From the list of characteristics given below, select the five which are relevant to non-metals and their compounds.
Write the letters corresponding to the correct characteristics.
A. Ductile
B. Conduct electricity
C. Brittle
D. Acidic oxides
E. Basic oxides
F. Discharged at anode
G. Discharged at cathode
H. Ionic chlorides
I. Covalent chlorides
J. Reaction with dilute sulphuric acid yields hydrogen.
K. 1, 2 or 3 valence electrons
L. 5, 6 or 7 valence electrons
To solve the question of identifying the five characteristics relevant to non-metals and their compounds from the provided list, we will analyze each option step by step.
1. A. Ductile:
- Non-metals are not ductile. Ductility is a property of metals, which can be drawn into wires. Therefore, this characteristic does not apply to non-metals.
- Conclusion: Not relevant.
2. B. Conduct electricity:
- Non-metals are generally poor conductors of electricity. This property is typical of metals. Hence, this characteristic does not apply to non-metals.
- Conclusion: Not relevant.
3. C. Brittle:
- Non-metals are brittle in nature. When subjected to stress, they tend to shatter rather than deform. This is a characteristic property of non-metals.
- Conclusion: Relevant.
4. D. Acidic oxides:
- Non-metals typically form acidic oxides. For example, sulfur forms sulfur dioxide (SO2), which is acidic in nature. This is a characteristic property of non-metals.
- Conclusion: Relevant.
5. E. Basic oxides:
- Basic oxides are primarily characteristic of metals. Non-metals do not commonly form basic oxides. Therefore, this characteristic does not apply to non-metals.
- Conclusion: Not relevant.
6. F. Discharged at anode:
- Non-metals are discharged at the anode during electrolysis. This is because they tend to gain electrons and form negative ions. Thus, this characteristic is relevant to non-metals.
- Conclusion: Relevant.
7. G. Discharged at cathode:
- This property is typical of metals, which are discharged at the cathode as they form positive ions. Therefore, this characteristic does not apply to non-metals.
- Conclusion: Not relevant.
8. H. Ionic chlorides:
- Ionic chlorides are formed by metals. Non-metals typically do not form ionic chlorides; they form covalent chlorides instead. Thus, this characteristic does not apply to non-metals.
- Conclusion: Not relevant.
9. I. Covalent chlorides:
- Non-metals can form covalent chlorides, such as carbon tetrachloride (CCl4). This is a characteristic property of non-metals.
- Conclusion: Relevant.
10. J. Reaction with dilute sulphuric acid yields hydrogen:
- Non-metals do not react with dilute sulfuric acid to produce hydrogen. This reaction is characteristic of metals. Therefore, this characteristic does not apply to non-metals.
- Conclusion: Not relevant.
11. K. 1, 2 or 3 valence electrons:
- This characteristic is typical of metals. Non-metals usually have more valence electrons. Therefore, this characteristic does not apply to non-metals.
- Conclusion: Not relevant.
12. L. 5, 6 or 7 valence electrons:
- Non-metals typically have 5, 6, or 7 valence electrons. For example, nitrogen has 5, oxygen has 6, and chlorine has 7 valence electrons. This is a characteristic property of non-metals.
- Conclusion: Relevant.
Final Selection of Relevant Characteristics:
The five characteristics relevant to non-metals and their compounds are:
- C. Brittle
- D. Acidic oxides
- F. Discharged at anode
- I. Covalent chlorides
- L. 5, 6 or 7 valence electrons
- Non-metals are not ductile. Ductility is a property of metals, which can be drawn into wires. Therefore, this characteristic does not apply to non-metals.
- Conclusion: Not relevant.
- Non-metals are generally poor conductors of electricity. This property is typical of metals. Hence, this characteristic does not apply to non-metals.
- Conclusion: Not relevant.
- Non-metals are brittle in nature. When subjected to stress, they tend to shatter rather than deform. This is a characteristic property of non-metals.
- Conclusion: Relevant.
