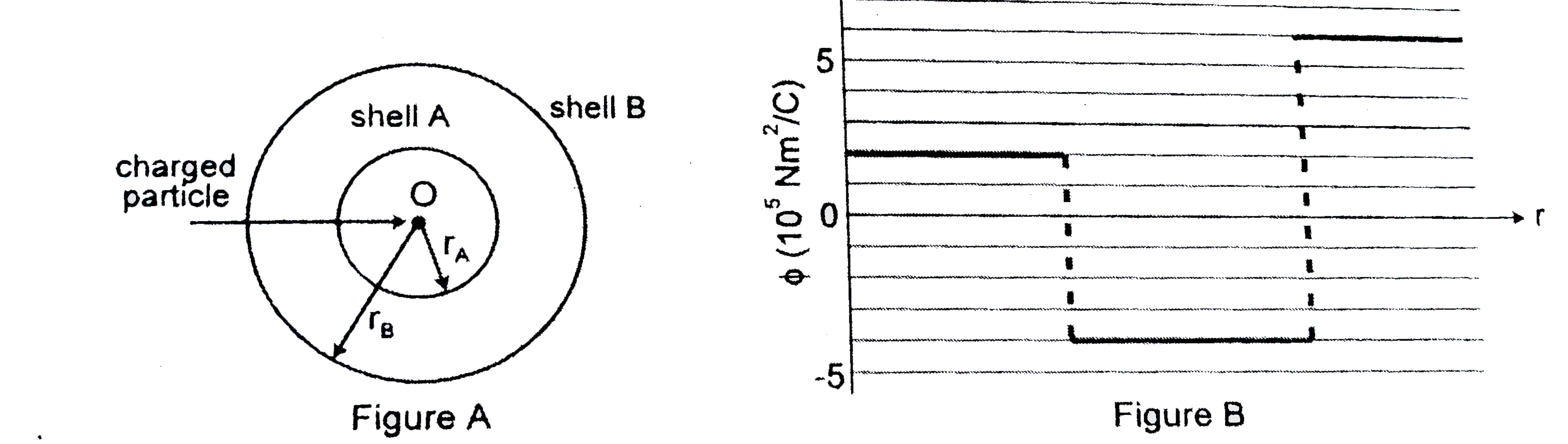
What is the charge on shell A ?A5.31μCB−5.31μCC−3.54μCD−1.77μCA charged particle is suspended at the center of two thin concentric spherical charged shells, made of nonconducting material. Figure shows cross section of the arrangement. Figure (b) gives the net flux ϕ through a Gaussian sphere centered on the particle, as a function of the radius r of the sphere.
 ,
,
What is the charge on the central particle?A0.2μCB2μCC1.77μCD3.4μC
A charged particle is suspended at the centre of two thin concentric spherical charged shells, made of non conducting material. Figure A shows cross section of the arrangement. Figure B gives the net flux ϕ through a Gaussian sphere centered on the particle, as a function of the radius r of the sphere.
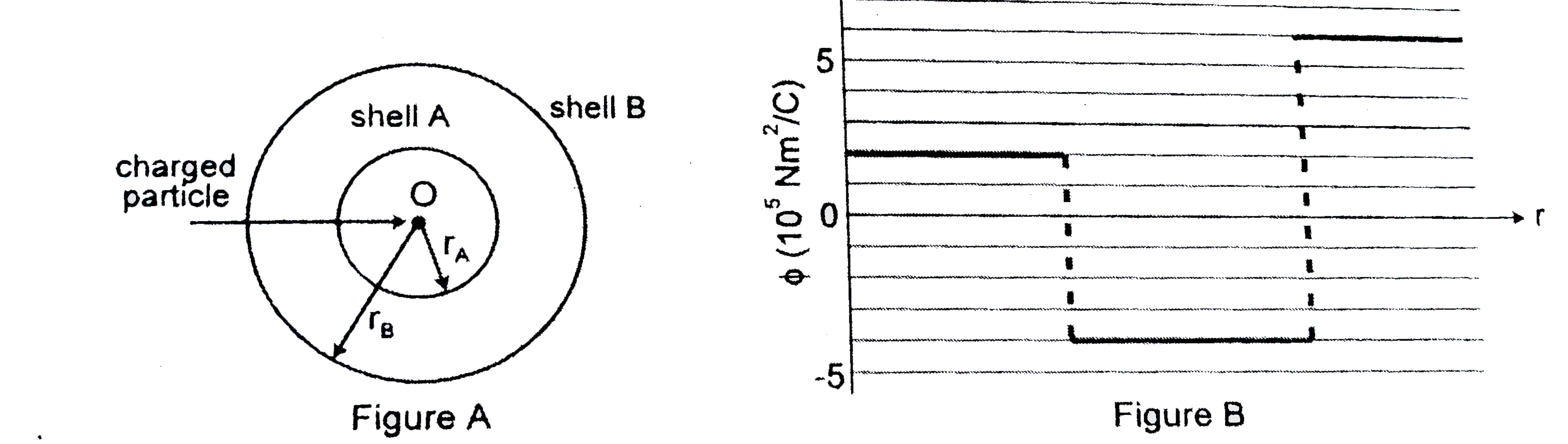
What is the charge on shell A ?
