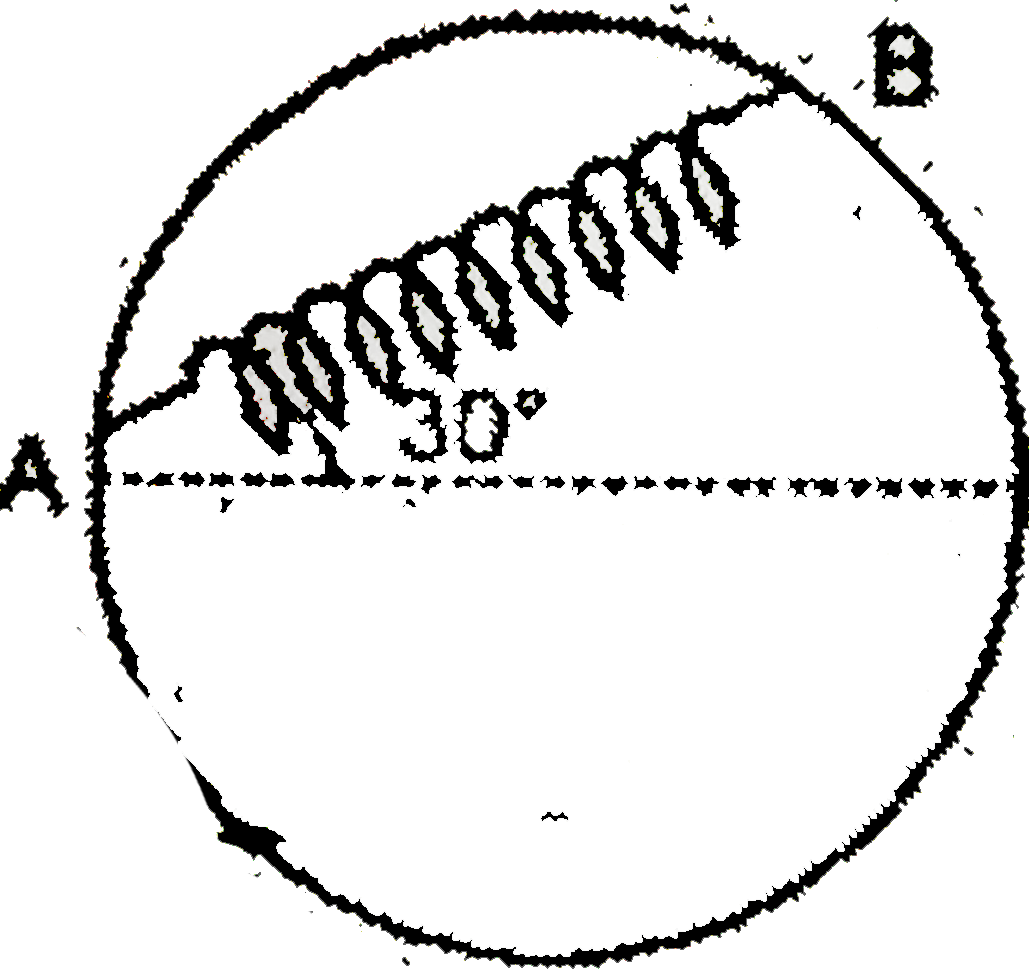
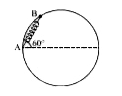
A bead of mass m is attached to one end of a spring of natural length R and spring is fixed at point A on a smooth vertical ring of radius R as shown in figure. The normal reaction at B just after it is released to move is

a. mg/2
√3mg
3√3mg
3√3mg2
The correct Answer is:D
Extension in the spring is
x=AB−R=2Rcos30∘−R=(√3−1)R
Spring force: F=kx=(√3+1)mgR×(√3−1)R=2mg
From the fig, we have
N=(F+mg)cos30∘=3√3mg2
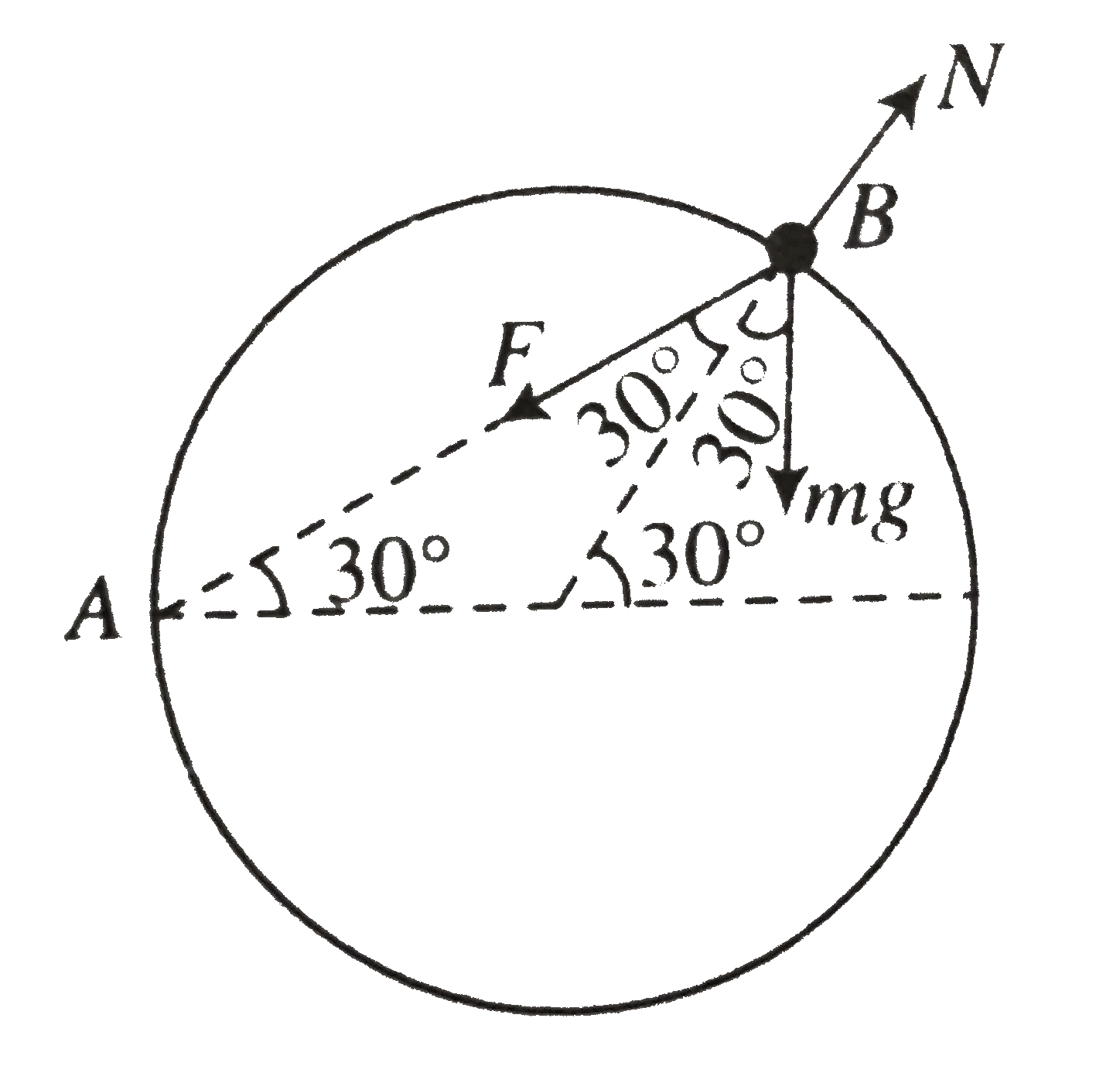
Topper's Solved these Questions
- NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 1BOOK - CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHCHAPTER - NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 1EXERCISE - Multiple Correct
11 Videos
- NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 1BOOK - CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHCHAPTER - NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 1EXERCISE - Assertion-reasoning
15 Videos
- NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 1BOOK - CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHCHAPTER - NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 1EXERCISE - Subjective
15 Videos
- MISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 2BOOK - CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHCHAPTER - MISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 2EXERCISE - INTEGER_TYPE
10 Videos
- NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 2BOOK - CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHCHAPTER - NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 2EXERCISE - Integer type
1 Video
Similar Questions
A block of mass m=10kg is suspended with the help of three strings as shown in fig. Find the tensions T1 and T2.

