An ideal gas is initially at temperature T and volume V. It's volume increases by ΔV due to an increase in temperature of ΔT, pressure remaining constant. The quantity μ=ΔVVΔT varies with temperature as -
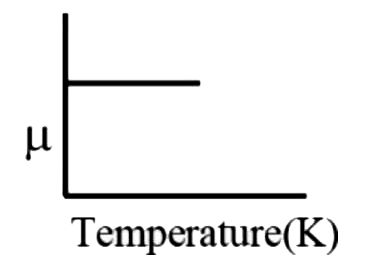
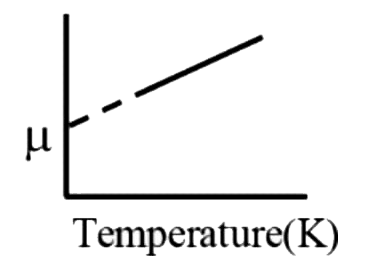
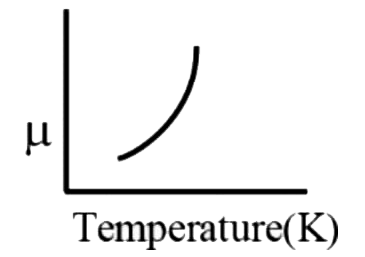
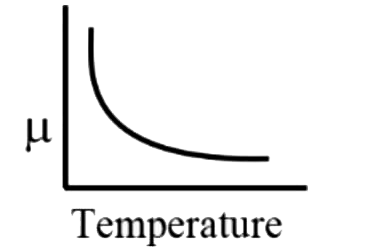
The correct Answer is:D
V=KT⇒ΔV=KΔT
∴ΔVΔT=K…….(i)
⇒μ=ΔVVΔT⇒μα1V⇒μα1T
So graph between u & T will be rectangular hyperbola.
टॉपर्स ने हल किए ये सवाल
समान प्रश्न
RH2 (ion exchange resin) can replace Ca2+ ions in hard water as:
RH2+Ca2+→Rca+2H+
If 1 L of hard water after passing through RH2 has pH = 3, then hardness in parts per million of Ca2+ is :
View SolutionAn excited hydrogen atom emits a photon of wavelength λ in returning to the ground state. If R is the Rydberg constant, then the quantum number n of the excited state is
View SolutionAn ideal gas is initially at temperature T and volume V. Its volume is increased by ΔV due to an increase in temperature ΔT, pressure remaining constant. The quantity δ=ΔVVΔT varies with temperature as
View SolutionAn ideal gas is initially at temperature T and volume V . Its volume is increased by DeltaV due to an increase in temperature Delta , pressure remaining constant . The quantity delta=DeltaV//VDeltaT varies with temperature as
View SolutionAn ideal gas is initially at temperature T and volume V. Its volume is increased by ΔV due to an increase in temperature ΔT, pressure remaining constant. The quantity δ=ΔVVΔT varies with temperature as
View SolutionAn ideal gas is initiaily at temperature T and volumoeV. lts volume is increased by Delta V due to an increase in temperature Delta T , pressure remaining constant. The quantity k = AV//(V Delta T) varies with temperature as:
View SolutionAn ideal gas is initially at temperature T and volume V. Its volume is increased by Delta V due to an increase in temperature Delta T . Pressure remaining constant. The physical quantity delta = ( Delta V)/( V Delta T) varies with temperature as :
View SolutionAn ideal gas is initially at temperature T and volume V. Its volume is increased by DeltaV due to an increase in temperature DeltaT, pressure remaining constant. The quantity delta=(DeltaV)/(VDeltaT) varies with temperature as
View SolutionAn ideal gas is initially at temperature T and volume V. ITS volume is increased by DeltaV due to an increase in temperature DeltaT , pressure remaining constant. The quantity delta = DeltaV//V DeltaT varies with temperature as
View Solutionएक आदर्श गैस प्रारम्भ में तापमान T और आयतन V पर होती है। इसके तापमान में ΔT की वृद्धि के कारण आयतन ΔV तक बढ़ जाता है, दाब नियत रहता है। मात्रा μ=ΔVVΔT तापमान के साथ किस रूप में परिवर्तित होती है?
View SolutionAn ideal gas is initially at temperature T and volume V. Its volume is increased by ΔV due to an increase in temperature DelatT, pressure remaining constant. The quantity δ=ΔVVΔT varies with temperature as :
View SolutionAn ideal gas is initially at temperature T and volume V. Its volume is increased by ΔV due to an increase in temperature ΔT, pressure remaining constant. The quantity δ=ΔVVΔT varies with temperature as :
View SolutionAn ideal gas is at temperature T and volume V.Its volume is increased by DeltaV due to an increases by DeltaT pressure remaining constant, the quantity delta = DeltaV/(VDeltaT) varies with temperature as
View SolutionAn ideal gas is initially at temperature T and volume V. Its volume is increased by DeltaV due to an increase in temperature DeltaT , pressure remaining constant. The quantity delta=(DeltaV)/((V DeltaT)) varies with temperature as:
View SolutionAn ideal gas is initially at temperature T and volume V. Its volume is increased by DeltaV due to an increase in temperature DeltaT, pressure remaining constant. The quantity delta=(DeltaV)/(VDeltaT) varies with temperature as
View SolutionThe variation of volume V, with temperature T, keeping pressure constant is called the coefficient of thermal expansion (alpha) of a gas, i.e., alpha=(1)/(V)((deltaV)/(deltaT))_(P) . For an ideal gas alpha is equal to
View Solution

