A light beam is travelling from Region I to IV (figure). The refractive index in regionals I,II,III and IV are n0=n02(n_0)/(6) and (n_0)/(8)respectively.The∠of∈cncethetaforwhichthebeamjustmissesenter∈gregionIVis−

sin−1(34)
sin−1(18)
sin−1(14)
sin−1(13)
The correct Answer is:B
∵n0>n02>n06>n08 , the ray of the light is travelling from a denser medium to rare media. For each refraction , we use the relation n1sinθ1=n2sinθ2

In this problem θ1>θ,θ2>θ1,θ3>θ2 and the beam of light will not enter region IV, if the angle of refraction in region IV is 90∘ .
For successive refractions, we get
n0sinθ=n2sinθ1=n4sinθ2=n08sin90∘
orn0sinθ=n08sin90∘
∴sinθ=18orθ=sin−1(18)
Thus (b) is the correct choice.
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
For a prism angle θ=600 the refractive indices of the left half and right half are resp, n1 and n2 (n2gen1) as shown in figure. The angle of incidence i is chosen such that the incident light rays will have minimum deviation if n1 = n2 = n = 1.5. For case of unequal refractive indices n1 = n and n2=n+∂at(n) the angle of emergence e=i+δ(e). Which of the following statement is/are correct?
View SolutionIntensity of a light beam can be defined as amount of light energy incident in unit time on a unit area held normal to the direction of beam. A light beam of intensity I0 has a circular cross section of diameter d0. This beam is travelling in a medium of refractive index μ=√2and gets incident on the medium – air boundary at an angle of incidence i=30°. Assume that entire light energy gets transmitted into air. Find the intensity (I) of transmitted light beam.
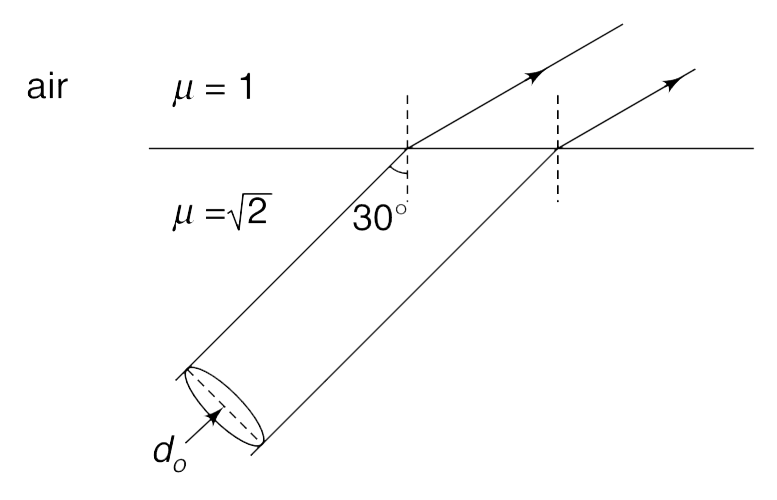
View Solution
Knowledge Check
A light beam is traveling from Region I to region IV (refer figure). The refractive indices in Region I, II, III, and IV are n0,n0/2,n0/6andn0/8 , respectively. The angle of incidence θ for which the beam just misses entering Region IV is
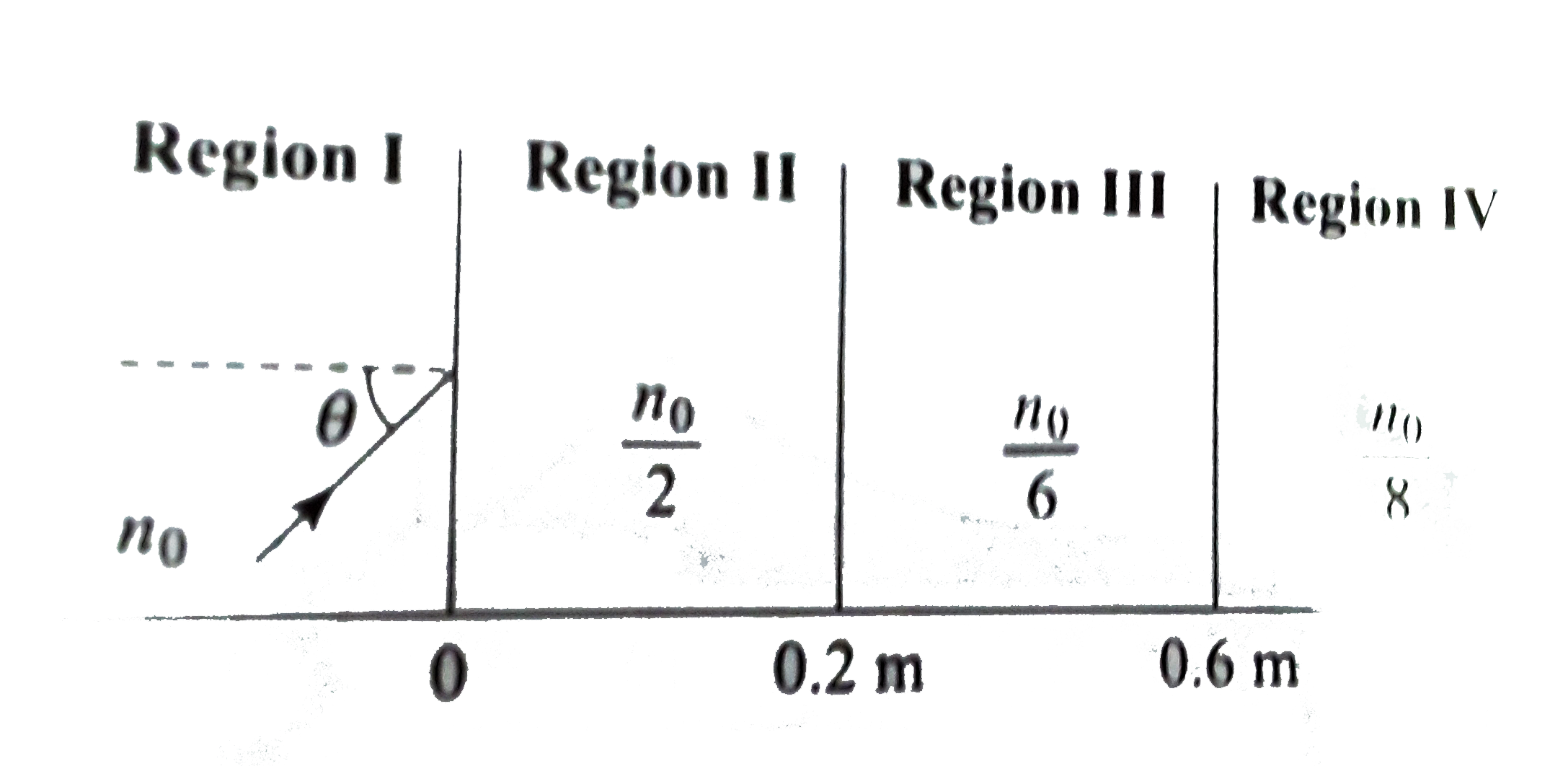 Asin−1(3/4)Bsin−1(1/8)Csin−1(1/4)Dsin−1(1/3)