View SolutionStatement I: The driver of a moving car sees a wall in front of him. To avoid collision, he should apply brakes rather than taking a turn away from the wall.
Statement II: Frictional force is needed to stop the car or taking a turn on a horizontal road.
View SolutionA hot- air balloon consists of a basket, one passenger, and some carge. Let the total mass be M. Even though there is an upward lift force on the balloon, the balloon is initially acceleration downwards at a rate of g/3.
(a) Draw a free-body diagram for the descending balloon.
(b) Find the upward lift force in terms of the initial total weight Mg.
(c ) The passenger notices that he is heading straight for a waterfall and decides he needs to go up. What fraction of the total weight must he drop overboard so that the balloon accelerates upward at a rate of g/2? Assume that the upward lift force remains the same.
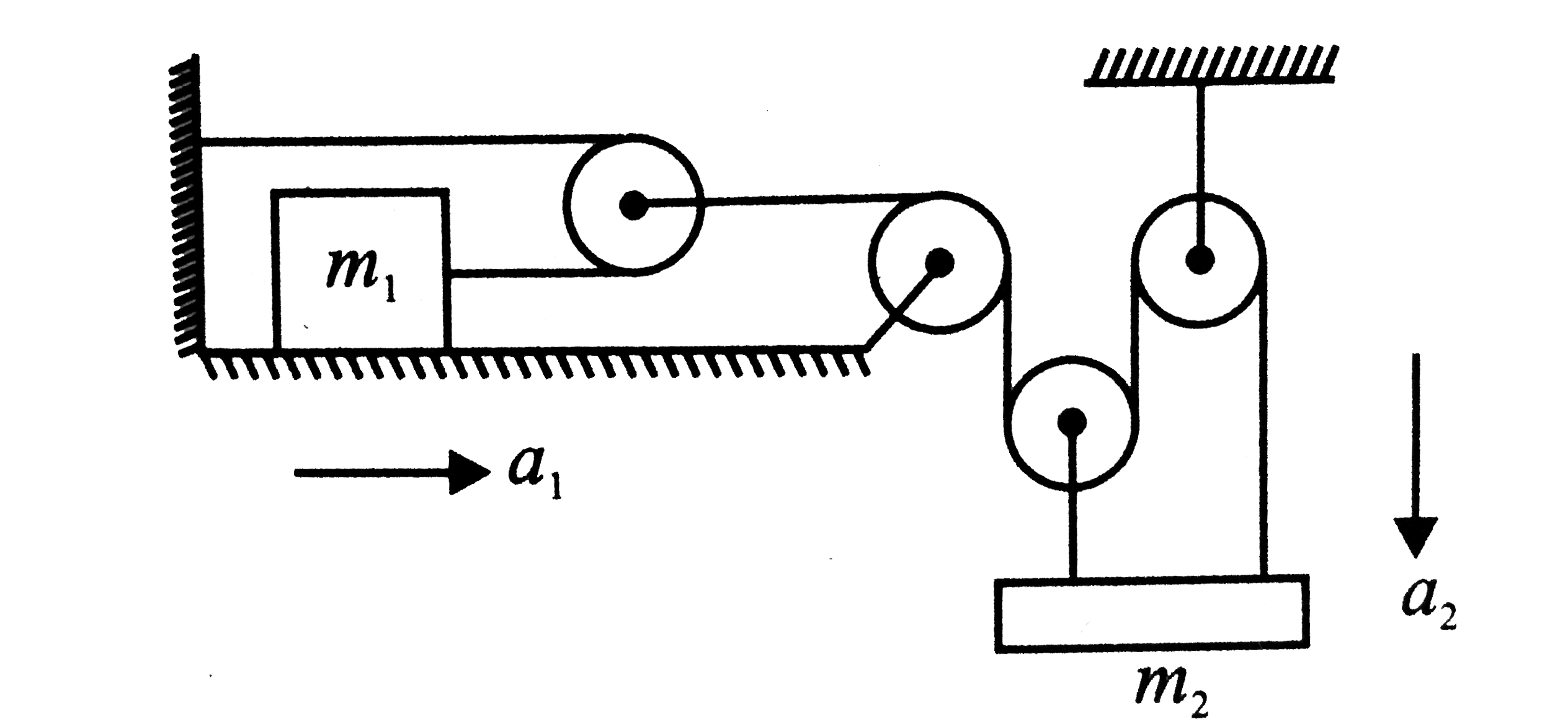
View SolutionTwo blocks are arranged as shown in figure. Find the ratio of a1/a2. (a1 is acceleration of m1 and a2 that of m2)
View SolutionA block is moving on an inclined plane making an angle 45∘ with the horizontal and the coefficient of friction is μ. The force required to just push it up the inclined plane is 3 times the force required to just prevent it from sliding down. If we define N=10μ, then N is