- Non-metals typically form acidic oxides. For example, sulfur forms sulfur dioxide (SO2), which is acidic in nature. This is a characteristic property of non-metals.
- Conclusion: Relevant.
- Basic oxides are primarily characteristic of metals. Non-metals do not commonly form basic oxides. Therefore, this characteristic does not apply to non-metals.
- Conclusion: Not relevant.
- Non-metals are discharged at the anode during electrolysis. This is because they tend to gain electrons and form negative ions. Thus, this characteristic is relevant to non-metals.
- Conclusion: Relevant.
- This property is typical of metals, which are discharged at the cathode as they form positive ions. Therefore, this characteristic does not apply to non-metals.
- Conclusion: Not relevant.
- Ionic chlorides are formed by metals. Non-metals typically do not form ionic chlorides; they form covalent chlorides instead. Thus, this characteristic does not apply to non-metals.
- Conclusion: Not relevant.
- Non-metals can form covalent chlorides, such as carbon tetrachloride (CCl4). This is a characteristic property of non-metals.
- Conclusion: Relevant.
- Non-metals do not react with dilute sulfuric acid to produce hydrogen. This reaction is characteristic of metals. Therefore, this characteristic does not apply to non-metals.
- Conclusion: Not relevant.
- This characteristic is typical of metals. Non-metals usually have more valence electrons. Therefore, this characteristic does not apply to non-metals.
- Conclusion: Not relevant.
- Non-metals typically have 5, 6, or 7 valence electrons. For example, nitrogen has 5, oxygen has 6, and chlorine has 7 valence electrons. This is a characteristic property of non-metals.
- Conclusion: Relevant.
The five characteristics relevant to non-metals and their compounds are:
- C. Brittle
- D. Acidic oxides
- F. Discharged at anode
- I. Covalent chlorides
- L. 5, 6 or 7 valence electrons
