Consider one mole of a perfect gas in a cyclinder of unit cross section with a piston attached, (figure) A spring (spring constant K) is attached (unstretched length L) to the piston and the bottom of the cylinder. Initially, the spring is unstretched and the gas is in equilibrium. A certain amount of heat Q is supplied to the gas causing an increase of volume from V0toV.
(a) What is the initial pressure of the system?
(b) What is the final pressure of the system?
(c) Using the first law of thermodynamics, write down a relation between Q,Pa,V,V0 and K.
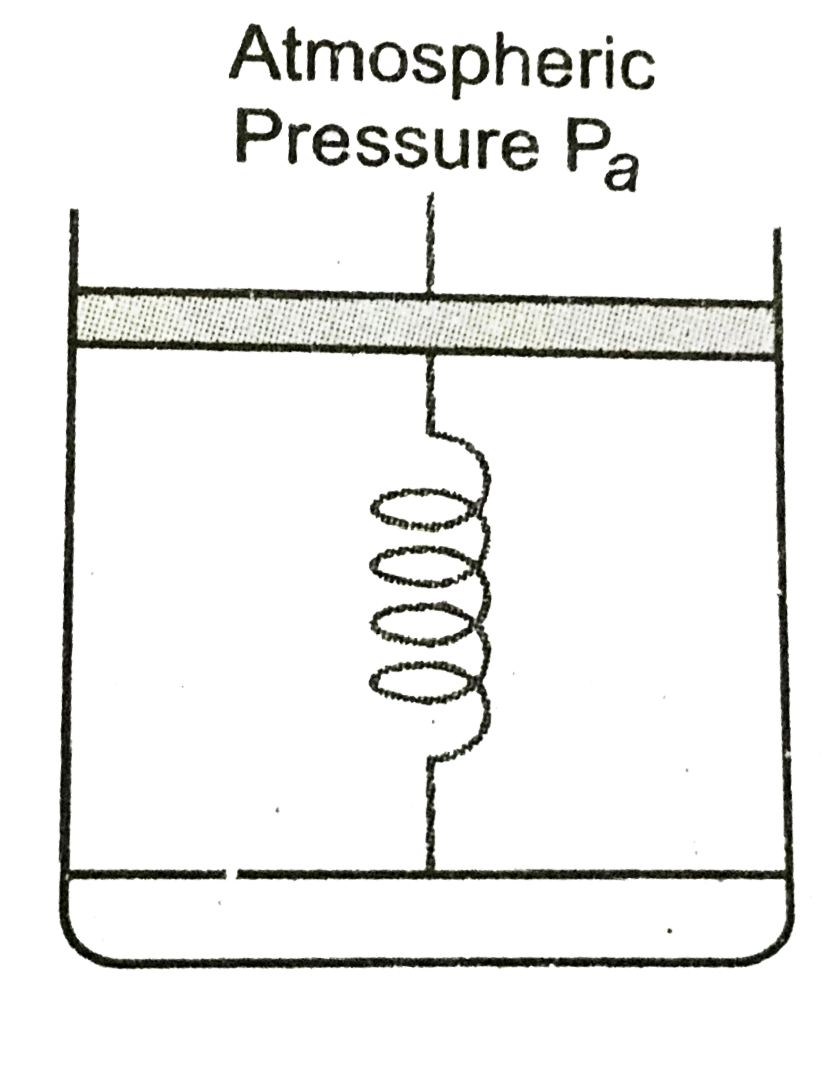
(a) Initially, the spring is unstretched and the gas is in equilibrium, therefore, initial pressure of the system Pi= atmospheric pressure= Pa
(b) On supplying heat, the gas expands from V0toV.
∴ Increase in volume of gas =V−V0
As cross sectional are of piston, A=1,
∴ extension in spring , x=(V−V0)A=(V−V0)
Force exerted by stretched spring on the piston,
F=kx=k(V−V0)(∴A=1)
∴ Final pressure of the system, Pf=Pi+P=Pa+K(V−V0)
(c ) If T is final temp. of the gas, then increase in internal energy, dU=Cv(T−T0)
Where T0==P0V0R=PaV0R, and T=PfVR=[Pa+k(V−V0)]VR
Also, dW=Pa(V−V0)+12kx2
From first law of thermodynamics, dQ=dU+dW
∴Q=Cv(T−T0)+Pa(V−V0)+12k(V−V0)2
This is the required. relation.
