A composite block is made of slabs A,B,C,D and E of different thermal conductivities (given in terms of a constant K and sizes (given in terms of length, L) as shown in the figure. All slabs are of same width. Heat 'Q' flows only from left to right through the blocks. Then in steady state
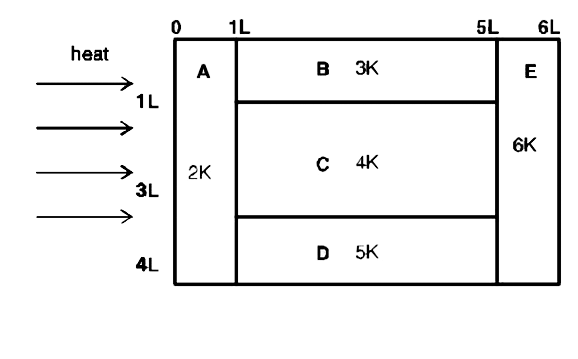
Heat flow through slabs A and E is same
Heat flow through slab E is maximum
Temperature difference across slab E is smallest.
Heat flow through C= heat flow through B + heat flow through D.
The correct Answer is:A, C, D
At steardy state, heat flow through A and E are same. So option (a) is correct and option (b) is incorrect.
c. ΔT=H×R , where H is heat currect. ltbr> 'H' is same for A and E but R is smallest. So option (c) is corrcet
d. HB=ΔTRB,HC=ΔTRC and HD=ΔTRD ,
From this option if, HC=HB+HD
⇒1RC=1RB+1RD
⇒4K(2Lb)4L=3K(Lb)4L+5K(Lb)4L
which is true. Here b is the wildth of slab.
Hence option (d) is also correct.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- ARCHIVES 1 VOLUME 6BOOK - CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHCHAPTER - ARCHIVES 1 VOLUME 6EXERCISE - Assertion-Reasoning
1 Video
- ARCHIVES 1 VOLUME 6BOOK - CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHCHAPTER - ARCHIVES 1 VOLUME 6EXERCISE - Comprehension
3 Videos
- ARCHIVES 1 VOLUME 6BOOK - CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHCHAPTER - ARCHIVES 1 VOLUME 6EXERCISE - Single Correct
54 Videos
- ARCHIVES 2 VOLUME 6BOOK - CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHCHAPTER - ARCHIVES 2 VOLUME 6EXERCISE - Integer
4 Videos
Similar Questions
Statement-1: The total translational kinetic energy of fall the molecules of a given mass of an ideal gas is 1.5 times the product of its pressure and its volume because.
Statement-2: The molecules of a gas collide with each other and the velocities of the molecules change due to the collision.
View SolutionA fixed thermally conducting cylinder has a radius R and height L0. The cylinder is open at its bottom and has a smaller hole at its top. A piston of mass M is held at a distance L from the top surface, as shown in the figure. The atmospheric pressure is P0.
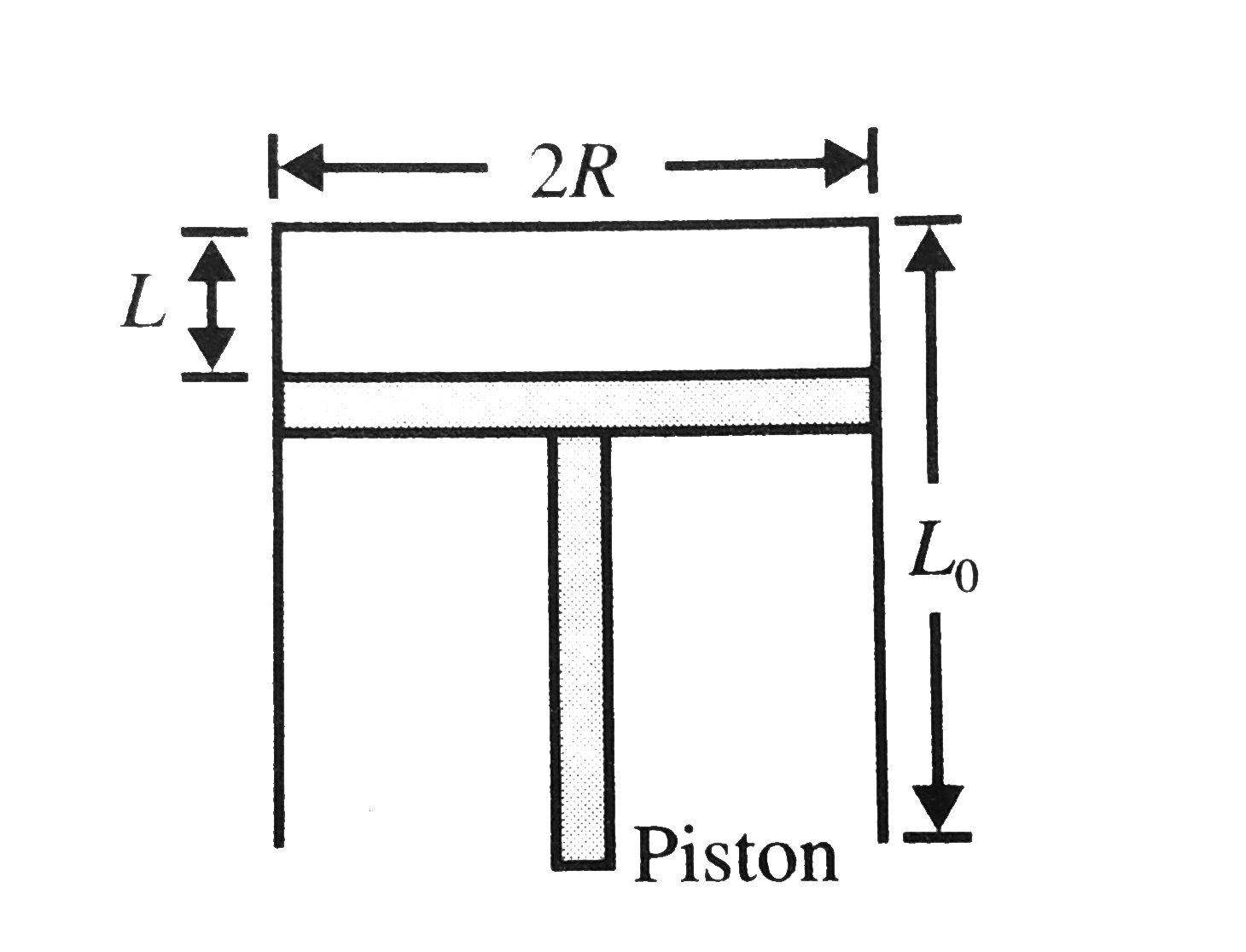
The piston is now pulled out slowly and held at a distance 2L from the top. The pressure in the cylinder between its top and the piston will then be
View SolutionA wall is made of equally thick layers A and B of different matierals. Thermal conduvtivity of A is twice that of B. In the stedy state, the temperature difference across the wall is 36∘C . The temperature difference across the layer A is
View SolutionA 20cm long string, having a mass of 1.0g, is fixed at both the ends. The tension in the string is 0.5N. The string is into vibrations using an external vibrator of frequency 100Hz. Find the separation (in cm) between the successive nodes on the string.
View SolutionA composite block is made of slabs A,B,C,D and E of different thermal conductivities (given in terms of a constant K and sizes (given in terms of length, L) as shown in the figure. All slabs are of same width. Heat 'Q' flows only from left to right through the blocks. Then in steady state

