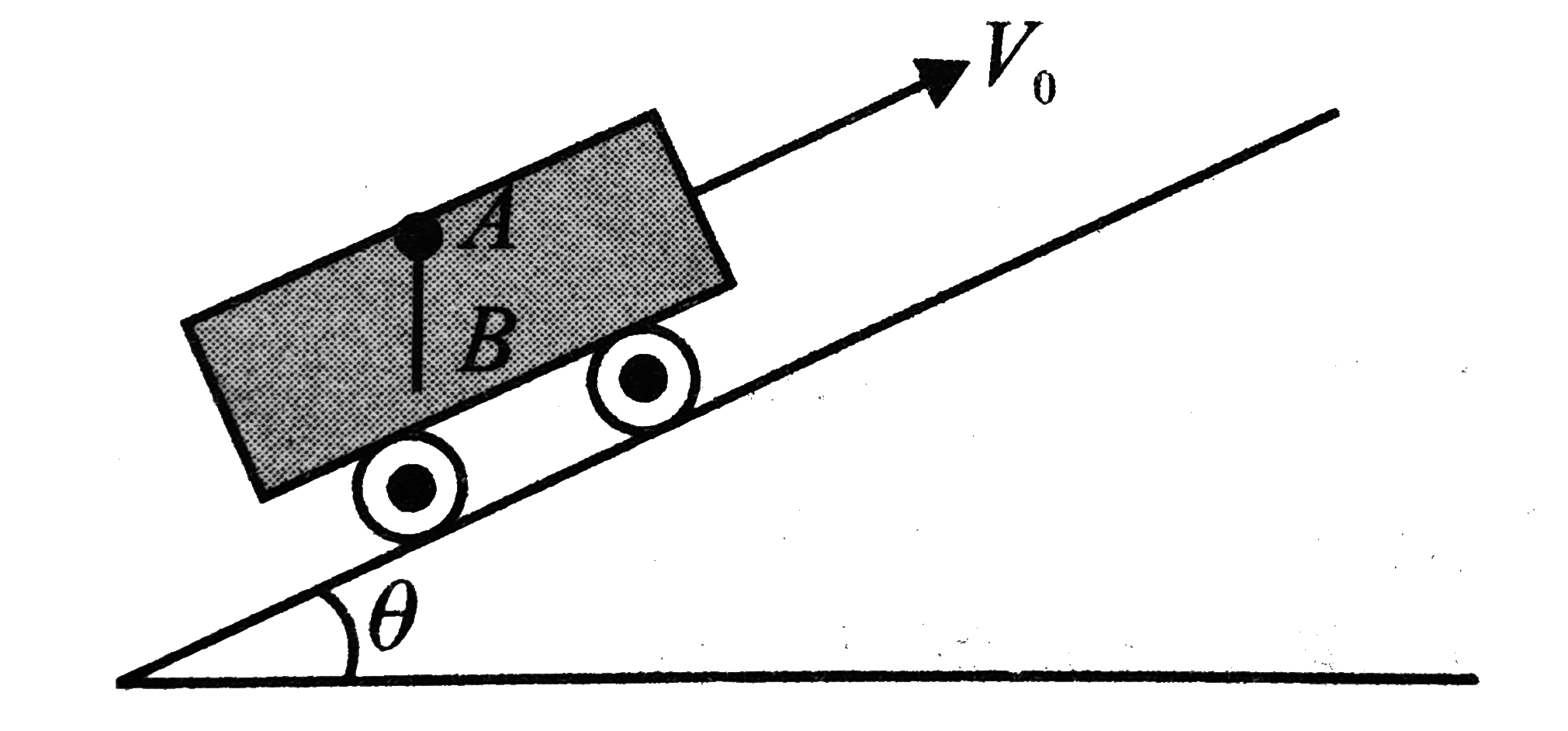
A uniform rod AB of length l and mass m hangs from point A in a car moving with velocity v0 on an inclined plane as shown in Fig. The rod can rotate in vertical plane about the axis at point A. if the car suddenly stops, the angular speed with which the rod starts rotating is
32v0lcosθ
v02cosθl
32v0lsinθ
52v0lsinθ
The correct Answer is:A
When the car is moving with the constant speed, the rod will be vertical. The centre of mass of the rod is moving with a velocity v0 parallel to the plane. Conserving agular momentum about A, we get
mv0l2cosθ=ml23ω⇒ω=32v0lcosθ
Topper's Solved these Questions
- RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2Book:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2Exercise:Multiple Correct
Explore 26 Videos
- RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2Book:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2Exercise:Linked Comprehension
Explore 71 Videos
- RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2Book:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2Exercise:Subjective
Explore 19 Videos
- RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 1Book:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 1Exercise:Integer
Explore 11 Videos
- SOUND WAVES AND DOPPLER EFFECTBook:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:SOUND WAVES AND DOPPLER EFFECTExercise:Integer
Explore 16 Videos
Similar Questions
A ring rolls without slipping on the ground. Its centre C moves with a constant speed u.P is any point on the ring. The speed of P with respect to the ground is v.
