(a) Obtain lens makers formula using the expression
n2v−n1u=(n2−n1)R
Here the ray of light propagating from a rarer medium of refractive index (n1) to a denser medium of refractive index (n2) is incident on the convex side of sperical refracting surface of radius of curvature R.
(b) Draw a ray diagram to show the umage formation by concave mirror when the object is kept between its focus and the pole. Using this diagram, derive the magnification formula for the image formed.
(a) 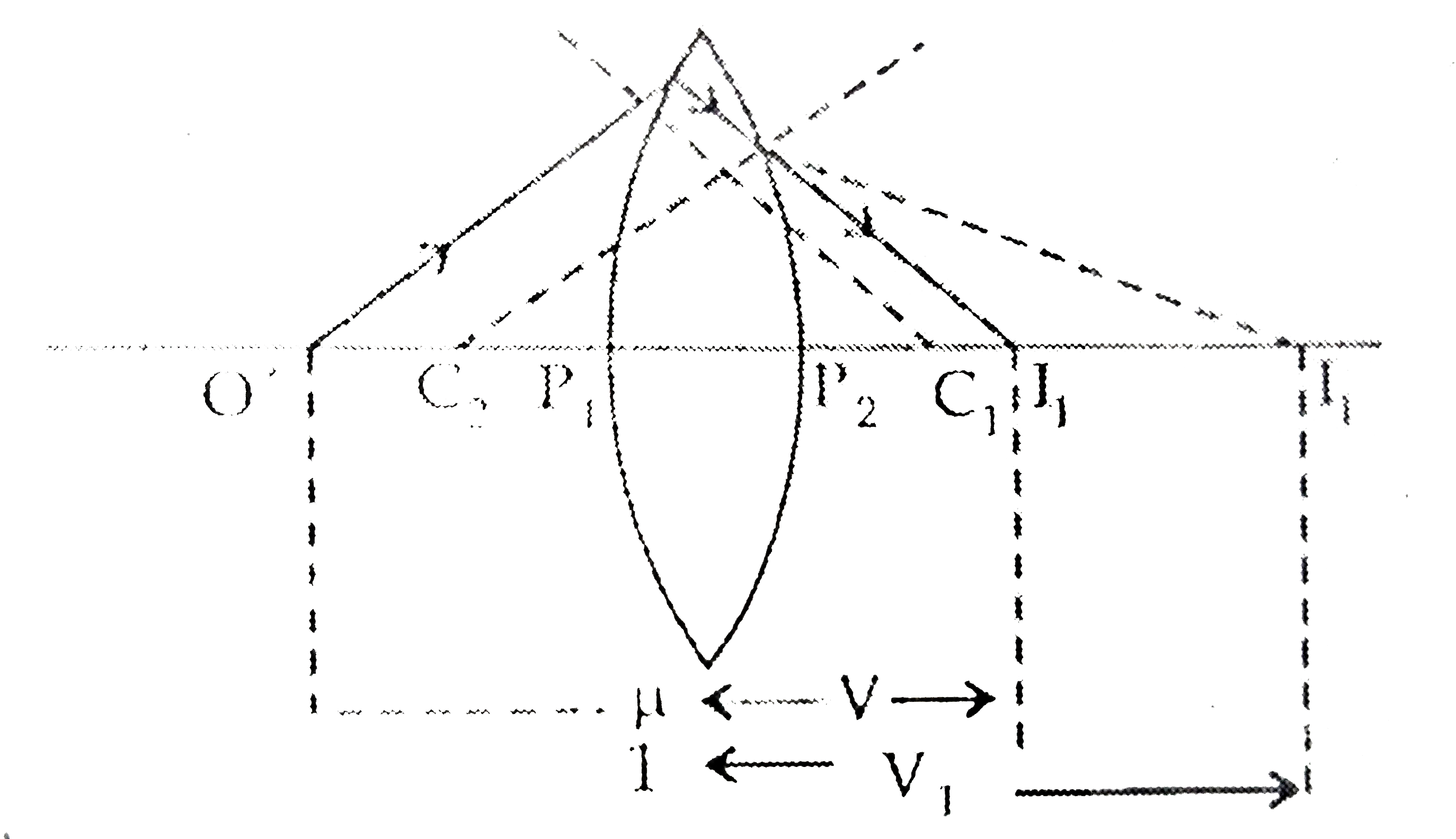
For reaction at the first surface
n2v−n1μ=(n2−n1)R1
For the second surface, I, acts as a virtual object (located in the denser medium) whose final real image is formed in the rarer medium at I. So, for refration at this surface is
n1V−n2v1=n1−n2R2
Form above two equations,
1v=1μ
=[n2n1−1][1R1=1R2]
The point, where image of an object, located at intinity is formed, is called the focus F, of the lens and the distance f gives its focal length.
