Can the force on unit N- pole between two isolated unlike poles be zero at any point?
To determine whether the force on a unit North Pole between two isolated unlike poles can be zero at any point, we can analyze the situation step by step.
1. Understanding the Setup:
- We have two isolated magnetic poles: Pole 1 (North Pole) and Pole 2 (South Pole).
- We place a unit North Pole (N) in between these two poles.
2. Analyzing Forces:
- The force exerted on the unit North Pole (N) by the South Pole (Pole 2) will be attractive, pulling the North Pole towards it.
- The force exerted on the unit North Pole (N) by the North Pole (Pole 1) will be repulsive, pushing the North Pole away from it.
3. Direction of Forces:
- Let’s denote the force on the unit North Pole due to Pole 1 as F1 (repulsive force) and the force due to Pole 2 as F2 (attractive force).
- Both forces F1 and F2 act in the same direction (towards Pole 2).
4. Condition for Zero Net Force:
- For the net force on the unit North Pole to be zero, the two forces must be equal in magnitude and opposite in direction.
- However, since both F1 and F2 are acting in the same direction, they can never cancel each other out.
5. Conclusion:
- Therefore, the net force on the unit North Pole between the two isolated unlike poles cannot be zero at any point. The forces will always be in the same direction and will not balance each other.
Final Answer:
The force on a unit North Pole between two isolated unlike poles can never be zero at any point.
---
- We have two isolated magnetic poles: Pole 1 (North Pole) and Pole 2 (South Pole).
- We place a unit North Pole (N) in between these two poles.
- The force exerted on the unit North Pole (N) by the South Pole (Pole 2) will be attractive, pulling the North Pole towards it.
- The force exerted on the unit North Pole (N) by the North Pole (Pole 1) will be repulsive, pushing the North Pole away from it.
- Let’s denote the force on the unit North Pole due to Pole 1 as F1 (repulsive force) and the force due to Pole 2 as F2 (attractive force).
- Both forces F1 and F2 act in the same direction (towards Pole 2).
- For the net force on the unit North Pole to be zero, the two forces must be equal in magnitude and opposite in direction.
- However, since both F1 and F2 are acting in the same direction, they can never cancel each other out.
- Therefore, the net force on the unit North Pole between the two isolated unlike poles cannot be zero at any point. The forces will always be in the same direction and will not balance each other.
The force on a unit North Pole between two isolated unlike poles can never be zero at any point.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- MAGNETISMBOOK - AAKASH SERIESCHAPTER - MAGNETISMEXERCISE - PROBLEMS (LEVEL-I)
21 Videos
- MAGNETISMBOOK - AAKASH SERIESCHAPTER - MAGNETISMEXERCISE - PROBLEMS (LEVEL-II)
16 Videos
- MAGNETISMBOOK - AAKASH SERIESCHAPTER - MAGNETISMEXERCISE - EXERCISE (SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS )
6 Videos
- LOGIC GATESBOOK - AAKASH SERIESCHAPTER - LOGIC GATESEXERCISE - Exercise (Very Short Answer)
7 Videos
- MOTION IN A PLANEBOOK - AAKASH SERIESCHAPTER - MOTION IN A PLANEEXERCISE - EXERCISE-3 (Circular Motion)
7 Videos
Similar Questions
The distance between a north pole of strength 6×10−3Am and a south pole of strength 8×10−3 Am is 10 cm. The poles are separated in air. Find the force between them.
View SolutionThe force between two poles is reduced to P newton, when their original separation is increased to x times, it is increased to Q newton, when their separation is made 1/xth of their original value. Then the relation between P and Q is
View SolutionDerive the equation for the couple acting on a bar magnet in a uniform magnetic field and hence deduce the definition of "magnetic moment".
View Solution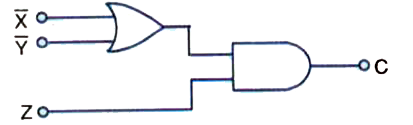
The output C in the above circuit is given by C = ---
View SolutionA particle 'P' is moving in a circle of radius 'a' with a uniform speed 'u' 'C' is the centre of the circle and AB is a diameter. The angular velocity of P about A and C are in the ratio
View SolutionForce between two unit pole strength placed at a distance of one metre is
View SolutionTwo similar magnetic poles, having pole strengths in the ration 1:3 and placed 1m apart. Find the point where a unit pole experiences no net force due to these two poles
View Solutionयदि दो समान ध्रुवों में से प्रत्येक का ध्रुव प्राबल्य दो गुना एवं उनके मध्य कि दूरी आधी कर दी जाये तो दोनों ध्रुवों के मध्य लगने वाला बल किस प्रकार परिवर्तित होगा ?
View Solutionदो सजातीय ध्रुवों के बीच प्रतिकर्षण बल F है । यदि दोनों ध्रुवों के बीच की दूरी दो गुनी कर दी जाये , तो प्रतिकर्षण बल का मान होगा -
View Solutionदो सजातीय ध्रुव , जिनमें ध्रुव - प्रबालयों का अनुपात 1 : 2 है , एक मीटर की दूरी पर रखे गये हैं । दोनों के मध्य बिंदु ज्ञात कीजिए , जहाँ पर एकांक ध्रुव पर लगने वाला नेट बल शून्य हो ।
View Solutionदो सजातीय चुम्बकीय ध्रुवो के बीच प्रतिकर्षण बल F है यदि दोनों ध्रुवो की ध्रुव प्रबलता तथा उनके बीच की दुरी दोगुनी कर दी जाए , तो प्रतिकर्षण बल का मान होगा :
View SolutionCan the force on unit N - pole between two isolated equal like poles be zero at any point?
View SolutionCan the force on unit N- pole between two isolated unlike poles be zero at any point?
View SolutionWhich type of magnetic force acts between (i) like poles (ii) unlike pole of two magnets?
View SolutionTwo similar magnetic poles, having pole strengths in the ration 1:3 and placed 1m apart. Find the point where a unit pole experiences no net force due to these two poles
View SolutionLike poles............. each other and unlike poles ...........
View Solution

