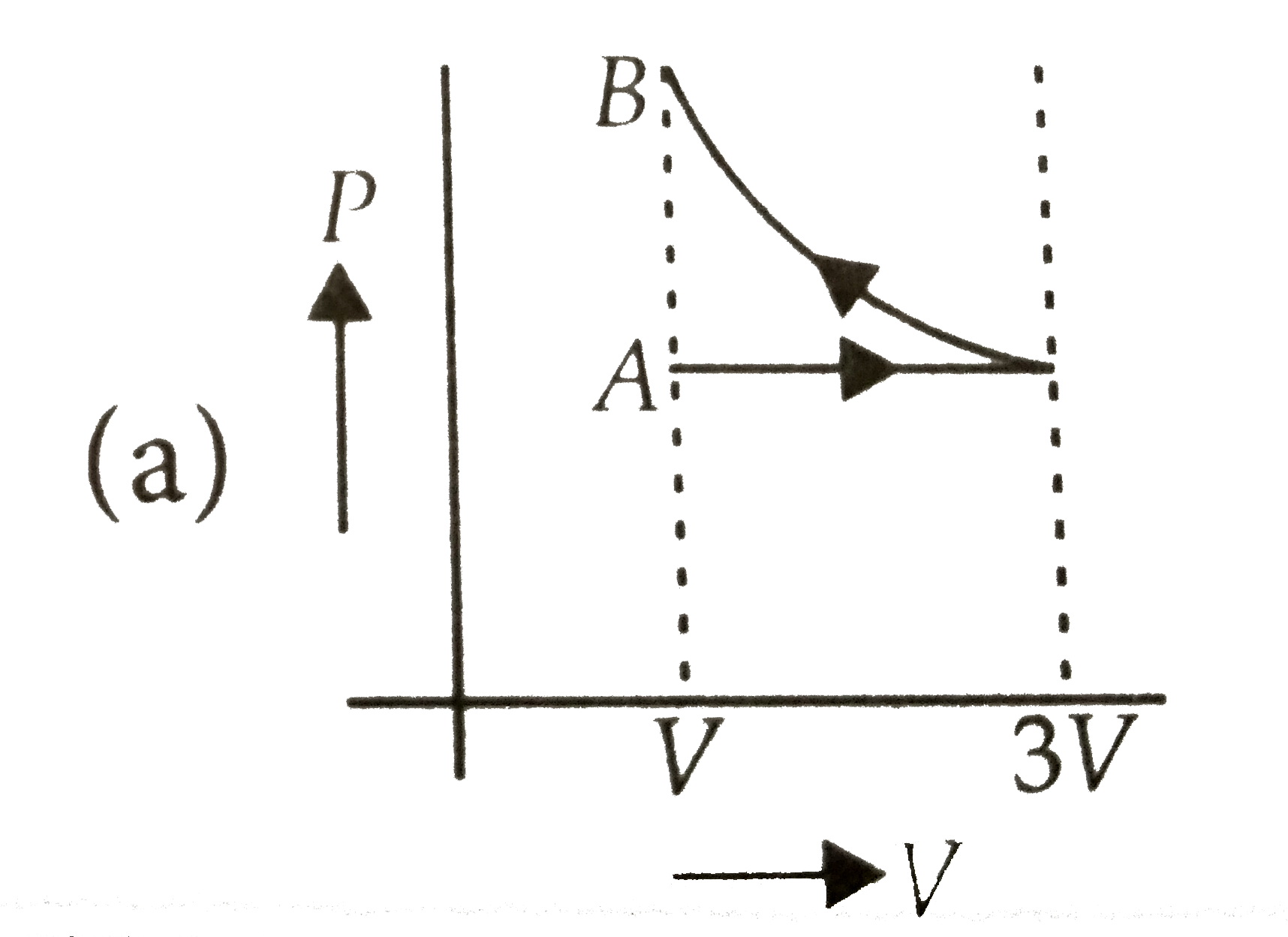
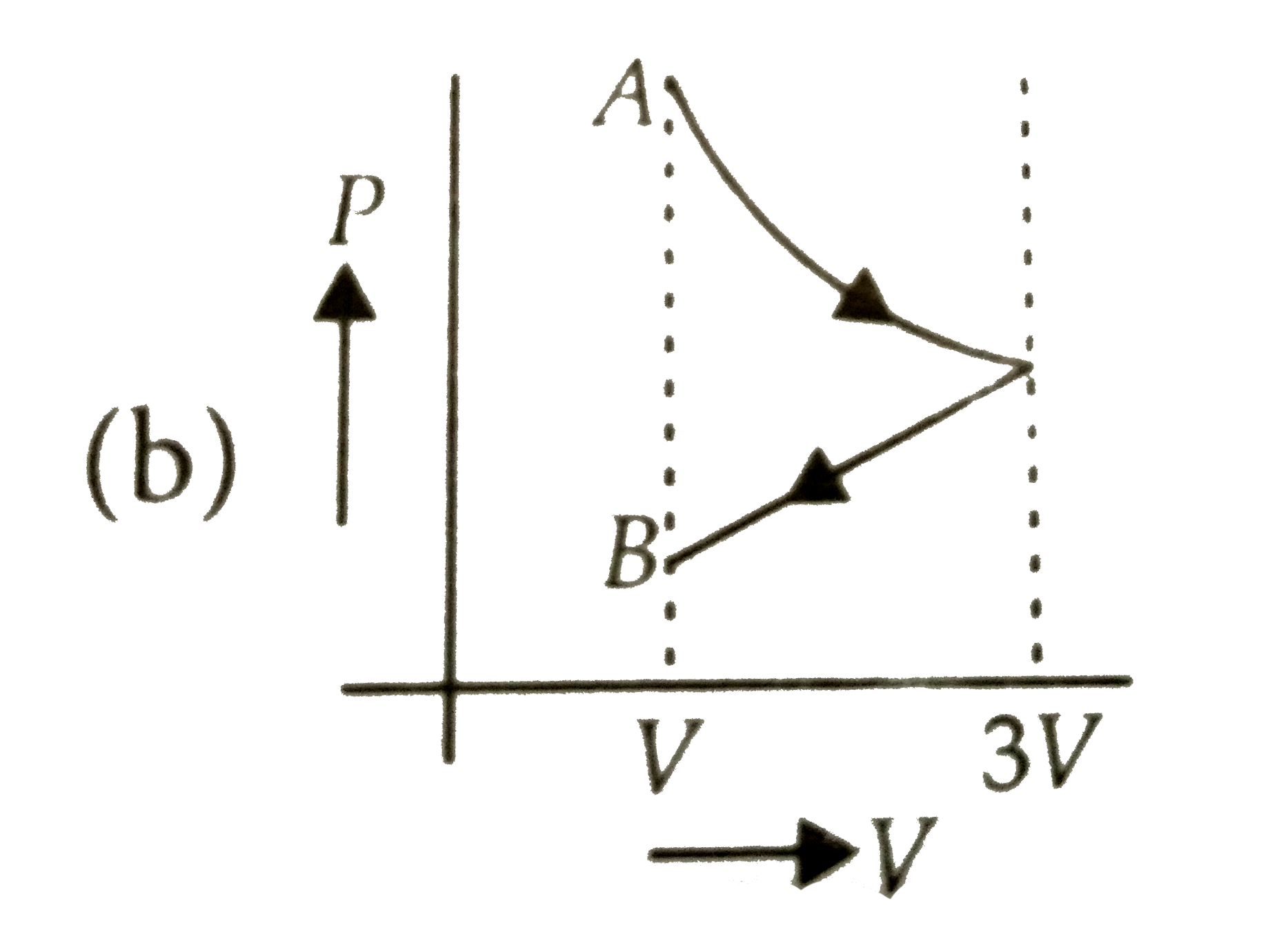
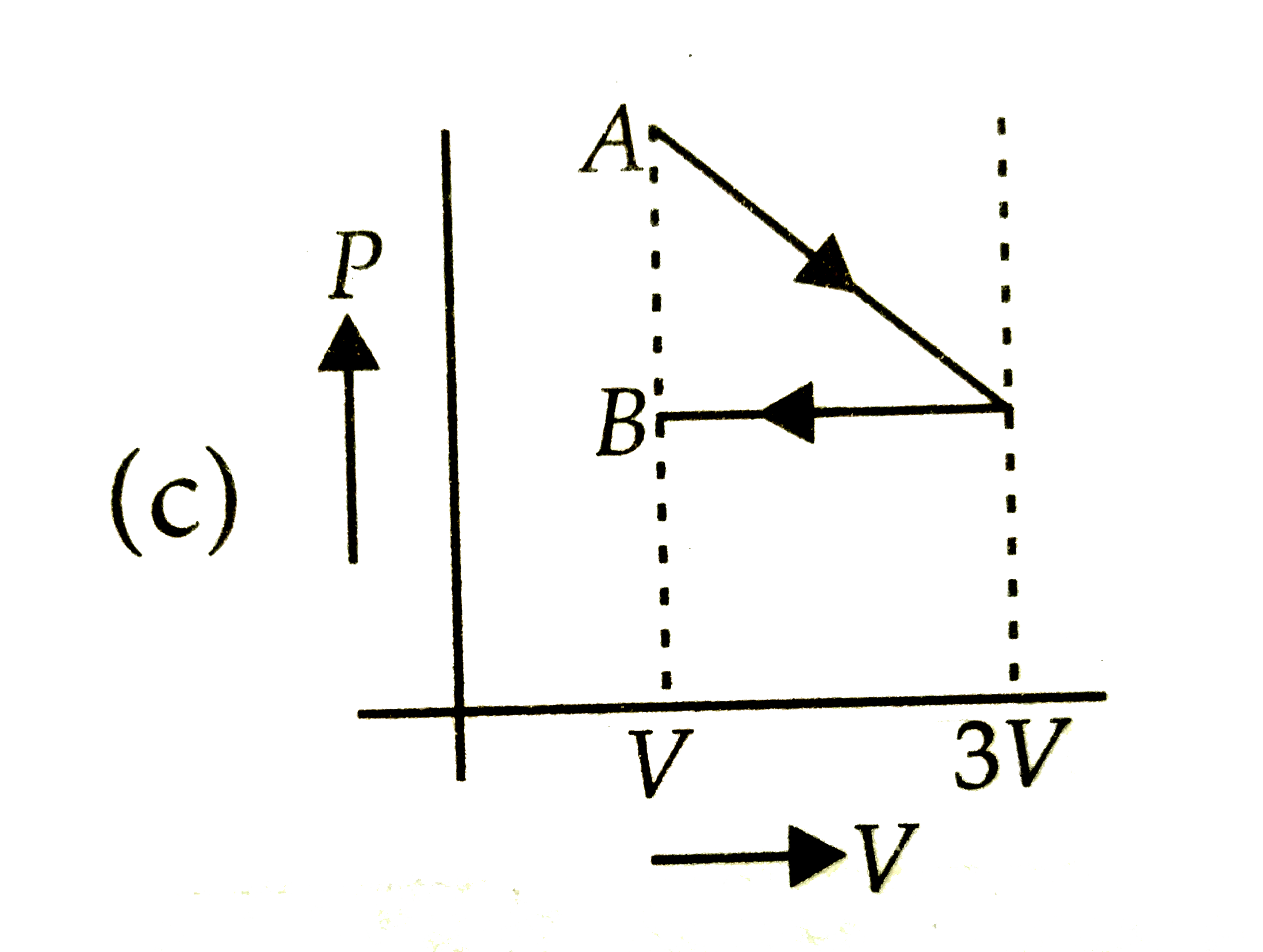
One mole of an ideal gas goes from an initial state A to final state B via two processs : It first undergoes isothermal expansion from volume V to 3V and then its volume is reduced from 3V to V at constant pressure. The correct P−V diagram representing the two process in (figure)
The correct Answer is:D
To solve the problem step by step, we will analyze the two processes that the ideal gas undergoes and then sketch the corresponding P-V diagram.
Step 1: Identify the Initial and Final States
- The initial state (A) has a volume of V.
- The final state (B) has a volume of V after going through two processes.
