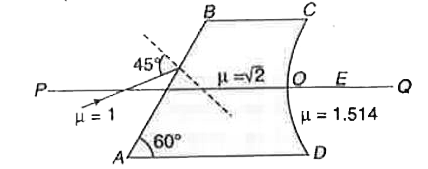
Figure shows an irregular block of material of refractive indec √2. A ray of light strikes the face AB as shown. After refraction, it is incident on a spherical surface CD of radius of curvature 0.4 m and enters a medium of refractive index 1.514 to meet PQ at E. Find the distance OE up to two places of decimal.
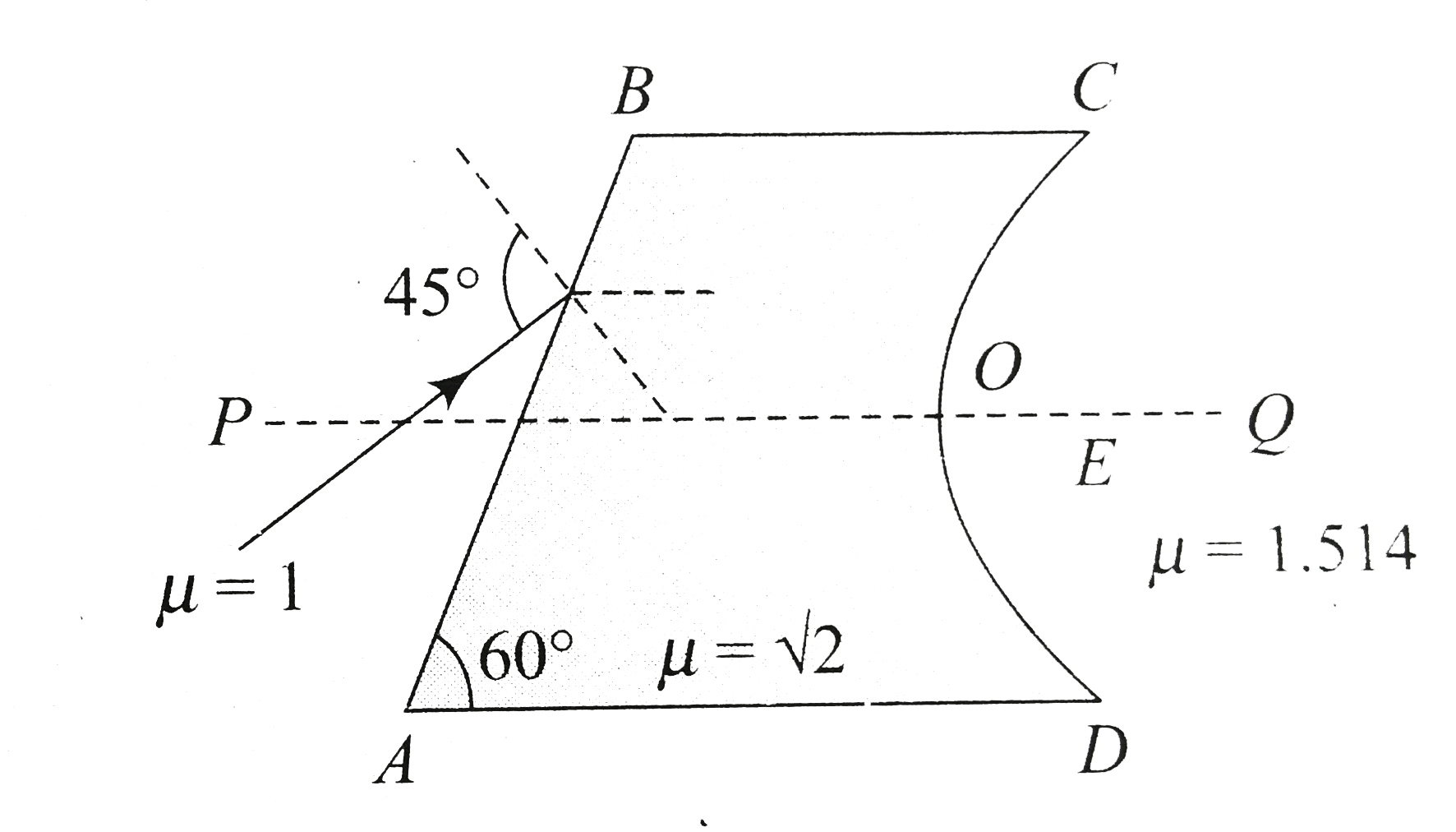
From Snell's law μ1sini=μ2sinr , we have
sinr=μ1μ2sini=1√2sin45∘=12⇒r=30∘.
This mean that the ray becomes parallel to side AD inside the slab.
