In the searle's experiment, after every step of loading, why should we wait for two minutes before taking the reading?( More than one options may be correct).
So that the wire can have its desired change in length
So that the wire can room temperature
So that vertical oscillations can get subsided
So that the wire has no change in its radius.
The correct Answer is:A, B, C
To answer the question "In Searle's experiment, after every step of loading, why should we wait for two minutes before taking the reading?", we can analyze the reasons step by step.
1. Understanding the Experiment: In Searle's experiment, we are dealing with a metal wire that is subjected to different loads. The primary goal is to measure the change in length of the wire as different weights are applied.
2. Reason for Waiting: The first reason for waiting two minutes is to allow the wire to reach its desired change in length after a load is applied. When a weight is added to the wire, it stretches, but this change does not happen instantaneously. The wire needs time to adjust to the new load and stabilize.
- Conclusion: This means that the first option (the wire can have its desired change in length) is correct.
3. Temperature Stabilization: When a load is applied to the wire, it can cause a slight increase in temperature due to internal friction and deformation. This temperature change can affect the material properties of the wire. Waiting for two minutes allows the wire to reach a stable temperature before taking measurements.
- Conclusion: Thus, the second option (so that the wire can have the same temperature) is also correct.
4. Damping Oscillations: When the load is applied, the wire may oscillate slightly before coming to rest. This oscillation can lead to inaccurate readings if taken immediately. Allowing time for the wire to settle ensures that we measure the final, stable length.
- Conclusion: Therefore, the third option (so that the vertical oscillations can subside) is also correct.
5. Incorrect Option: The fourth option suggests that we wait to ensure that the wire does not change its cross-sectional area. However, the cross-sectional area of a wire does change when it is stretched under load, and this is a normal behavior of materials under tension. Thus, this option is incorrect.