View SolutionA man of mass 100kg stands at the rim of a turtable of radius 2m and moment of inertia 4000kgm2 mounted on a vertical frictionless shaft at its centre. The whole system is initially at rest. The man now walks along the outer edge of the turntable with a velocity of 1m/s relative to the earth
a. With what angular velocity and in what direction does the turntable rotate?
b. Through what angle will it have rotated when the man reaches his initial position on the turntable?
c. Through what angle will it have rotated when the man reaches his initial position relative to the earth?
View SolutionA uniform thin circular ring of mass m(m=0.4kg) and radius R has a small particle of the same mass m fixed on it as shown in Fig. The line joining the particle to centre is initially horizontal. The ground is frictionless. Find the contact force (magnitude) exerted by the ground on the ring, when the system is released from rest.

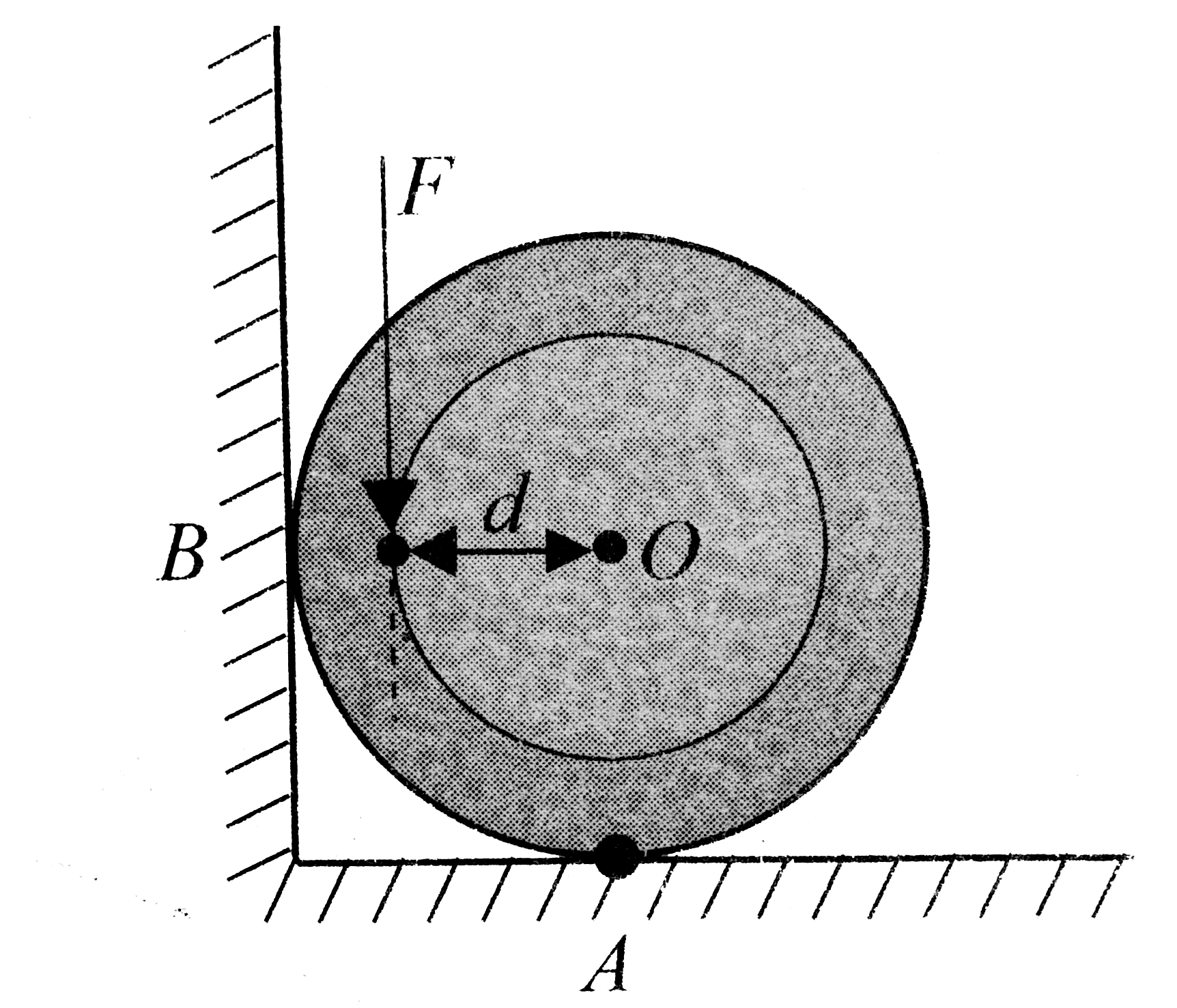
View SolutionA solid cylinder with r=0.1m and mass M=2kg is placed such that it is in contact with the vertical and a horizontal surface as shown in Fig. The coefficient of friction is μ=(1/3) for both the surfaces. Find the distance (in CM) from the centre of the cylinder at .which a force F=40N should be applied vertically so that the cylinder just starts rotating in anticlockwise direction.
