Ten millilitre of a gaseous hydrocarbon was burnt completely in 80 ml of O2 at STP. The volume of the remaining gas is 70 ml. The volume became 50 ml, on treatment with NaOH. The formula of the hydrocarbon is:
C2H6
C2H4
C3H8
C3H6
The correct Answer is:B
To solve the problem step by step, we will analyze the combustion of the gaseous hydrocarbon and the subsequent reactions.
Step 1: Identify the hydrocarbon
Let the hydrocarbon be represented as CxHy.
Step 2: Write the balanced combustion reaction
When the hydrocarbon burns in oxygen, it produces carbon dioxide and water:
CxHy+O2→CO2+H2O
Step 3: Determine the volumes of gases involved
From the problem, we know:
- Volume of hydrocarbon burnt = 10 mL
- Volume of oxygen used = 80 mL
- Volume of remaining gas after combustion = 70 mL
Step 4: Calculate the volume of unreacted oxygen
The volume of gas remaining after combustion is 70 mL. This volume consists of unreacted oxygen and possibly other gases. The volume of unreacted oxygen can be calculated as:
Remaining gas=Unreacted O2+CO2+H2O
Since water is in vapor form and not counted in the gas volume, we can focus on the unreacted oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Step 5: Calculate the volume of carbon dioxide produced
When the gas is treated with NaOH, the volume reduces to 50 mL. NaOH absorbs carbon dioxide, so the change in volume (70 mL to 50 mL) indicates the volume of CO2 produced:
Volume of CO2=70 mL−50 mL=20 mL
Step 6: Relate the volume of CO2 to the hydrocarbon
From the combustion reaction, we know that:
Volume of CO2=10x mL
Setting this equal to the volume of CO2 produced:
10x=20⟹x=2
Step 7: Determine the volume of unreacted oxygen
Now, we can find the volume of unreacted oxygen. The total volume of oxygen initially was 80 mL. The volume of oxygen consumed can be calculated using the stoichiometry of the reaction:
Volume of O2=x+y410 mL
Substituting x=2:
Volume of O2=80−(2+y4)⋅10
The remaining volume after combustion is 70 mL, which includes unreacted oxygen:
70=80−(2+y4)⋅10
Solving for y:
70=80−20−2y⟹2y=10⟹y=5
Step 8: Write the final formula of the hydrocarbon
Now we have x=2 and y=5, so the formula of the hydrocarbon is:
C2H5
Conclusion
The formula of the hydrocarbon is C2H5, which corresponds to ethane.
Let the hydrocarbon be represented as CxHy.
When the hydrocarbon burns in oxygen, it produces carbon dioxide and water:
CxHy+O2→CO2+H2O
From the problem, we know:
- Volume of hydrocarbon burnt = 10 mL
- Volume of oxygen used = 80 mL
- Volume of remaining gas after combustion = 70 mL
The volume of gas remaining after combustion is 70 mL. This volume consists of unreacted oxygen and possibly other gases. The volume of unreacted oxygen can be calculated as:
Remaining gas=Unreacted O2+CO2+H2O
Since water is in vapor form and not counted in the gas volume, we can focus on the unreacted oxygen and carbon dioxide.