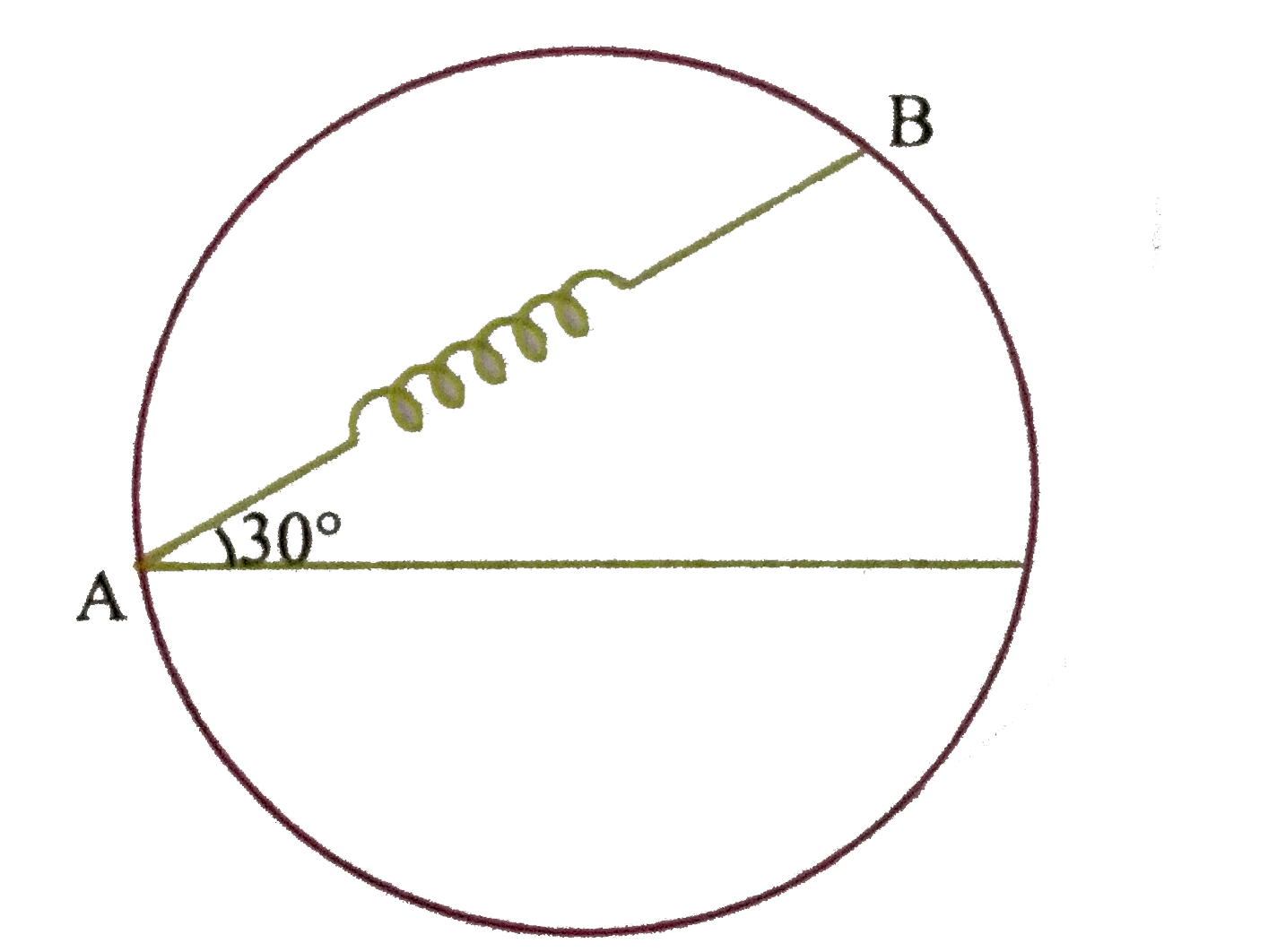
View SolutionA Bead of mass m is attached to one end of a spring of natural length 'R' and spring cosntant 'k=(√3+1)mgR'. The other end of the spring is fixed at point 'A' on a smooth vertical ring of radius 'R' as shown
View Solution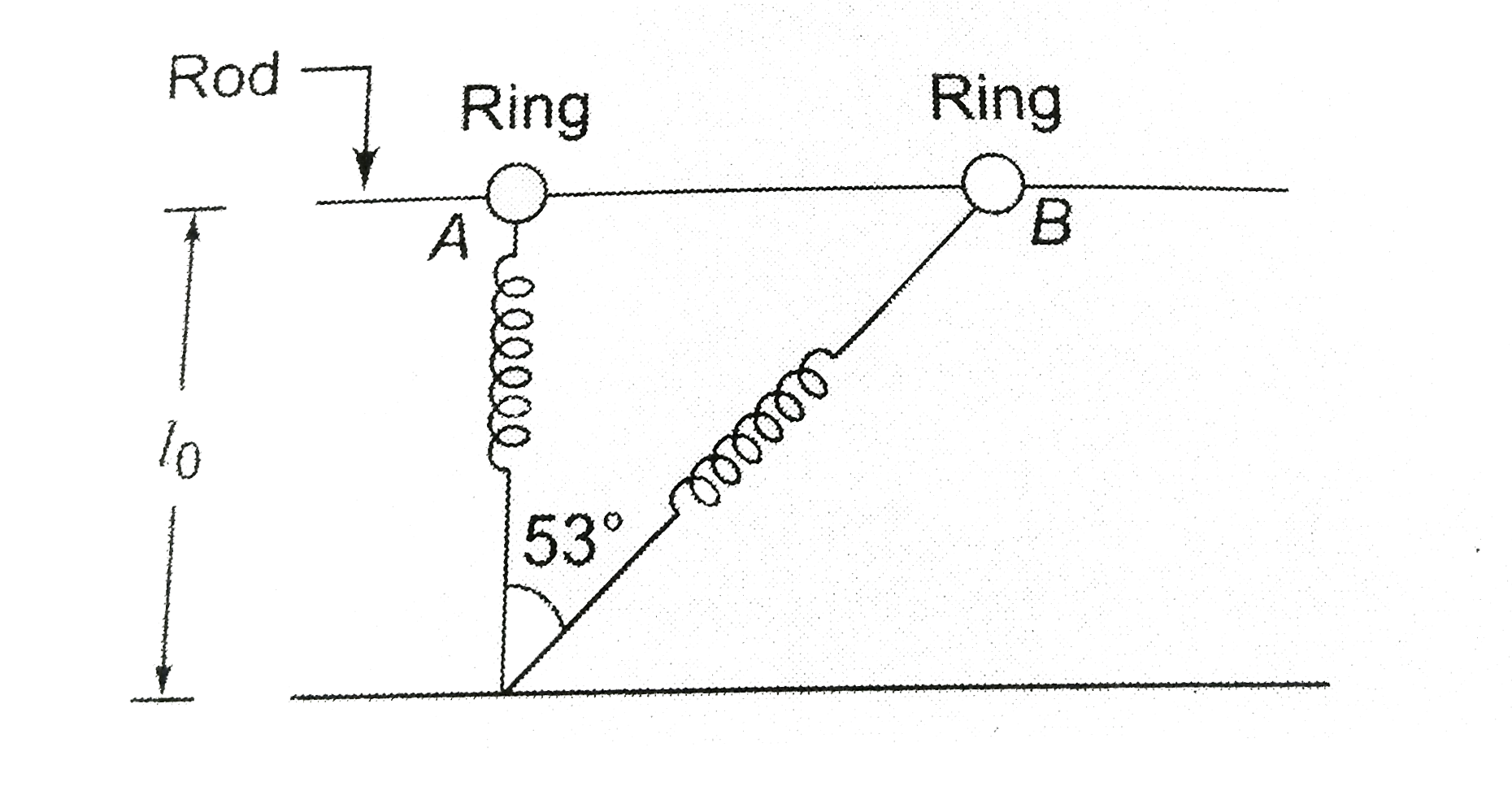
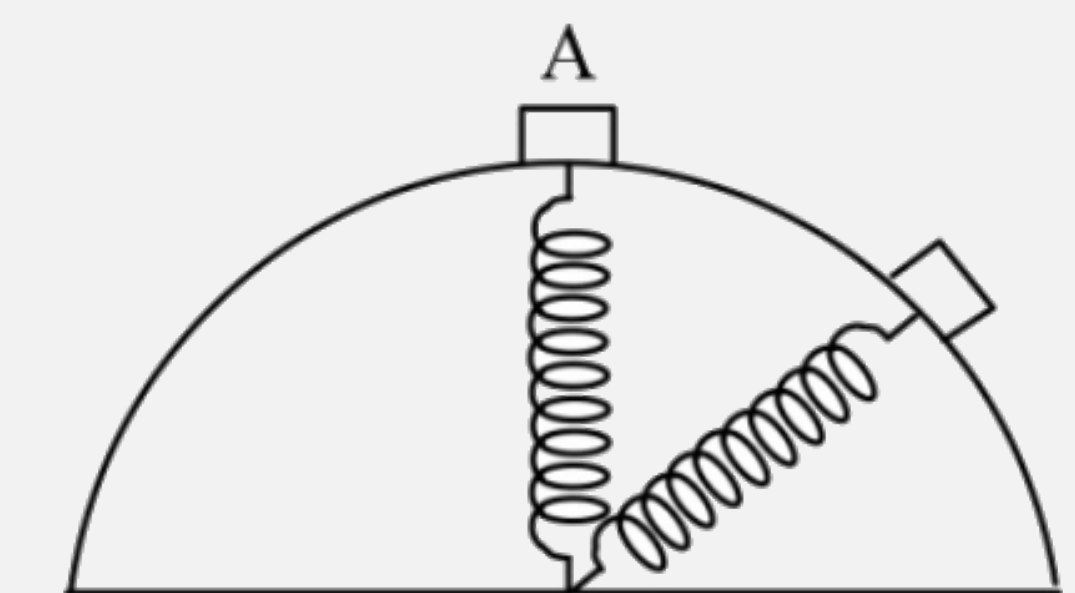
A ring of mass m is attached to a horizontal spring of spring constant k and natural length l0. The other end of the spring is fixed and the ring can slide on a horizontal rod as shown. Now the ring is shifted to position B and released Find the speed of the ring when the spring attains its natural length.
View SolutionA Bead of mass m is attached to one end of a spring of natural length 'R' and spring cosntant 'k=((sqrt3+1)mg)/R' . The other end of the spring is fixed at point 'A' on a smooth vertical ring of radius 'R' as shown
View SolutionA ring of mass m can slide over a smooth vertical rod. The ring is connected to a spring of force constant K=(4mg)/R where 2R is the natural length of the spring. The other end spring is fixed to the ground at a horizontal distance 2R from the base of the rod. the mass is released at a height of 1.5 R from ground.