This implies that for the second face CD, u=∞
Given R=0.4m
Now, we have
μ3v−μ2u=μ3−μ2R⇒1.514v−√2∞=1.514−√2R
⇒v=1.514×0.41.514−1.414=1.514×0.40.1
=6.056m=6.06m (up to two decimal places).
Topper's Solved these Questions
- GEOMETRICAL OPTICSBook:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:GEOMETRICAL OPTICSExercise:Exercise1.1
Explore 14 Videos
- GEOMETRICAL OPTICSBook:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:GEOMETRICAL OPTICSExercise:Exercise1.2
Explore 20 Videos
- GEOMETRICAL OPTICSBook:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:GEOMETRICAL OPTICSExercise:Integer Type
Explore 4 Videos
- ELECTRON,PHONTS,PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT & X-RAYSBook:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:ELECTRON,PHONTS,PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT & X-RAYSExercise:dpp 3.3
Explore 15 Videos
- HEATING EFFECT OF CURRENTBook:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:HEATING EFFECT OF CURRENTExercise:Thermal Power in Resistance Connected in Circuit
Explore 27 Videos
Similar Questions
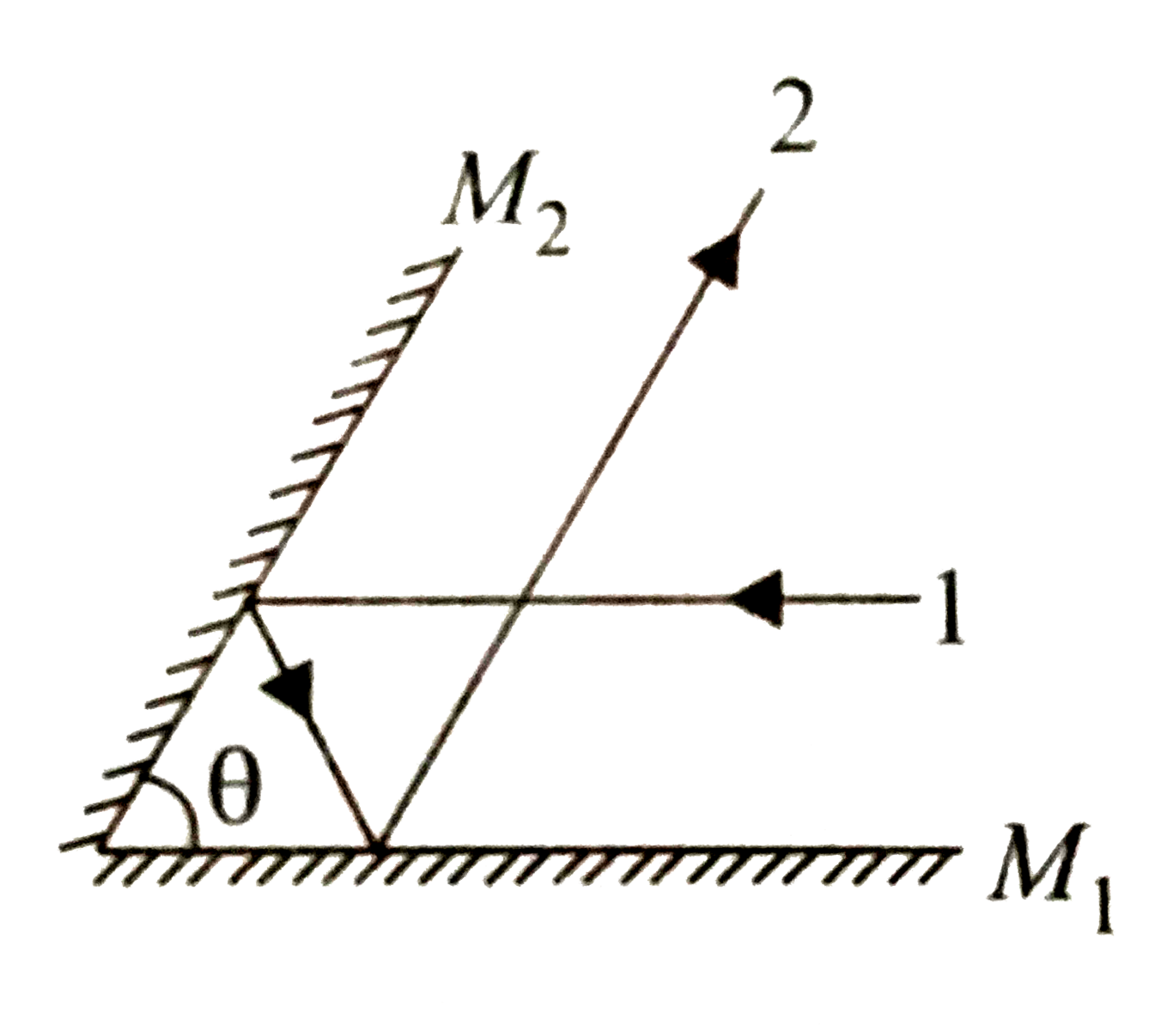
Two plane mirrors, M1 and M2 are inclined at angle θ as shown in the figure. A ray of light 1, which is parallel to M1 strikes M2 and after two reflections, the rays is 2 becomes parallel to M2, The angle θ is
View SolutionState the following statements as TRUE or FALSE.