Similar Questions
Consider one mole of perfect gas in a cylinder of unit cross section with a piston attached as shown in figure. A spring (spring constant k) is attached (unstretched length L ) to the piston and to the bottom of the cylinder. Initially the spring is unstretched and the gas is in equilibrium. A certain amount of heat Q is supplied to the gas causing an increase of value from V0 to V1.
(a) What is the initial pressure of the system ?
(b) What is the final pressure of the system ?
(c) Using the first law of thermodynamics, write down a relation between Q, Pa, V, V0 and k.
View SolutionConsider one mole of perfect gas on a cylinder of units cross-section with a piston attached (figure). A spring (spring constant K ) is attached ( unstretched length L ) to the piston and to the bottom of the cylinder . Initially the spring is unstretched and the gas is in equilibrium. A certain amount of heat Q is supplied to the gas causing an increase of value from V_(0) to V_(1) . (a) What is the initial pressure of the system ? (b) What is the final pressure of the system? (c) Using the first law of thermodynamic, write down a relation between Q, p_(a),V,V_(0) and K.
View SolutionTwo moles of an ideal monatomic gas are confined within a cylinder by a massless and frictionless spring loaded piston of cross-sectional area 4 xx 10^(-3) m^2 . The spring is, initially, in its relaxed state. Now the gas is heated by an electric heater, placed inside the cylinder, for some time. During this time, the gas expands and does 50 J of work in moving the piston through a distance 0.10 m. The temperature of the gas increases by 50 K. Calculate the spring constant and the heat supplied by the heater.
View SolutionS is a piston of mass M which can slide inside a cylinder without friction. The walls of the cylinder is adiabatic and the piston is diathermic and area of cross section of cylinder is A. Length of the cylinder is 2l_0 . Initial pressure of each chamber is P_0 . Volume of the chambers are equal. Initially spring is unstretched and has spring constant k. The spring is fixed with piston and wall of the cylinder as shown in the figure. Find out its time period when piston is given small displacement.
View SolutionConsider a mole ideal gas filled with a piston-mounted transverse cut cylinder. A segmental (segmental constant k) is attached to the piston and cylinder bottom (uncorrected length L). In the beginning, the segregation is uncovered and the gas is in equilibrium. When a certain quantity of heat is supplied to the gas 9 in the volume of the gas V_(0) From V_(1) Grows up to. (a) What is the initial pressure of the body? (b) What is the final pressure of the body? (c) Using the first law of heat dynamics Q.P _(a), V , V _(0) Write between and k
View SolutionConsider one mole of perfect gas in a cylinder of uniform cross section with a piston attached (Fig). A spring (spring constant k) is attached (unstretched lengthL) to the piston and to the bottom of the cylinder. Initially the spring is unstretched and the gas is in equilibrium. A certain amount of heat Q is supplied to the gas causing an increase of volume from V0 to V1.
a) What is the initial pressure of the system
b) What is the final pressure of the system
c) Using the first law of thermodynamics, write down a relation between Q,Pa,V,V0andK .
View SolutionA cylinder fitted with a spring loaded piston, shown in the figure, contains 0.01(m)3 gas at a pressure of 105Pa. The cross-sectional area of the piston is 0.05m2. Initially, the spring does not touch the piston but atmospheric pressure of 105Pa acts on the piston. The gas is slowly heated till the volume is increased to three times the original value. If the forcé constant of the spring is 25kNm, calculate the work done (in kJ ) by the gas.
'(##CEN_KSR_PHY_JEE_C15_E01_031_Q19##)'
View SolutionA horizontal cylinder has two sections of unequal cross-section, in which two pistons can move freely. The pistons are joined by a string. Some gas is trapped between the pistons . Spring is massless and in natural length. If this gas is heated, the spring will .
View Solution