View SolutionA bead of mass 'm' is attached to one end of a spring of natural length R & spring constant k=(√3+1)R. The other end of the spring is fixed at point A on a smooth vertical ring of radius R as shown. The normal reaction at B just after it is released to move is
View SolutionA bead of mass m can slide without friction on a fixed circular horizontal ring of radius 3R having a centre at the point C. The bead is attached to one of the ends of spring of spring constant k. Natural length of spring is R and the other end of the spring is R and the other end of the spring is fixed at point O as shown in the figure. If the bead is released from position A, then the kinetic energy of the bead when it reaches point B is
View SolutionA bead of mass m can slide without friction along a vertical ring of radius R. One end of a spring of force constant k=3mgR is connected to the bead and the other end is fixed at the centre of the ring. Initially, the bead is at the point A and due to a small push it starts sliding down the ring. If the bead momentarily loses contact with the ring at the instant when the spring makes an angle 60∘ with the vertical, then the natural length of the spring is
View Solutionएक चिकने अर्धवृत्ताकार आकृति की R त्रिज्या वाली तार की ऊर्ध्व तल में स्थित है। लीक के निम्नतम बिन्दु O पर 3R4 स्वाभाविक लम्बाई की एक भारहीन स्प्रिंग का एक सीरा जुड़ा है। स्प्रिंग का दूसरा सीरा m द्रव्यमान के एक छल्ले बिन्दु P पर स्थितरावस्था में है तब स्प्रिंग उर्ध्व से 60∘ का कोण बनाती है। स्प्रिंग नियतांक k=mg/R है। जब छल्ले को मुक्त किया जाता है तब
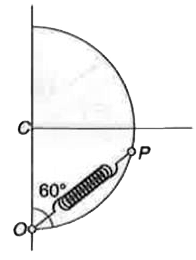
(a) छल्ले का बल निर्देशांक आरेख बनाइये।
(b) छल्ले के स्पर्शरेखीय त्वरण तथा अभिलम्ब प्रतिक्रिया के मान ज्ञात कीजिए।
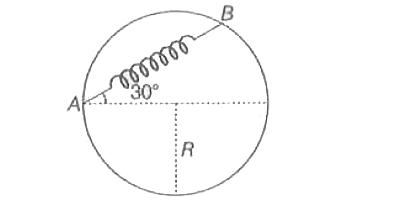
View SolutionA bead of mass 100 g is attached to one end of a spring of natural length L and spring constant k=(√3+1)mgL, where m is the mass of bead. The other end of the spring is fixed at point A on a smooth vertical ring of radius R as shown in the figure. The normal reaction at B just after it is released to move is (take, g=9.8ms−2)
View Solutionm द्रव्यमान का एक मोती प्राकृतिक लम्बाई √3R तथा स्प्रिंग नियतांक k=(√3+1)mgR की एक स्प्रिंग के एक सिरे से जुडी हुई है । स्प्रिंग का दूसरा सिरा चित्र में दर्शाइए अनुसार R त्रिज्या की एक चिकनी दृढ़ ऊर्ध्वधर वलय पर बिंदु A पर दृढ़ है । B पर अभिलम्ब प्रतिक्रिया (Normal reaction) ठीक मोती के मुक्त होने के पश्चात क्या है ?
View Solutionएक m द्रव्यमान का मनका R प्राकृतिक लम्बाई की स्प्रिंग के एक सिरे जिसका बल नियतांक k=(√3+1)mgR से जोड़ा जाता है। स्प्रिंग का दूसरा सिरा चित्रानुसार चिकनी R त्रिया की ऊर्ध्वाधर वलय के बिंदु A पर स्थिर (fixed) है। इसको (मनका) गति के लिए छोड़ने के तुरंत बाद B पर अभिलम्ब प्रतिक्रिया बल क्या होगा।
View Solution