View SolutionThe average power transmitted across a cross section by two sound waves moving in the same direction are equal. The wavelength of two sound waves are in the ratio of 1:2, then find the ratio of their pressure amplitudes.
View SolutionA uniform rod of mass m is rotated about an axis passing through point O as shown. Find angular momentum of the rod about rotational law.
View SolutionA uniform rod of mass m and length l rotates in a horizontal plane with an angular velocity ω about a vertical axis passing through one end. The tension in the rod at a distance x from the axis is
View SolutionA uniform rod AB of length l and mass m hangs from point A in a car moving with velocity v_(0) on an inclined plane as shown in Fig. The rod can rotate in vertical plane about the axis at point A . if the car suddenly stops, the angular speed with which the rod starts rotating is
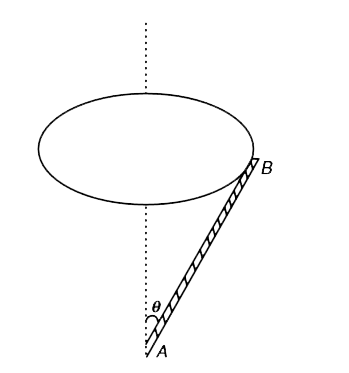
View SolutionA uniform rod AB of mass m and length L rotates about a fixed vertical axis making a constant angle theta with it as shown in figure. The rod is rotated about this axis, so that point B the free end of the rod moves with a uniform speed V in the horizontal plane then the angular momentum of the rod about the axis is:
View SolutionA uniform rod of mass m and length L is fixed to an axis, making an angle θ with it as shown in the figure. The rod is rotated about this axis so that the free end of the rod moves with a uniform speed ‘v’. Find the angular momentum of the rod about the axis. Is the angular momentum of the rod about point A constant?