View SolutionA charged particle is suspended at the centre of two thin concentric spherical charged shells, made of non conducting material. Figure A shows cross section of the arrangement. Figure B gives the net flux ϕ through a Gaussian sphere centered on the particle, as a function of the radius r of the sphere.
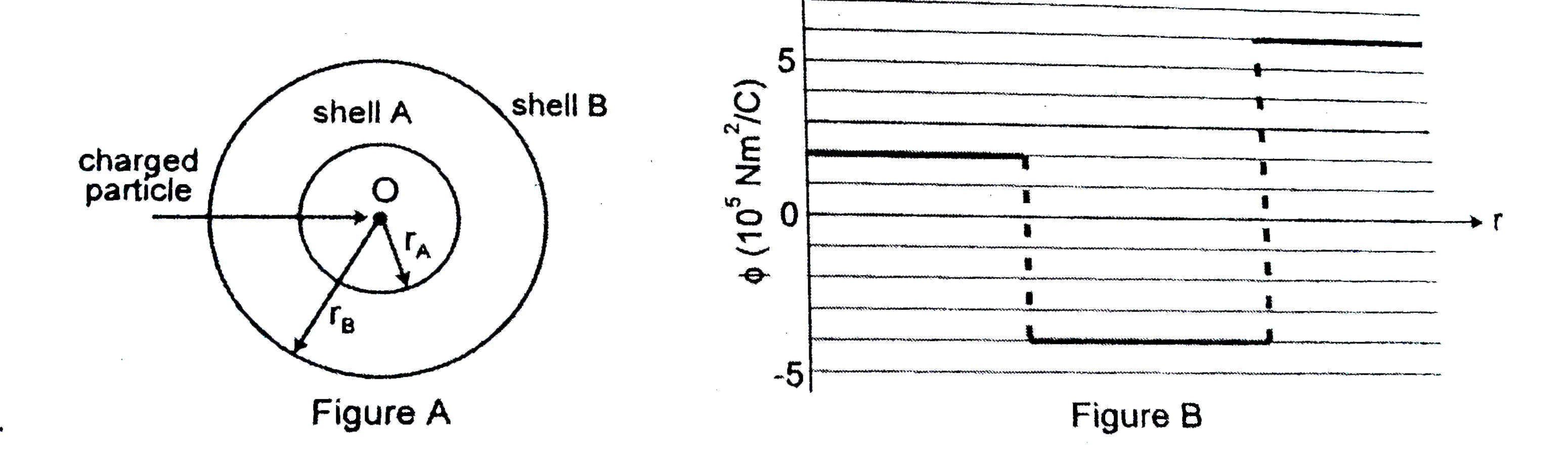
What is the charge on the central particle ?
View SolutionA non-conducting spherical shell of radius R surrounds a point charge q (q at center). The electric flux through a cap of the shell of half angle θ is:
View SolutionAn infinite, uniformly charged sheet with surface charge density σ cuts through a spherical Gaussian surfance of radius R at a distance X from its center, as shown in the figure. The electric flux Φ through the Gaussian surfce is .

View SolutionGraph shows magnitude of electric field (E), charge enclosed (qenclosed⟩) within the concentic sphere and net flux (ϕ) through a concentric spherical Gaussian surface as a function of distance (r) from centre of a uniformly positive charged solid sphere of radius R. Choose the correct option (s):
View Solution