View SolutionThe temperature across two different slabs A and B are shown I the steady state (as shown Fig) The ratio of thermal conductivities of A and B is
View SolutionThe diagram shows four slabs of different materials with equal thickness, placed side by side. Heat flows from left to right and the steady-state temperatures of the interfaces are given. Rank the materials according to their thermal conductivities, smallest to largest.
View SolutionTwo slabs A and B of different materials but of the same thickness are joined end to end to form a composite slab. The thermal conductivities of A and B are K1 and K2 respectively. A steady temperature difference of 12∘C is maintained across the composite slab. If K1=K22, the temperature difference across slab A is
View SolutionTwo slabs A and B of different materials but of the same thickness are joined end to end to form a composite slab . The thermal conductivities of A and B are K1 and K2 respectively . A steady temperature difference of 12∘C is maintained across the composite slab . If K1=K22 , the temperature difference across slab A is
View SolutionA composite slab consists of two slabs A and B of different materials but of the same thickness placed one on top of the other. The thermal conductivities of A and B are k_(1) and K_(2) respectively. A steady temperature difference of 12^(@)C is maintained across the composite slab. If k_(1) = K_(2)//2 , the temperature difference across slab A will be:
View SolutionA parallel-sided slab is made of two different materials. The upper half of the slab is made of material X, of thermal conductivity λ, the lower half is made of material Y, of thermal conductivity 2λ. In the steady state, the left hand face of the composite slab is at a higher, uniform temperature than the right-hand face, and the flow of heat through the slab is parallel to its shortest sides. What fraction of the total heat flow through the slab passes through material X ?
View Solutionअलग-अलग ताप चालकताओं (K के मात्रक में ) तथा अलग अलग साइजों (L के मात्रक में) के A,B,C,D व E स्लैबो को चित्र में दर्शाये अनुसार जोड़ा गया है। सब स्लैबों की चौड़ाई समान है । ऊष्मा Q का चालन सिफ A से E की दिशा में है तब साम्यावस्था में
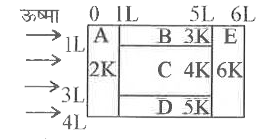
View SolutionA composite block is made of slabs A,B,C,D and E of different thermal conductivities (given in terms of a constant K) and sizes (given in terms of length, L) as shown in the figure. All slabs are of same width. Heat 'Q' flows only from left to right through the blocks. Then in steady state
View SolutionTwo slabs A and B of different materials but of the same thicknesss are joined end to end to form a composite slab. The thermal conductivities of A and B are K1 and K2 respectively. A steady temperature difference of 12∘C is maintained across the composite slab. If K1=K22, the temperature difference across slabs A is
View SolutionA composite slab is made of two parallel layers of two different materials of thermal conductivities K_1 and K_2 are of same thickness. Show that the equivalent thermal conductivity of the slab is (2K_1 K_2)/( K_1 + K_2)
View Solution