View SolutionA mechanism consists of a part which is translated with a velocity u and a rod AB of length L and mass M hinged at A The rod rotates about axis A with angular velocity omega the kinetic energy of rod when it is vertical as shown is
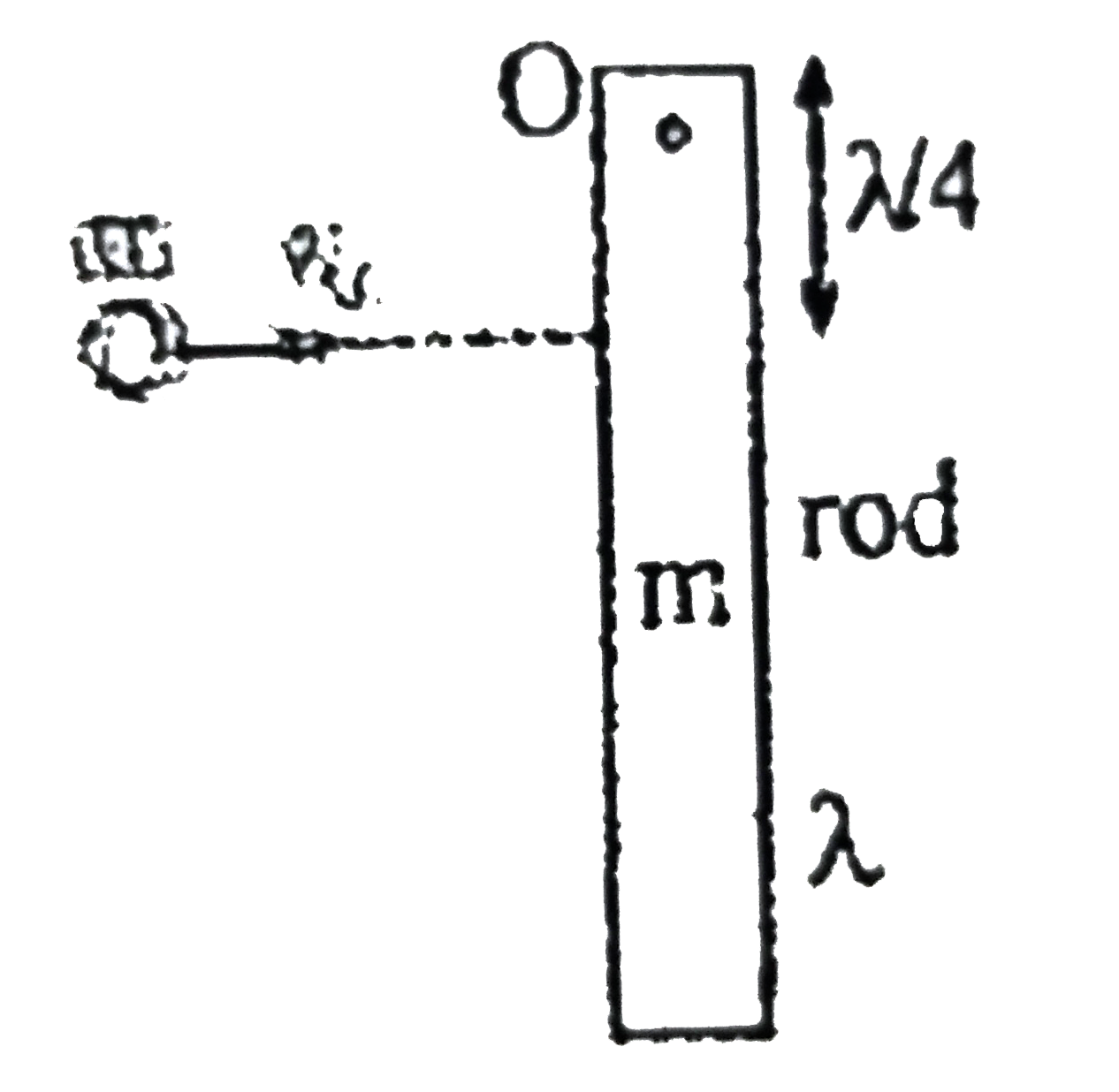
View SolutionRod of m and length l is free to rotate about point U in vertical plane. A particle having same mass m moving horizontally with velocity v0 his the rod perpendicular at distance l4 from the top end 'O' and stops. Find impulse due to hinge on the rod due to collision.