When the gas is treated with NaOH, the volume reduces to 50 mL. NaOH absorbs carbon dioxide, so the change in volume (70 mL to 50 mL) indicates the volume of CO2 produced:
Volume of CO2=70 mL−50 mL=20 mL
From the combustion reaction, we know that:
Volume of CO2=10x mL
Setting this equal to the volume of CO2 produced:
10x=20⟹x=2
Now, we can find the volume of unreacted oxygen. The total volume of oxygen initially was 80 mL. The volume of oxygen consumed can be calculated using the stoichiometry of the reaction:
Volume of O2=x+y410 mL
Substituting x=2:
Volume of O2=80−(2+y4)⋅10
The remaining volume after combustion is 70 mL, which includes unreacted oxygen:
70=80−(2+y4)⋅10
Solving for y:
70=80−20−2y⟹2y=10⟹y=5
Now we have x=2 and y=5, so the formula of the hydrocarbon is:
C2H5
The formula of the hydrocarbon is C2H5, which corresponds to ethane.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- PURIFICATION OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS AND QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE ANALYSISBook:CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISHChapter:PURIFICATION OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS AND QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE ANALYSISExercise:Assertion Reasoning Type
Explore 5 Videos
- PURIFICATION OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS AND QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE ANALYSISBook:CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISHChapter:PURIFICATION OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS AND QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE ANALYSISExercise:Multiple Correct Answers Type
Explore 10 Videos
- PERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS AND GENERAL INORGANIC CHEMISTRYBook:CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISHChapter:PERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS AND GENERAL INORGANIC CHEMISTRYExercise:Exercises (Archives )Subjective
Explore 4 Videos
- REDOX REACTIONSBook:CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISHChapter:REDOX REACTIONSExercise:Archives (Integers)
Explore 1 Video
Similar Questions
8.4 " mL of " gaseous hydrocarbon A was burnt with 50 " mL of " O2 in a eudiometer tube. The volume of the products after cooling to room temperature was 37.4 mL. When reacted with NaOH, the volume contracted to 3.8 mL. What is the molecular formula of A.
View SolutionTwenty millilitres of a gaseous hydrocarbon (A) was exploded with excess of oxygen in eudiometer tube. On cooling, the volume was reduced by 50ml. On further treatement with KOH solution, there was a further contraction of 40 ml.
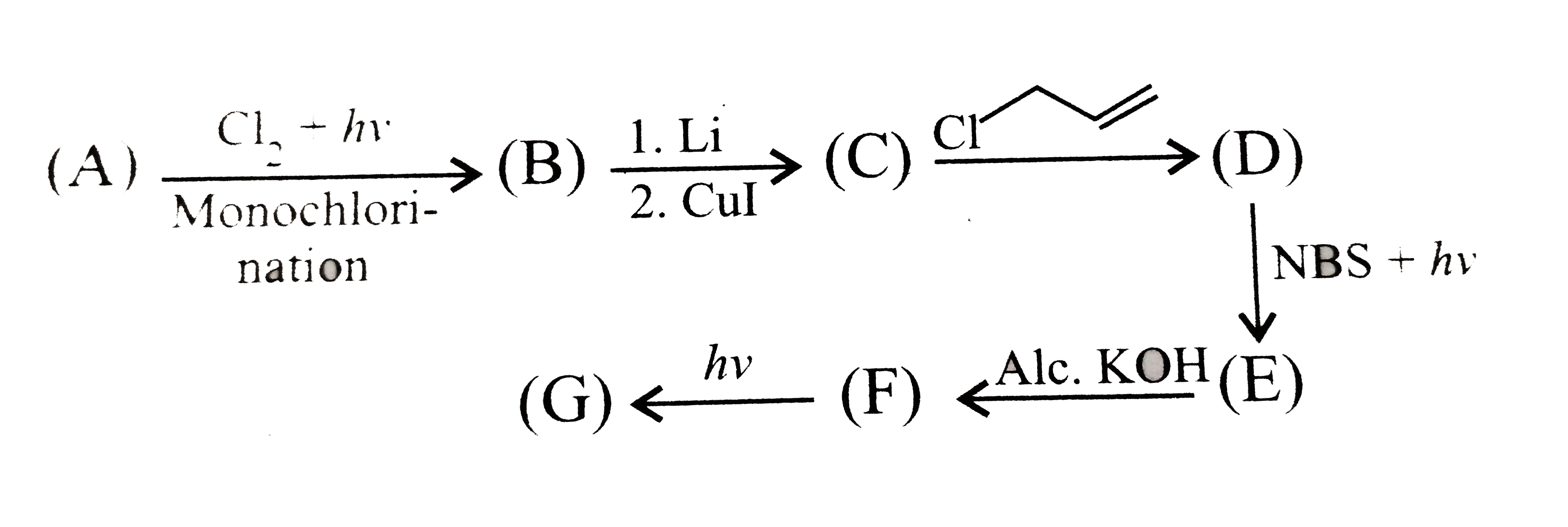
The molecular formula of the hydrocarbon (A) is:
View SolutionFifteen milliliters of gaseous hydrocarbo (A) was required for complete combustion 357 ml of air (21 % oxygen by volume) and gaseous products occupied 327 ml (all volumes being measured at STP).