- Conclusion: The fourth option is not correct.
Final Answer:
The correct reasons for waiting two minutes before taking the readings in Searle's experiment are:
- The wire can have its desired change in length.
- The wire can have the same temperature.
- The vertical oscillations can subside.
Therefore, options 1, 2, and 3 are correct.
---
The correct reasons for waiting two minutes before taking the readings in Searle's experiment are:
- The wire can have its desired change in length.
- The wire can have the same temperature.
- The vertical oscillations can subside.
টপার এই প্রশ্নগুলো সমাধান করেছে
- GENERAL PHYSICSBook:DC PANDEY ENGLISHChapter:GENERAL PHYSICSExercise:MATCH THE COLUMN
Explore 6 Videos
- GENERAL PHYSICSBook:DC PANDEY ENGLISHChapter:GENERAL PHYSICSExercise:INTEGER_TYPE
Explore 2 Videos
- GENERAL PHYSICSBook:DC PANDEY ENGLISHChapter:GENERAL PHYSICSExercise:INTEGER_TYPE
Explore 2 Videos
- FLUID MECHANICSBook:DC PANDEY ENGLISHChapter:FLUID MECHANICSExercise:Medical entranes gallery
Explore 49 Videos
- GRAVITATIONBook:DC PANDEY ENGLISHChapter:GRAVITATIONExercise:(C) Chapter Exercises
Explore 45 Videos
সম্পর্কিত প্রশ্ন
Vernier constant is the (One or more than one correct option may be correct )
View SolutionThe figure represents the instantaneous picture of a transverse harmonic wave travelling along the negative x-axis . Choose the correct alternative(s) realted to the movement of the nine points shown in the figure [more than one option may be correct ]
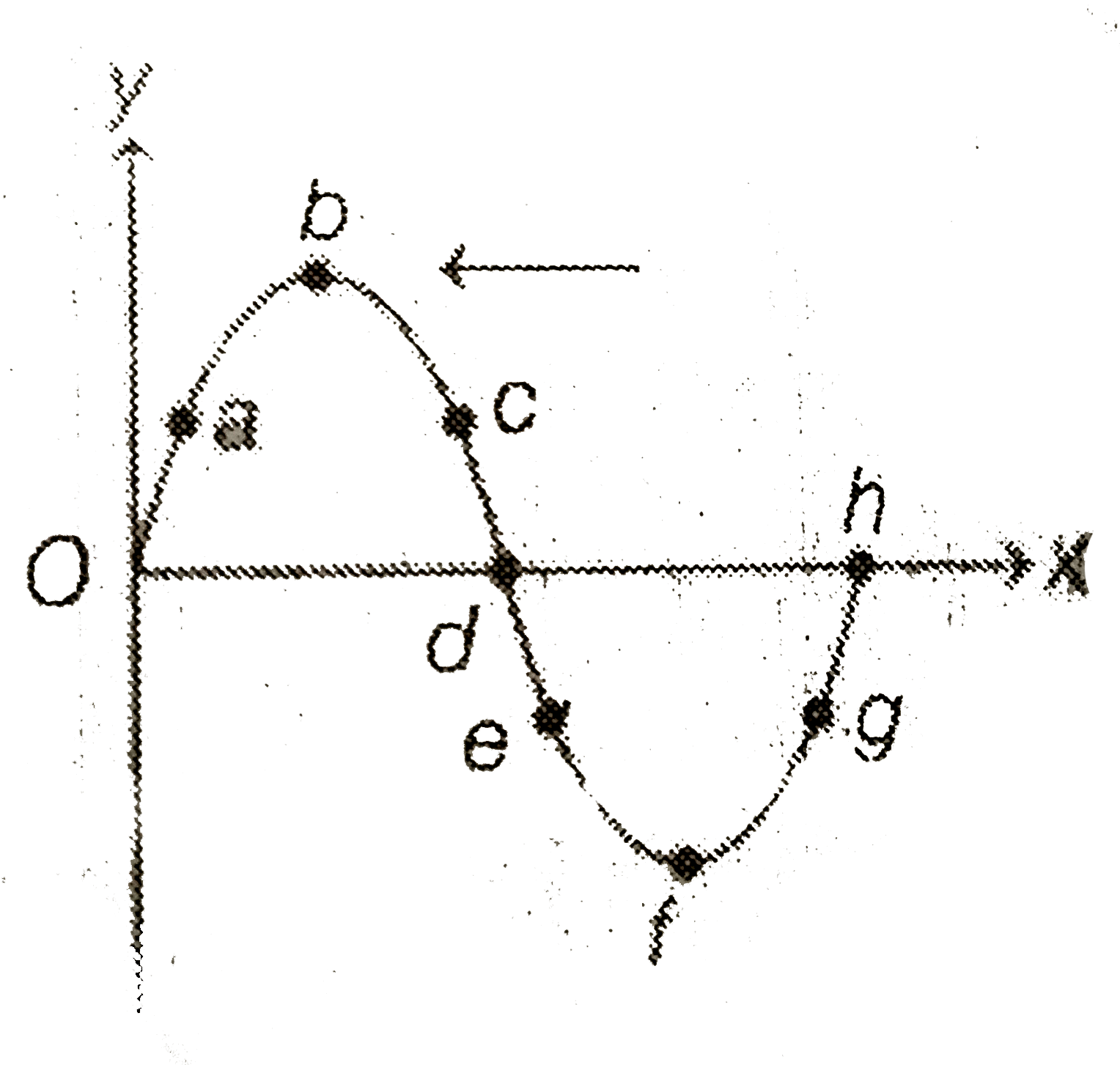
The point moving with maximum with speed is /are
View SolutionThe figure represents the instantaneous picture of a transverse harmonic wave travelling along the negative x-axis . Choose the correct alternative(s) realted to the movement of the nine points shown in the figure [more than one option may be correct ]

The stationary point is /are
View SolutionThe figure represents the instantaneous picture of a transverse harmonic wave travelling along the negative x-axis . Choose the correct alternative(s) realted to the movement of the nine points shown in the figure [more than one option may be correct ]
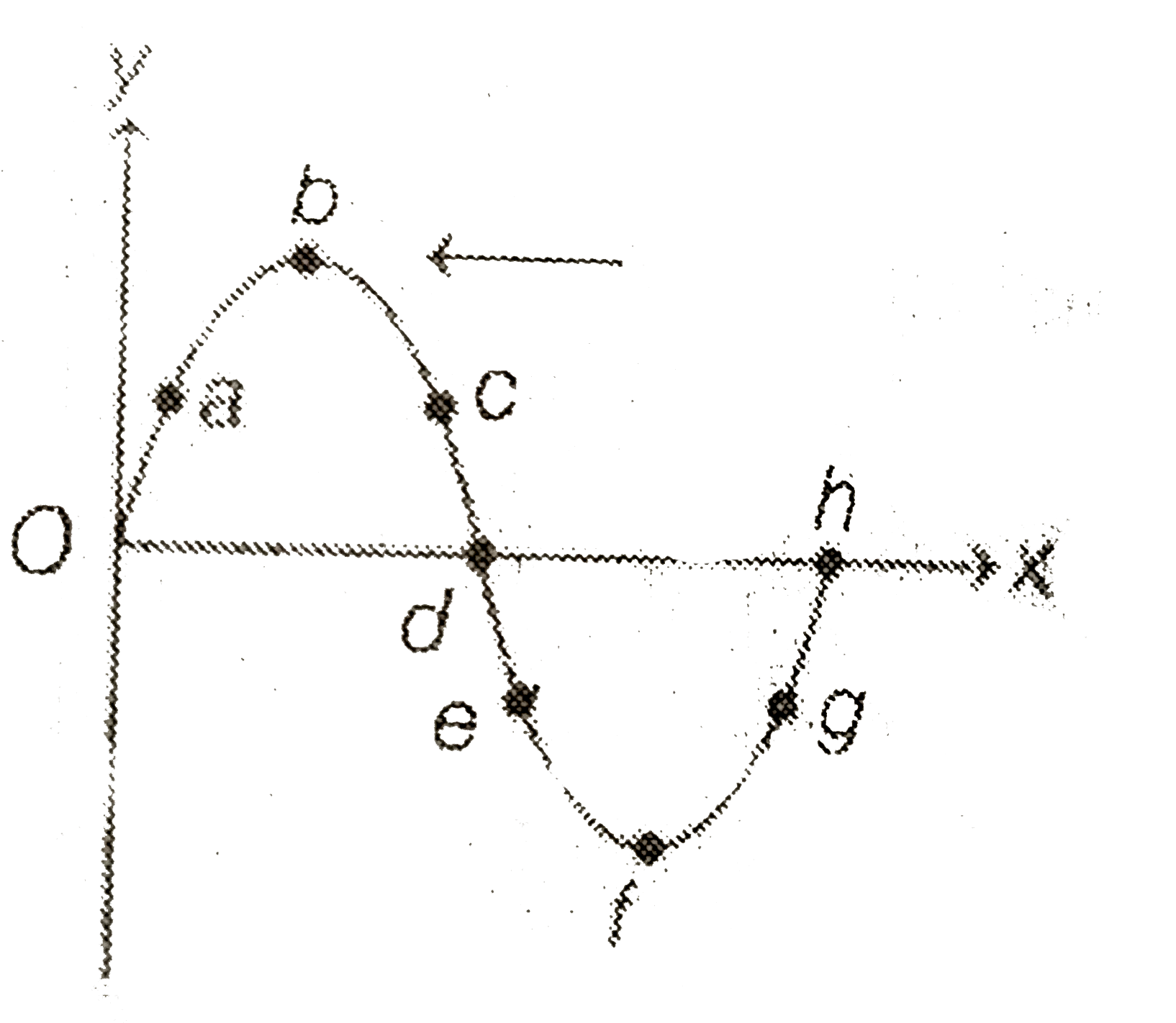
The points moving downward is /are