So, for μ=∝,v=+f
1f[n2n1−1][1R1=1R2]
(b) 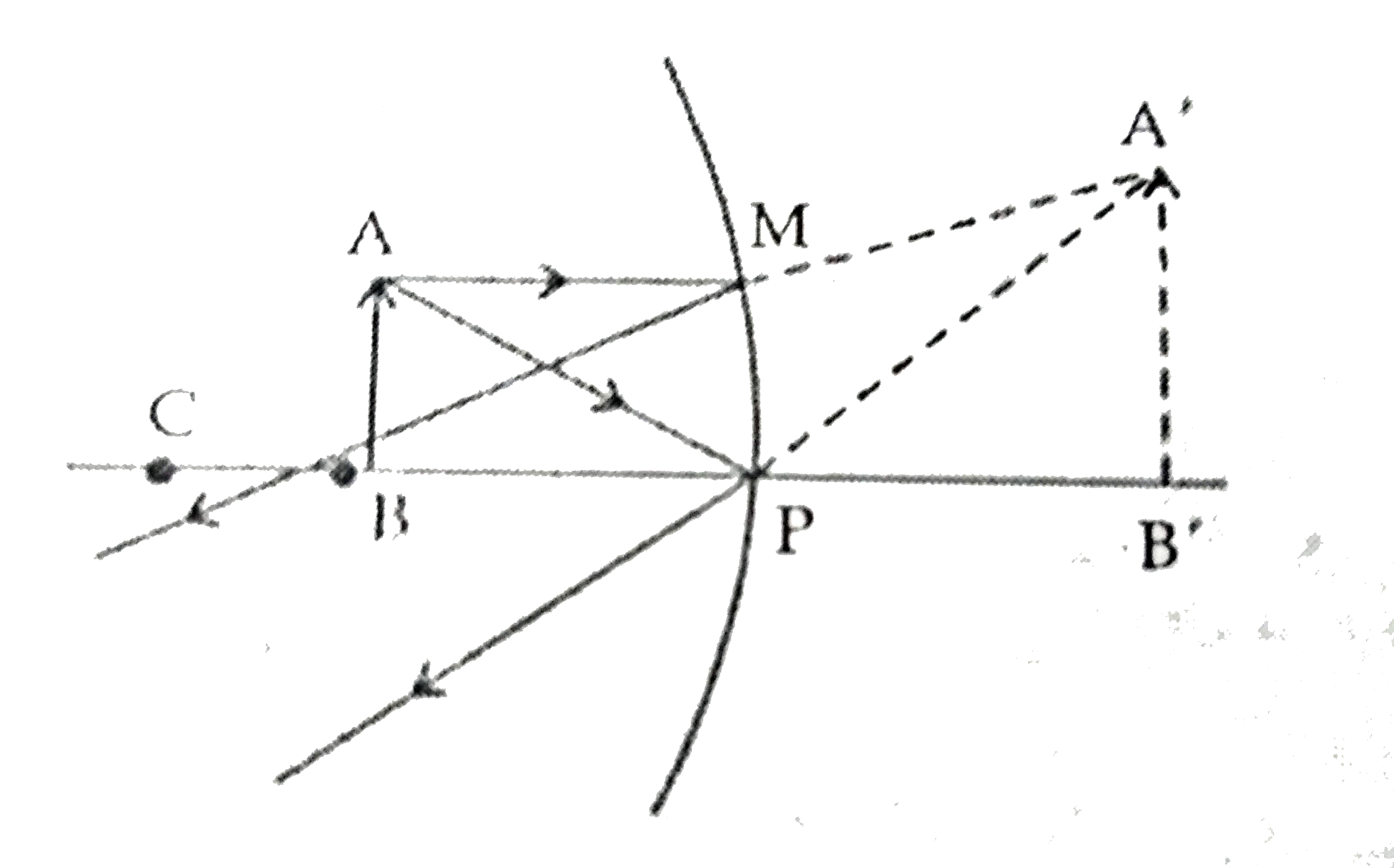
ΔABP is similar to ΔA'B'P
So, A'B'AB=B'PBP
Now, A'B'=I,AB=O.B'P'=+v
andBP=−u
So, magnifiction M=IO=−vu.
Similar Questions
Obtain lens maker's formula using the expression n2v−n1u=n2−n1R, propagating from a rarer medium of refractive index (n1) to a denser medium of refractive index (n2) is incident on the convex side of spherical refracting surface of radius of curvature R.
View SolutionA ray of light passes from vaccum into a medium of refractive index n. If the angle of incidence is twice the angle of refraction, then the angle of incidence is
View Solution
Knowledge Check
A ray of light travels from a medium of refractive index n1 to
a medium of refractive index n2. If angle of incidence is i and
angle of refraction is r, than sinisinr is equal toAa n1Bb n2Cc n2n1Dd n1n2A ray of light goes from a medium of refractive index n1 to a medium of refractive index n2. The angle of incidence is I and the angle of refraction is r. Then, sin i/sin r is equal to
An1Bn2C(n1)/(n2)D(n2)/(n1)Monochromatic light of wavelength λ1 travelling in medium of refractive index n1 enters a denser medium of refractive index n2. The wavelength in the second medium is
A(a) λ1(n1n2)B(b) λn2n1C(c) λ1D(d) λ(n2−n1n1)
A glass slab made of a material of refractive index n1 is kept in a medium of refractive index n2.
A light ray is incident on the slab. Draw the path of the rays of light emerging from the glass slab, if n1=n2
View SolutionLight travels from medium 1 (refractive index = n1) to medium 2 (refractive index = n2 ). If it is found that deviation d=r-i. We can say that
View SolutionWhen a lens of refractive index n1 is placed in a liquid of refractive index n2, the lens looks to be disappeared only if
View SolutionA ray of light passes from vaccum into a medium of refractive index n. If the angle of incidence is twice the angle of refraction, then the angle of incidence is
View SolutionA ray of light passes from vaccume into a medium of refractive index n. if the angle of incidence is twice the angle of refraction, then the angle of incidence is
View Solution

