If the principal source point S was to be moved a little upwards, towards the slit S1 from its usual symmetrical position with respect to the two slits S1andS2 discuss how the interference pattern, obtained on the screen, would get affected.
To analyze how the interference pattern is affected when the principal source point S is moved upwards towards slit S1, we can follow these steps:
1. Understand the Initial Setup:
- We have two slits, S1 and S2, which are equidistant from a central source point S. The screen is placed at a distance where the interference pattern is observed.
2. Identify the Shift in Source Position:
- The problem states that the source point S is moved upwards towards slit S1. This means that the distances from the source to the two slits will no longer be equal.
3. Effect on Path Lengths:
- When the source S is moved closer to S1, the path length from S to S1 decreases while the path length from S to S2 increases. This results in a difference in the path lengths from the source to each slit.
4. Determine the New Central Maximum:
- The central maximum, which is originally located directly opposite the midpoint between S1 and S2, will now shift downwards on the screen. This is because the increased path length to S2 will cause a phase difference that alters the position of the maxima.
5. Fringe Shift:
- The entire interference pattern will shift downwards on the screen. The spacing between the fringes (fringe width) remains unchanged because it depends on the wavelength of light and the distance between the slits and the screen, which have not changed.
6. Conclusion:
- In summary, moving the source point S upwards towards S1 results in a downward shift of the entire interference pattern on the screen, while the fringe width remains constant.
- We have two slits, S1 and S2, which are equidistant from a central source point S. The screen is placed at a distance where the interference pattern is observed.
- The problem states that the source point S is moved upwards towards slit S1. This means that the distances from the source to the two slits will no longer be equal.
- When the source S is moved closer to S1, the path length from S to S1 decreases while the path length from S to S2 increases. This results in a difference in the path lengths from the source to each slit.
- The central maximum, which is originally located directly opposite the midpoint between S1 and S2, will now shift downwards on the screen. This is because the increased path length to S2 will cause a phase difference that alters the position of the maxima.
- The entire interference pattern will shift downwards on the screen. The spacing between the fringes (fringe width) remains unchanged because it depends on the wavelength of light and the distance between the slits and the screen, which have not changed.
- In summary, moving the source point S upwards towards S1 results in a downward shift of the entire interference pattern on the screen, while the fringe width remains constant.
Similar Questions
In a Young.s double slit experiment , a monochromatic source if wavelength lambda is used to illmunate the two slits S_(1) and S_(2) The slits S_(1)and S_(2) are identical and source S is placed symmetrically as shown .Interference pattern is observed on a screen at a distance D from the centre of slit . The distance between the slits is d . If the resultant intensity at P is same as that O , then the distance OP cannot be
View SolutionIn a Young.s double slit experiment , a monochromatic source if wavelength λ is used to illmunate the two slits S1andS2

The slits S1andS2 are identical and source S is placed symmetrically as shown .Interference pattern is observed on a screen at a distance D from the centre of slit . The distance between the slits is d .If the source is moved by up by a very small disatnce y0 , the central maxima will shift
View SolutionIn a Young.s double slit experiment , a monochromatic source if wavelength lambda is used to illmunate the two slits S_(1) and S_(2) The slits S_(1)and S_(2) are identical and source S is placed symmetrically as shown .Interference pattern is observed on a screen at a distance D from the centre of slit . The distance between the slits is d .If the size of slit S_(1) is slightly decreased , them
View SolutionIn a modified YDSE, sources S is kept in front of slit S_(1) . Find the phase difference at point O that is equidistant from slits S_(1) and S_(2) and point P that is in front of slit S_(1) in the following situations. A liquid of refractive index mu is filled between the screen and slits.
View SolutionIn a young's doule slits experiment, a monochromatic source of wavelength λ is used to illuminate the two slits
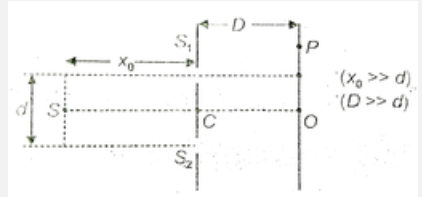
S1 and S2. The slitss S1 and S2 are identical and source S is placed symmetrically as shown. interference pattern is observed on a screen at a distance D from the centre of slit. The distance between the slits is d.
If the resultant intensity at P is same as that O, then the distance OP can not be
View SolutionIn a young's doule slits experiment, a monochromatic source of wavelength λ is used to illuminate the two slits
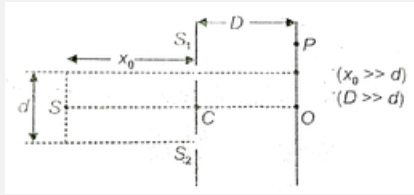
S1 and S2. The slitss S1 and S2 are identical and source S is placed symmetrically as shown. interference pattern is observed on a screen at a distance D from the centre of slit. The distance between the slits is d.
If the source is moved up by a very small distance y0, the central maxima will shift
View SolutionIn a young's doule slits experiment, a monochromatic source of wavelength λ is used to illuminate the two slits

S1 and S2. The slitss S1 and S2 are identical and source S is placed symmetrically as shown. interference pattern is observed on a screen at a distance D from the centre of slit. The distance between the slits is d.
If the size of slits S1 is slightly decreased, then
View Solution