a. A convex mirror cannot from a real image for a real object.
b. The image formed by a convex mirror is always diminished and erect.
c. Virtual image formed by a concave mirror is always enlarged.
d. Only in the case of a concave mirror, it may happen that the object and its image move in same direction.
e. In the case of a concave mirror, the image always move faster than the object.
f. If an object is placed in front of a diverging mirror at a distance equal to its focal length, then the height of image formed is half of the height of object.
g. For two positions of an object , a concave mirror can form englarged image.
h. Concave mirror is used as a rear view mirror in motor vehicles.
i. If some portion of the mirror ois covered, then complete image will be formed but of reduced brightness.
j. A plane mirror always forms an erect iamge of same size as that of the object.
k. The image formed by a plane mirror has left-right reversal.
l. A virtual object means a converging beam.
View SolutionThe focal length of a thin biconvex lens is 20cm. When an object is moved from a distance of 25cm in front of it to 50cm, the magnification of its image changes from m25 to m50. The ration m25/m50 is
View SolutionThe figure shows different graphs between stopping potential (V0) and frequency (v) for photosensitive surface of cesium , potassium , sodium and lithium. The plots are parallel. Correct ranking of the targets according to their work function greatest forst will be

View SolutionA room AC run for 5 hour at a voltage of 220V The wiring of the room constant of Cu of 1mm ratio and a length of 10m consumption per day is 10 commerclal unit What fraction of it goes in the joule heated in wire? What would happen if the wiring is made of aluminum of the same distances? [ρcu=1.7×10−8Ω,ρA1=2.7×10−8Ωm]
View SolutionA cubical block of glass of refractive index n_1 is in contact with the surface of water of refractive index n_2. A beam of light is incident on vertical face of the block. After refraction a total internal reflection at the base and refraction at the opposite face take place. The ray emerges at angle theta as shown. The value of theta is given by
View SolutionFigure shows an irregular block of material of refractive indec sqrt(2) . A ray of light strikes the face AB as shown. After refraction, it is incident on a spherical surface CD of radius of curvature 0.4 m and enters a medium of refractive index 1.514 to meet PQ at E. Find the distance OE up to two places of decimal.
View Solutionचित्र में एक प्रकाश की किरण वायु से पारदर्शी गुटके में प्रवेश करती है। यदि गुटके के पदार्थ का अपवर्तनांक √2 हो तो अपवर्तन कोण का मान ज्ञात कीजिये।

View SolutionA ray of light travelling in air is incident at 45^(@) on a medium of refractive index sqrt(2) . The angle of refractive in the medium is
View SolutionA ray of light incidents on a refraction surface at 30 @ with the surface.If the angle of refraction is 45 @ refractive index of the medium is qquad sqrt3 sqrt3 /2 sqrt(3/2)
View Solutionचित्र में √2 अपवर्तनांक वाले पदार्थ से बना एक असममित ब्लॉक है| प्रकाश की एक किरण पृष्ठ AB पर चित्रानुसार 600 आपतित होती है| अपवर्तन के पश्चात यह एक गोलीय पृष्ठ CD ( वक्रता त्रिज्या 0.4 मी) पर आपतित होती है तथा 1.514 अपवर्तनांक वाले माध्यम में प्रवेश करती है तथा PQ के बिंदु E पर मिलती है | दूरी OE का मान दशमलव के दो स्थान तक ज्ञात कीजिए |
View Solutionएक प्रकाश की किरण निर्वात से अपवर्तनांक μ वाले माध्यम में प्रवेश करती है। यदि आपतन कोण, अपवर्तन कोण से दोगुना है, तो आपतन कोण है
View SolutionThe refracting angle of a prism is 60^(@) and the refractive index of its material is sqrt((7)/(3)). Find the minimum angle of incidence of a ray of light falling on one refracting face of the prism such that the emerging ray will graze the other refracting face.
View SolutionA light ray is incident on an irregular shaped slab of refractive index sqrt(2) at an angle of 45^@ with the normal on the incline face as shown in the figure. The ray finally emerges from the curved surface in the medium of the refractive index mu = 1.514 and passes through point E. If the radius of curved surface is equal to 0.4 m. find the distance OE correct upto two decimal places.
View SolutionA ray of light incidents on a refracting surface at 30^(@) with the surface . If the angle of refraction is 45^(@) refractive index of the medium is
View Solution