Step 2: Process 1 - Isothermal Expansion
- The gas undergoes an isothermal expansion from volume V to 3V.
- In an isothermal process, the temperature remains constant. According to the ideal gas law, PV=nRT, where n is the number of moles and R is the gas constant.
- Since n and R are constants, the product PV remains constant during this process.
- As the volume increases from V to 3V, the pressure must decrease. This relationship is inversely proportional, which means the graph will be a hyperbola that slopes downwards.
Step 3: Process 2 - Isobaric Compression
- The second process is a constant pressure (isobaric) process where the volume decreases from 3V to V.
- Since the pressure remains constant during this process, the P-V diagram will show a horizontal line at the pressure level corresponding to the pressure at volume 3V.
- The line will extend from 3V to V, indicating that the volume is decreasing while the pressure remains constant.
Step 4: Sketch the P-V Diagram
- On the P-V diagram:
- Start at point A (volume V, pressure PA).
- Draw a curve from point A to point C (volume 3V, pressure PC), indicating the isothermal expansion.
- From point C, draw a horizontal line to point B (volume V, pressure PC), indicating the isobaric compression.
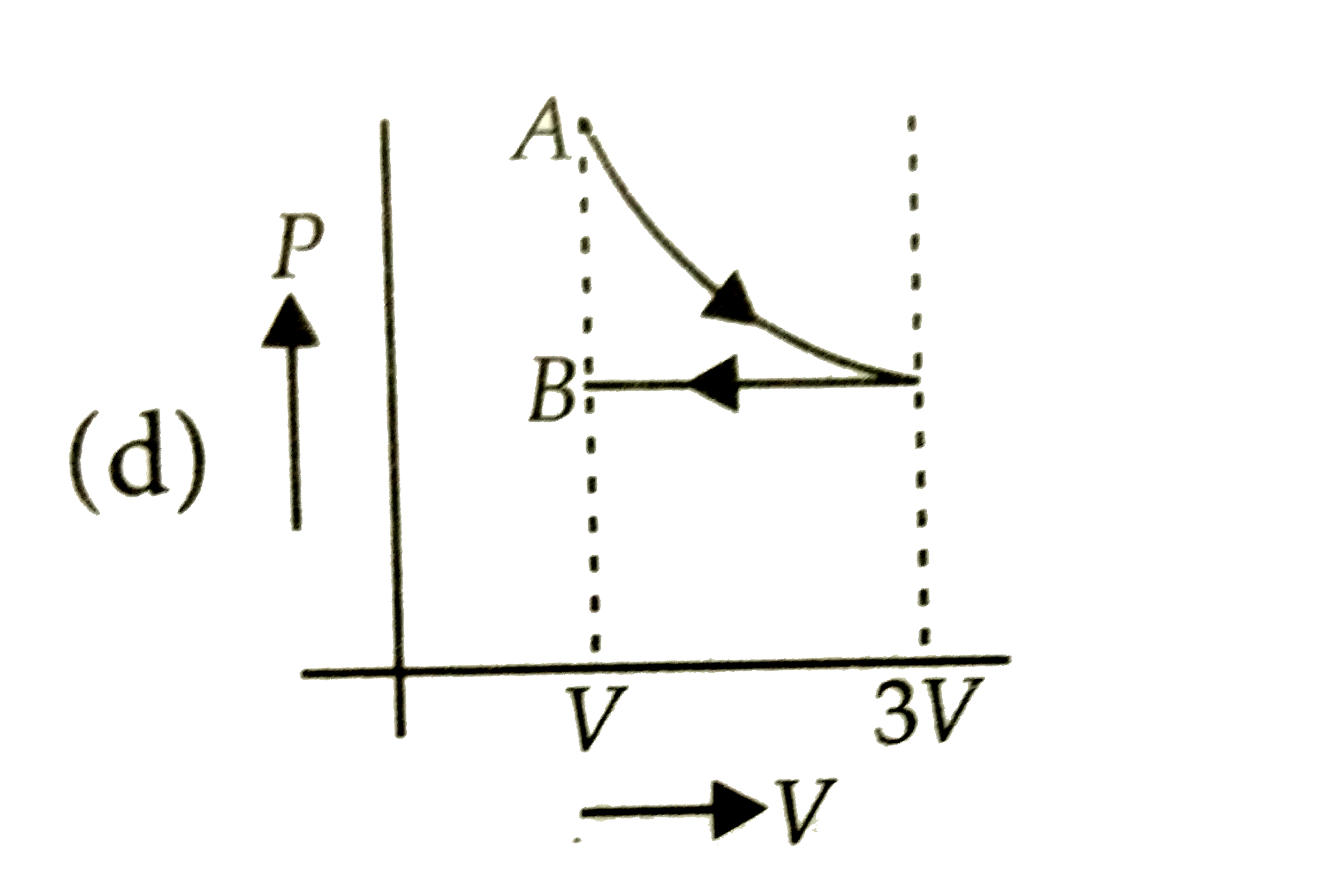
Step 5: Identify the Correct P-V Diagram
- Based on the description of the processes, we can now identify the correct P-V diagram from the options provided. The correct diagram should show:
- A downward-sloping curve from V to 3V for the isothermal process.