The molecular formula of the hydrocarbon (A) is:
View SolutionTwenty millilitres of a gaseous hydrocarbon (A) was exploded with excess of oxygen in eudiometer tube. On cooling, the volume was reduced by 50ml. On further treatement with KOH solution, there was a further contraction of 40 ml.
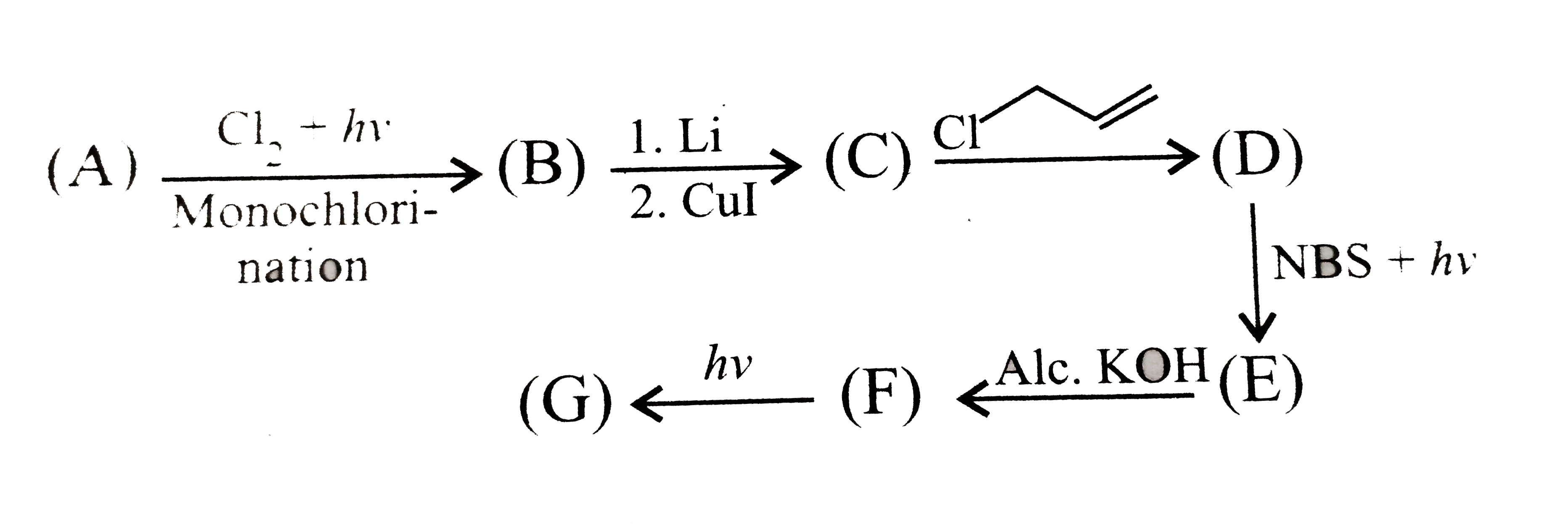
Compound (G) is:
View SolutionTwenty millilitres of a gaseous hydrocarbon (A) was exploded with excess of oxygen in eudiometer tube. On cooling, the volume was reduced by 50ml. On further treatement with KOH solution, there was a further contraction of 40 ml.