Topper's Solved these Questions
- METALS AND NON METALSBook:S CHAND IIT JEE FOUNDATIONChapter:METALS AND NON METALSExercise:QUESTION BANK-15 (Fill in the boxes with letters to give the correct answer with the help of the given clues)
Explore 15 Videos
- METALS AND NON METALSBook:S CHAND IIT JEE FOUNDATIONChapter:METALS AND NON METALSExercise:QUESTION BANK-16
Explore 1 Video
- METALS AND NON METALSBook:S CHAND IIT JEE FOUNDATIONChapter:METALS AND NON METALSExercise:QUESTION BANK-15 (Answer true or false)
Explore 10 Videos
- HYDROGENBook:S CHAND IIT JEE FOUNDATIONChapter:HYDROGENExercise:SELF ASSESSMENT SHEET
Explore 28 Videos
- SYNTHETIC FIBRES AND PLASTICSBook:S CHAND IIT JEE FOUNDATIONChapter:SYNTHETIC FIBRES AND PLASTICSExercise:Self Assessment Sheet - 14
Explore 29 Videos
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
Benzene diazonium chloride on boiling with dilute sulphuric acid, gives
ATolueneBBenzoic acidCBenzeneDPhenolThe cathode reaction in electrolysis of dilute sulphuric acid with Platinum electrode is
AOxidationBReductionCBoth oxidation and reductionDNeutralizationMatch the compounds given in List I with their characteristic reactions given in List II Select the correct option
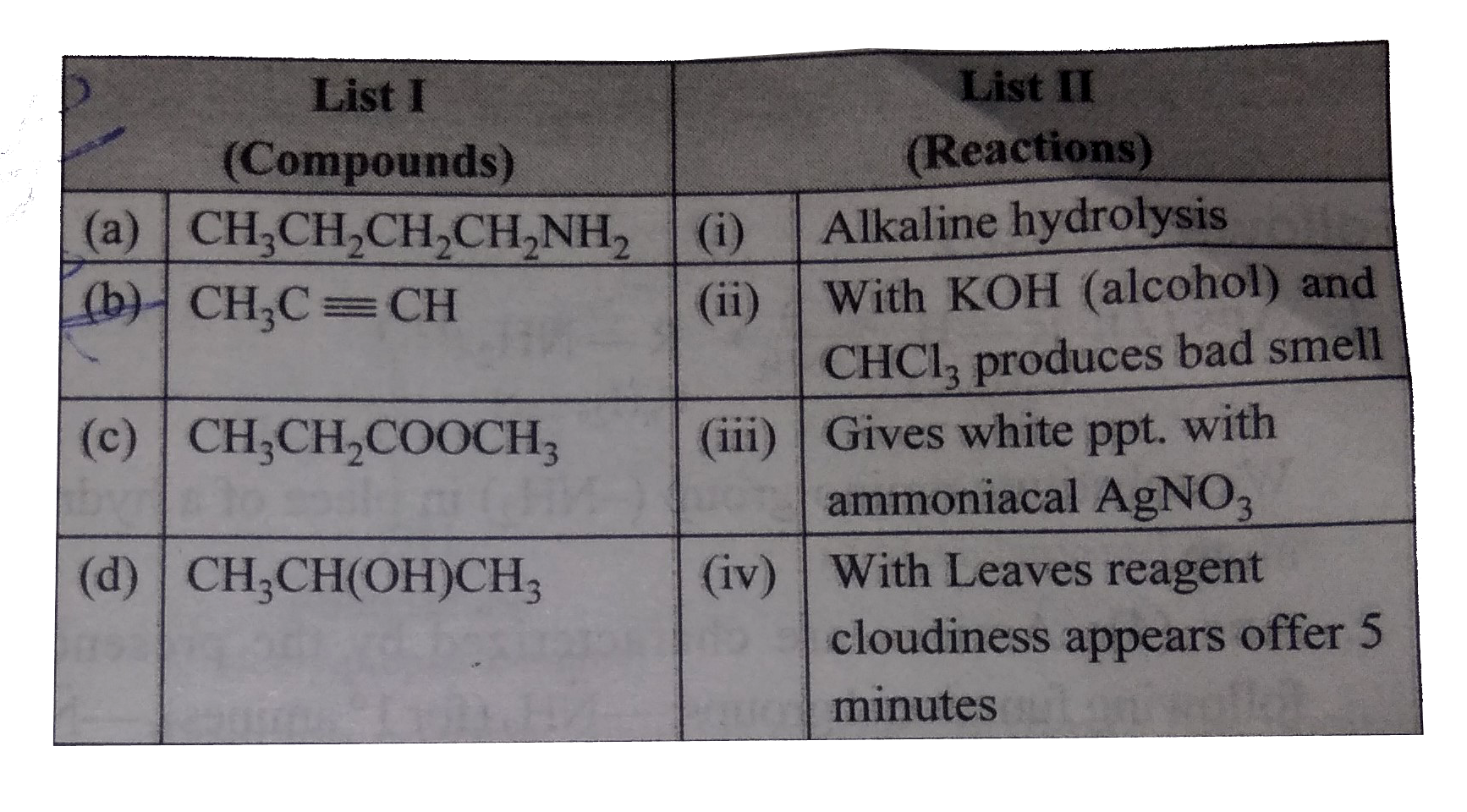 .A(ii) (i) (iv) (iii)B(iii) (ii) (i) (iv)C(ii) (iii) (i) (iv)D(iv) (ii) (iii) (i)
.A(ii) (i) (iv) (iii)B(iii) (ii) (i) (iv)C(ii) (iii) (i) (iv)D(iv) (ii) (iii) (i)
Dilute sulphuric acid is added to barium chloride solution.
View SolutionName two non-metals which are both brittle and non-ductile.
View SolutionMatch List-I (Soil Type) with List-II (Characteristics) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists -

View SolutionThe characteristic properties of metals are
I Malleability
II Ductility
III Formation of acidic oxides
View SolutionThe electrolytic decomposition of dilute sulphuric acid with platinum electrode, cathodic reaction is:
View Solution