View SolutionThe figure represents the instantaneous picture of a transverse harmonic wave travelling along the negative x-axis . Choose the correct alternative(s) realted to the movement of the nine points shown in the figure [more than one option may be correct ]

The points moving upward is /are
View SolutionA condition where an individual heterozygous for two pairs of linked genes (AaBb) possesses the two dominant genes on one homologous chromosomes pair and two recessive on the other it is said to be
(a) Cis-arrangement
(b) Trans-arrangement
(c) Partly cis partly trans
(d) More than one option is correct
View SolutionOne day in the morning, Ramesh filled up 1//3 bucket of hot water from geyser, to take bath, Remaining 2//3 was to be filled by cold water (at room temperature) to bring mixture to a comfortable temperature. Suddenly Ramesh had to attend to something which would take some times, say 5 -10 minutes before he could take bath. Now he had two options : (i) fill the remaining bucket completely by cold water and then attend to the work, (ii) first attend to the work and fill the remaining bucket just before taking bath. Which option do you think would have kept water warmer ? Explain.
View SolutionA man throws ball with the same speed vertically upwards one after the other at an interval of 2 seconds. What should be the speed of the throw so that more than two ball are in the sky at any time (Given g=10m22)
View SolutionTwo students performed the same experiment separately and each one of them recorded two readings of mass which are given below. Correct reading of mass is 3.0 g. On the basis of given data, mark the correct option out of the following statements.

View SolutionThe rate law expresison is given for a typical reaction, n1A+n2B→P as r=k[A]n[B]n2. The reaction completes only in one step and A and B are present in the solution. If the reaction occurs in more than one step, then the rate law is expressed by consdering the slowest step, i.e., for SNl reaction r=k[RX]. If the eraction occurs in more than one step and the rates of the steps involved are comparable, then steady state approximation is conisdered, i.e., the rate of formation of intermediate is always equal to the rate of decompoistion of the intermediate. Conisder the reaction:
⎡⎢ ⎢⎣I2k2⇐⇒k12I(rapid equilibrium)H2+2Ik3−−→2HI(slow)⎤⎥ ⎥⎦
If we increase the concentration of I2 two times, then the rate of formation of HI will
View Solution