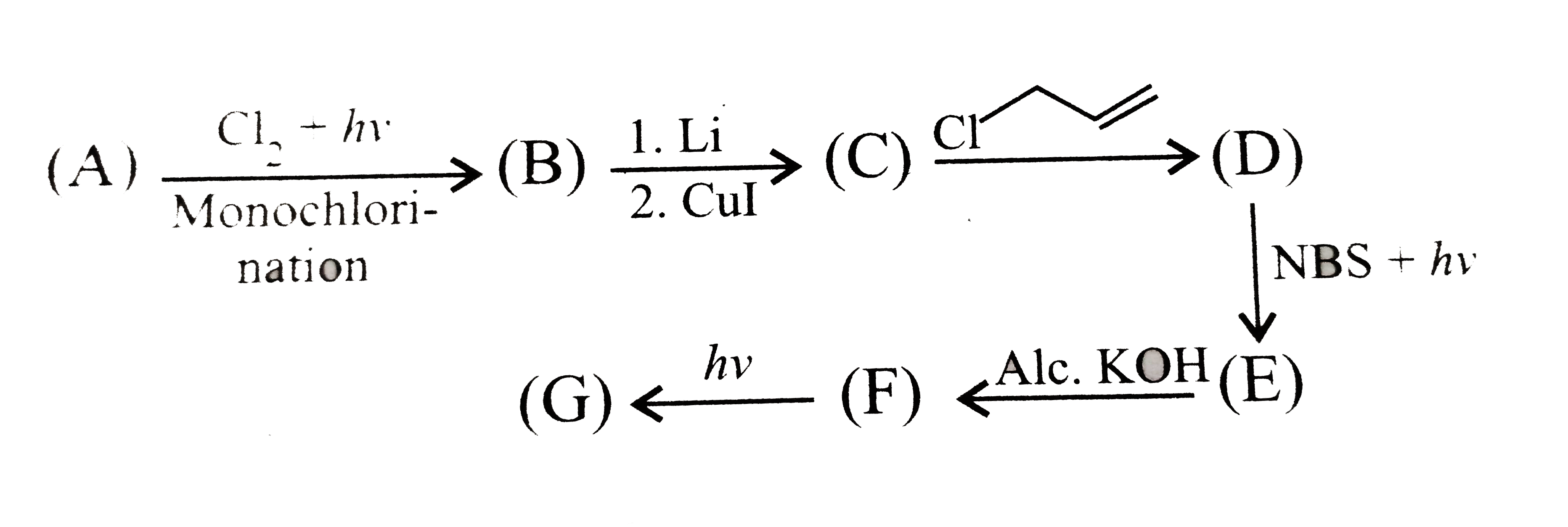
Compound (D) is:
View SolutionTwenty millilitres of a gaseous hydrocarbon (A) was exploded with excess of oxygen in eudiometer tube. On cooling, the volume was reduced by 50ml. On further treatement with KOH solution, there was a further contraction of 40 ml.
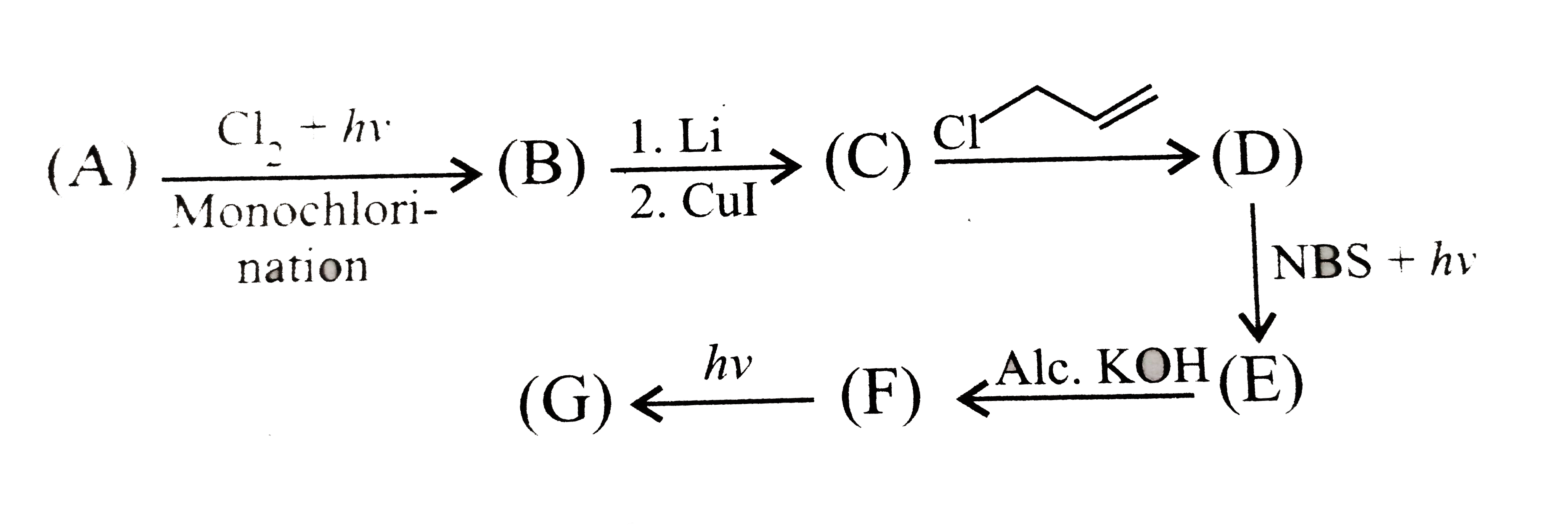
Compound (E) is:
View SolutionTwenty millilitres of a gaseous hydrocarbon (A) was exploded with excess of oxygen in eudiometer tube. On cooling, the volume was reduced by 50ml. On further treatement with KOH solution, there was a further contraction of 40 ml.