Asin−1(3/4)Bsin−1(1/8)Csin−1(1/4)Dsin−1(1/3)An intially parallel cyclindrical beam travels in a medium of refractive index μ(I)=μ0+μ2I, where μ0 and μ2 are positive constants and I is intensity of light beam. The intensity of the beam is decreasing with increasing radius.
Answer the following questions :
As the beam enters the medium, it willAconvergeBdiverge near the axis and converge near the peripheryCtravel as a cyclindrical beamDdivergeAn intially parallel cyclindrical beam travels in a medium of refractive index μ(I)=μ0+μ2I, where μ0 and μ2 are positive constants and I is intensity of light beam. The intensity of the beam is decreasing with increasing radius.
Answer the following questions :
The initial shape of the wavefront of the beam isAconcaveBconvex near the axis and concave near the peripheryCplanarDconvex
An intially parallel cyclindrical beam travels in a medium of refractive index μ(I)=μ0+μ2I, where μ0 and μ2 are positive constants and I is intensity of light beam. The intensity of the beam is decreasing with increasing radius.
Answer the following questions :
The speed of light in the medium is
View SolutionA ray of light travels from a medium of refractive index n1 to
a medium of refractive index n2. If angle of incidence is i and
angle of refraction is r, than sinisinr is equal to
View SolutionA ray of light goes from a medium of refractive index n1 to a medium of refractive index n2. The angle of incidence is I and the angle of refraction is r. Then, sin i/sin r is equal to
View SolutionA light ray enters into a medium whose refractive index varies along the x-axis as n(x)=n0√1+x4 where n0=1. The medium is bounded by the plates x=0,x=1 & y=0. It the ray enters at the origin at an angle 30∘ with x-axis

View SolutionA ray of light travels from a medium of refractive index n into air. If the angle of incidence at the plane surface of separation is θ. And the correspoonding angle of deviation is δ, the variation δ with θ is shown correctly in the figure.
View Solution

