An impulse J is applied on a ring of mass m along a line passing through its centre O. the ring is placed on a rough horizontal surface. The linear velocity of centre of ring once it starts rolling without spilling is

J/m
J/2m
J/4m
J/3m
The correct Answer is:B
Let v be the velocit of COM of ring just after the impule is applied and v' its velocity when pure rolling starts. Angular velocity ω of the ring at this instant will be ω=v′r.
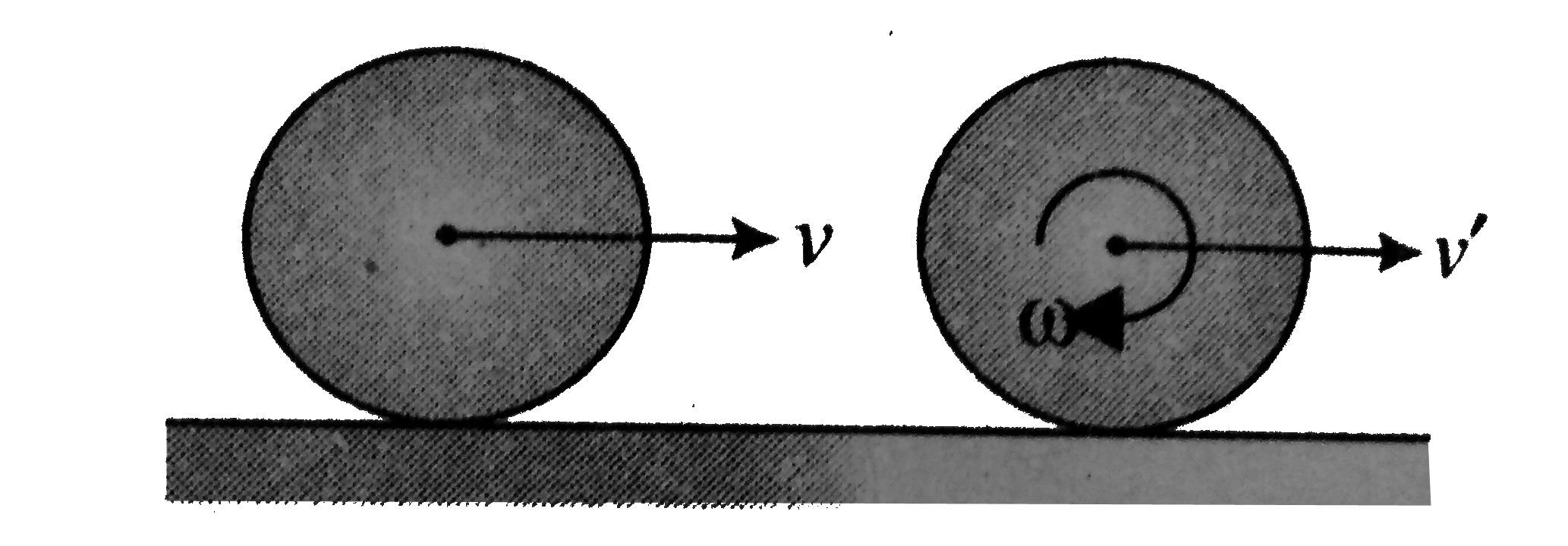
From impulse =change in linear momentum, we have
J=mv
or v=Jm.....i
Between the two positions shown in figure, force of friction on the ring acts backwards. So angular momentum of the ring about bottommost point will remain conserved
∴Li=Lf
or mr=mv'r+Iω
mv'r+(mr2)(v′r)=2mg'r
v'=v2=J2m (from equation)
Topper's Solved these Questions
- RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2Book:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2Exercise:Multiple Correct
Explore 26 Videos
- RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2Book:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2Exercise:Linked Comprehension
Explore 71 Videos
- RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2Book:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2Exercise:Subjective
Explore 19 Videos
- RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 1Book:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 1Exercise:Integer
Explore 11 Videos
- SOUND WAVES AND DOPPLER EFFECTBook:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:SOUND WAVES AND DOPPLER EFFECTExercise:Integer
Explore 16 Videos
Similar Questions
A ring rolls without slipping on the ground. Its centre C moves with a constant speed u.P is any point on the ring. The speed of P with respect to the ground is v.