View SolutionA rod AB of mass m and length L is rotating in horizontal plane about one of its ends which is pivoted. The constant angular speed with which the rod is rotating is omega . The force applied on the rod by the pivot is
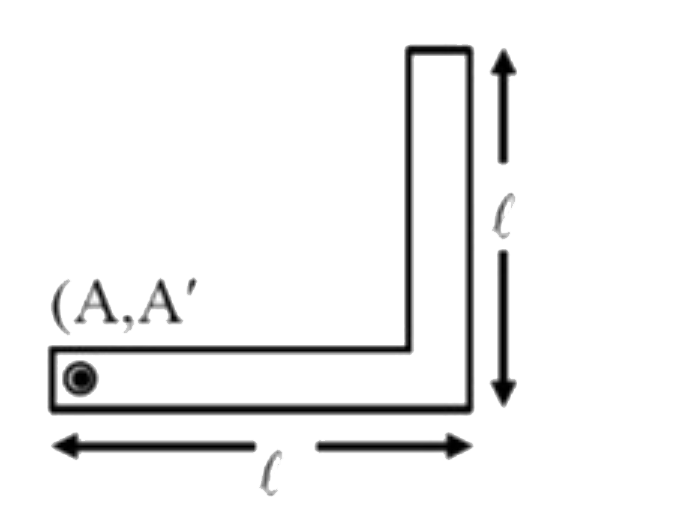
View SolutionA L shaped rod of mass M is free to rotate in a vertical plane about axis A A as shown in figure. Maximum angular acceleration of rod is
View Solution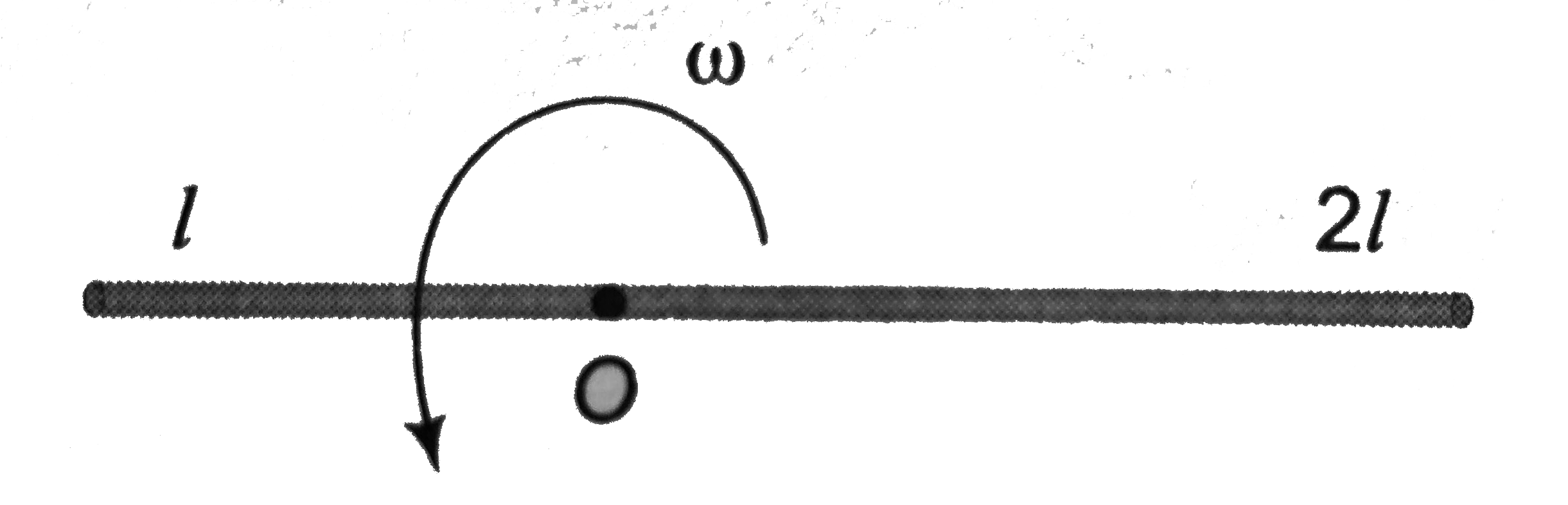
A uniform rod of mass m is rotated about an axis passing through point O as shown. Find angular momentum of the rod about rotational law.
View Solution