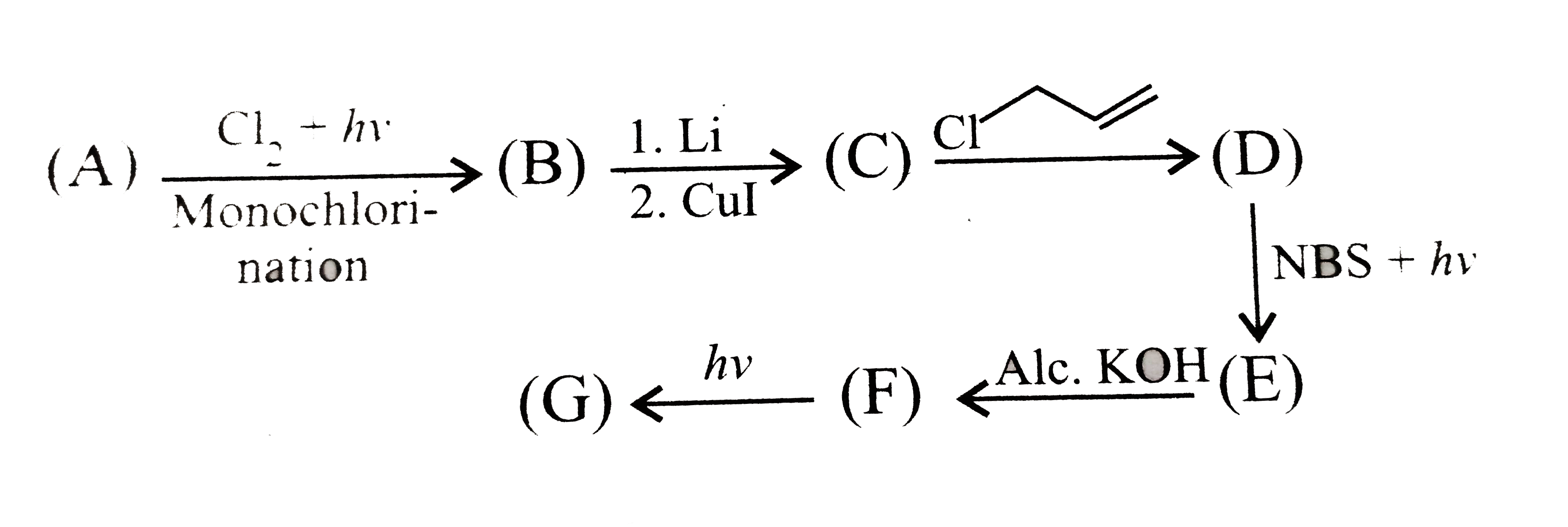
Compound (C) is:
View Solution15 " mL of " a gaseous hydrocarbon A requried for complete combustion. 357 " mL of " air (21% oxygen by volume) and gaseous products occupied 327 mL (all volumes being measured at STP. The molecular formula of the hydrocarbon A is
(a). C2H6
(b). C2H4
(c). C3H6
(d). C3H6
View SolutionA sample of a gaseous hydrocarbon is burnt in excess oxygen. The
products of the reaction are 8L of CO2(g) 10 L of H2O(g), all at
0∘C and 1 atm pressure. The formula of the hydrocarbon is-
View Solution10 ml of gaseous hydrocarbon on combution gives 20ml of CO2
and 30ml of H2O(g). The hydrocarbon is :-
View Solution