View SolutionA man of mass 100kg stands at the rim of a turtable of radius 2m and moment of inertia 4000kgm2 mounted on a vertical frictionless shaft at its centre. The whole system is initially at rest. The man now walks along the outer edge of the turntable with a velocity of 1m/s relative to the earth
a. With what angular velocity and in what direction does the turntable rotate?
b. Through what angle will it have rotated when the man reaches his initial position on the turntable?
c. Through what angle will it have rotated when the man reaches his initial position relative to the earth?
View SolutionA uniform thin circular ring of mass m(m=0.4kg) and radius R has a small particle of the same mass m fixed on it as shown in Fig. The line joining the particle to centre is initially horizontal. The ground is frictionless. Find the contact force (magnitude) exerted by the ground on the ring, when the system is released from rest.

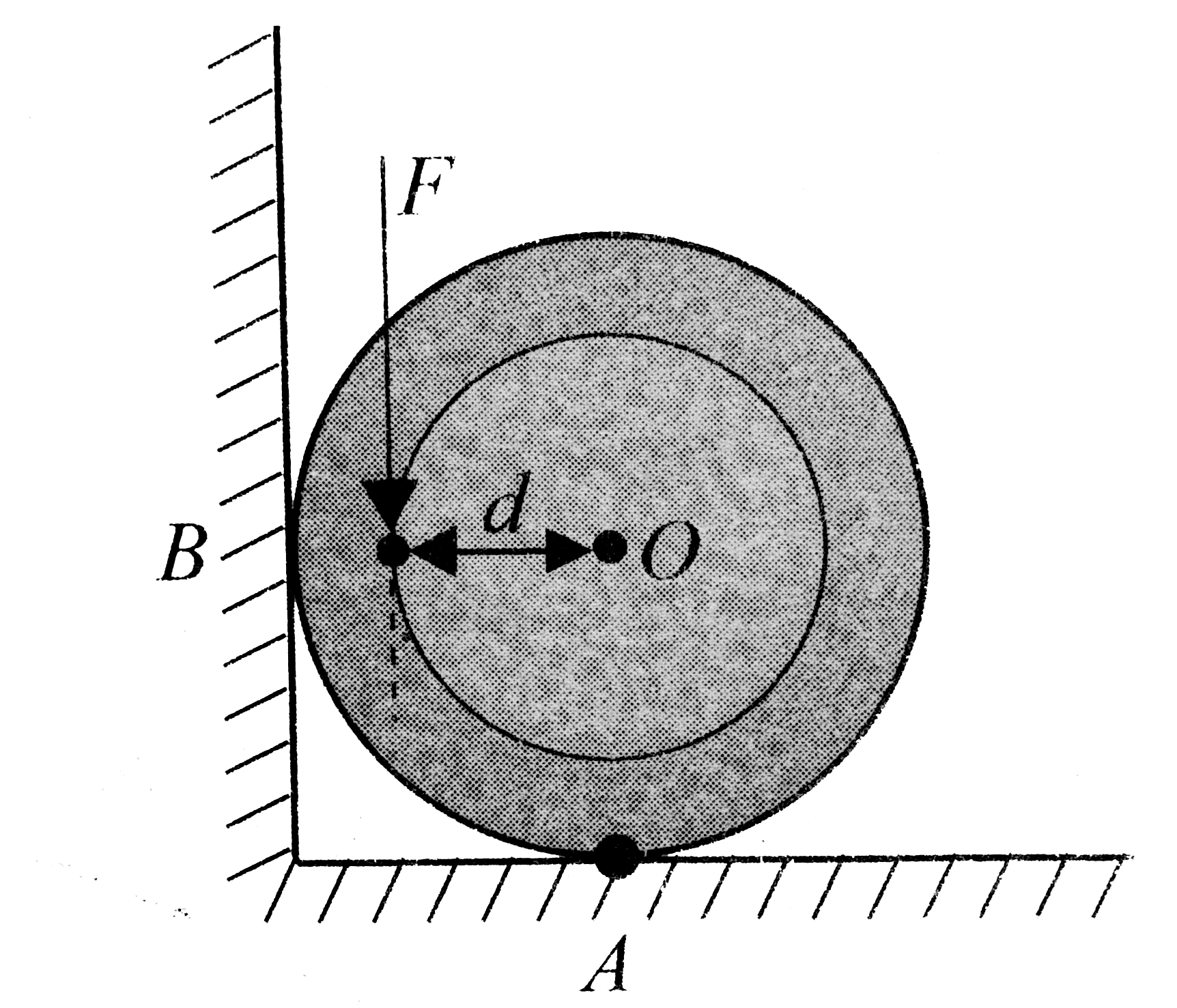
View SolutionA solid cylinder with r=0.1m and mass M=2kg is placed such that it is in contact with the vertical and a horizontal surface as shown in Fig. The coefficient of friction is μ=(1/3) for both the surfaces. Find the distance (in CM) from the centre of the cylinder at .which a force F=40N should be applied vertically so that the cylinder just starts rotating in anticlockwise direction.