- A horizontal line from 3V to V for the isobaric process.
Conclusion
The correct P-V diagram representing the two processes is option D, as it accurately reflects the isothermal expansion followed by the isobaric compression.
- The initial state (A) has a volume of V.
- The final state (B) has a volume of V after going through two processes.
- The gas undergoes an isothermal expansion from volume V to 3V.
- In an isothermal process, the temperature remains constant. According to the ideal gas law, PV=nRT, where n is the number of moles and R is the gas constant.
- Since n and R are constants, the product PV remains constant during this process.
- As the volume increases from V to 3V, the pressure must decrease. This relationship is inversely proportional, which means the graph will be a hyperbola that slopes downwards.
- The second process is a constant pressure (isobaric) process where the volume decreases from 3V to V.
- Since the pressure remains constant during this process, the P-V diagram will show a horizontal line at the pressure level corresponding to the pressure at volume 3V.
- The line will extend from 3V to V, indicating that the volume is decreasing while the pressure remains constant.
- On the P-V diagram:
- Start at point A (volume V, pressure PA).
- Draw a curve from point A to point C (volume 3V, pressure PC), indicating the isothermal expansion.
- From point C, draw a horizontal line to point B (volume V, pressure PC), indicating the isobaric compression.
- Based on the description of the processes, we can now identify the correct P-V diagram from the options provided. The correct diagram should show:
- A downward-sloping curve from V to 3V for the isothermal process.
- A horizontal line from 3V to V for the isobaric process.
The correct P-V diagram representing the two processes is option D, as it accurately reflects the isothermal expansion followed by the isobaric compression.
Similar Questions
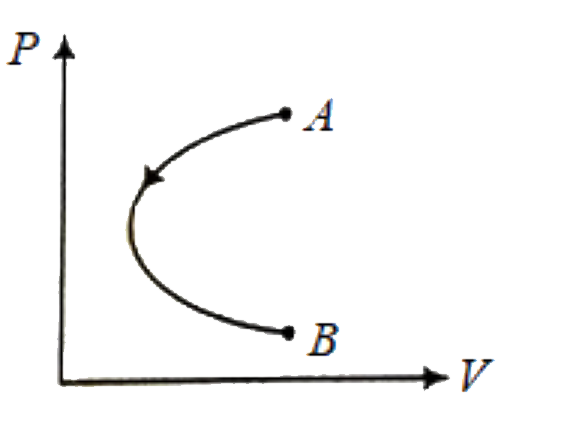
P - V diagram of an ideal gas is shown. The gas undergoes from initial state A to final state B such that initial and final volumes are same. Select the correct alternative for given process AB.