View SolutionThe average power transmitted across a cross section by two sound waves moving in the same direction are equal. The wavelength of two sound waves are in the ratio of 1:2, then find the ratio of their pressure amplitudes.
View SolutionA uniform ring of radius R is given a back spin of angular velocity V_(0)//2R and thrown on a horizontal rough surface with velocity of centre to be V_(0) . The velocity of the centre of the ring when it starts pure rolling will be
View SolutionAn impulse J is applied on a ring of mass m along a line passing through its centre O . The ring is placed on a rough horizontal surface. The linear velocity of centre of ring once it starts rolling without slipping is
View SolutionA particle of mass m is placed at a distance x from the centre of ring along the line through the centre of the ring and perpendicular to its plane. if xlt lta , the particle of mass m will:
View SolutionA ring and a disc of same mass roll without slipping along a horizontal surface with same velocity. If the K.E. of ring is 8J , then that of disc is
View SolutionFour identical spheres having mass M and radius R are fixed tightly within a massless ring such that the centres of all spheres lie in the plane of ring. The ring is kept on a rough horizontal table as shown. The string is wrapped around the ring can roll without slipping. The other end of the string is passed over a massless frictionless pulley to a block of mass M. A force F is applied horizontally on the ring, at the same level as the centre, so that the system is in equilibrium. The moment of inertia of the combined ring system about the centre of ring will be
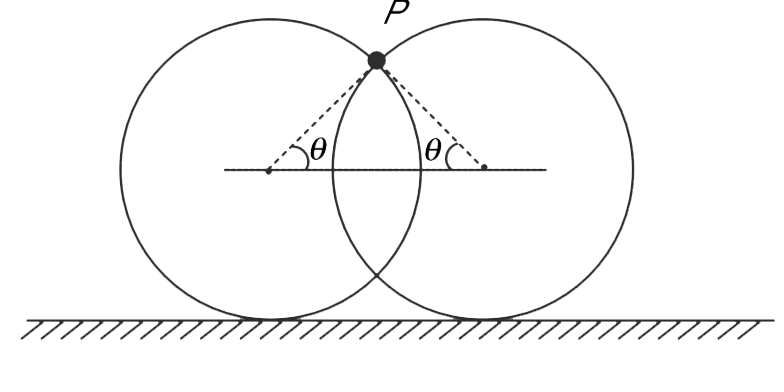
View SolutionTwo identical rings, each of mass M and radius R, are standing on a rough horizontal surface. The rings overlap such that the horizontal line passing through their centre makes an angle of θ=45∘ with the radius through their intersection point P. A small object of mass m is placed symmetrically on the rings at point P and released. Calculate the acceleration of the centre of the ring immediately after the release. There is no friction between the small object and the rings. The friction between the small object and the rings, and the friction between the rings and the ground is large enough to prevent slipping.
View SolutionIn a diagram shown, a rod of mass M has been fixed on a ring of the same mass. The whole system has been placed on a perfectly rough surface. The system is gently displaced so that the ring starts rolling. The velocity of the centre of the ring when the rod becomes horizontal is (the length of the rod is equal to the radius of the ring)

View SolutionA uniform thin ring of mass 0.4kg rolls without slipping on a horizontal surface with a linear velocity of 10 cm/s. The kinetic energy of the ring is
View SolutionA ring and a disc of same mass roll without slippling along a horizontal surface with same velocity. If the K.E of ring is 8J, then that of disc is
View SolutionA ring and a disc of same mass roll without slippling along a horizontal surface with same velocity. If the K.E of ring is 8J, then that of disc is
View SolutionA ring and a disc of same mass roll without slippling along a horizontal surface with same velocity. If the K.E of ring is 8J, then that of disc is
View Solution