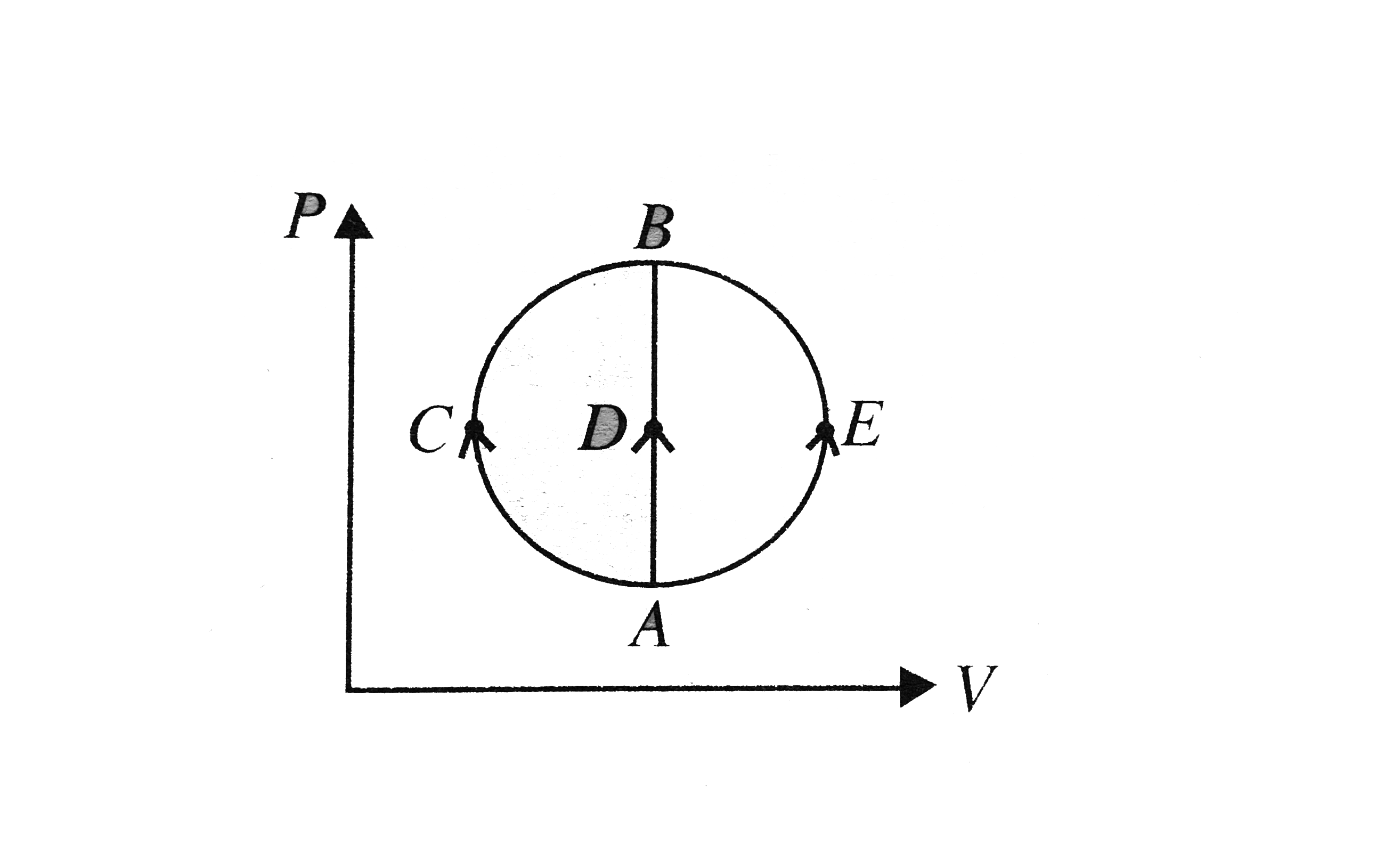
View SolutionOne mole of an ideal gas is taken from state A to state B by three different processes (a) ACB, (b) ADB and (c ) AEB as shown in the P−V diagram. The heat absorbed by the gas is
View Solution
Knowledge Check
An ideal gas undergoes isothermal process from some initial state i to final state f. Choose the correct alternatives.
A1.dU=dQB2. dU=-dWC3. dU=0D4. dU=dWThe initial state of certain gas (PiViTi).It undergoes expansion till its volume becomes Vf at constant temperature T. The correct plot of P-V diagram for it is
A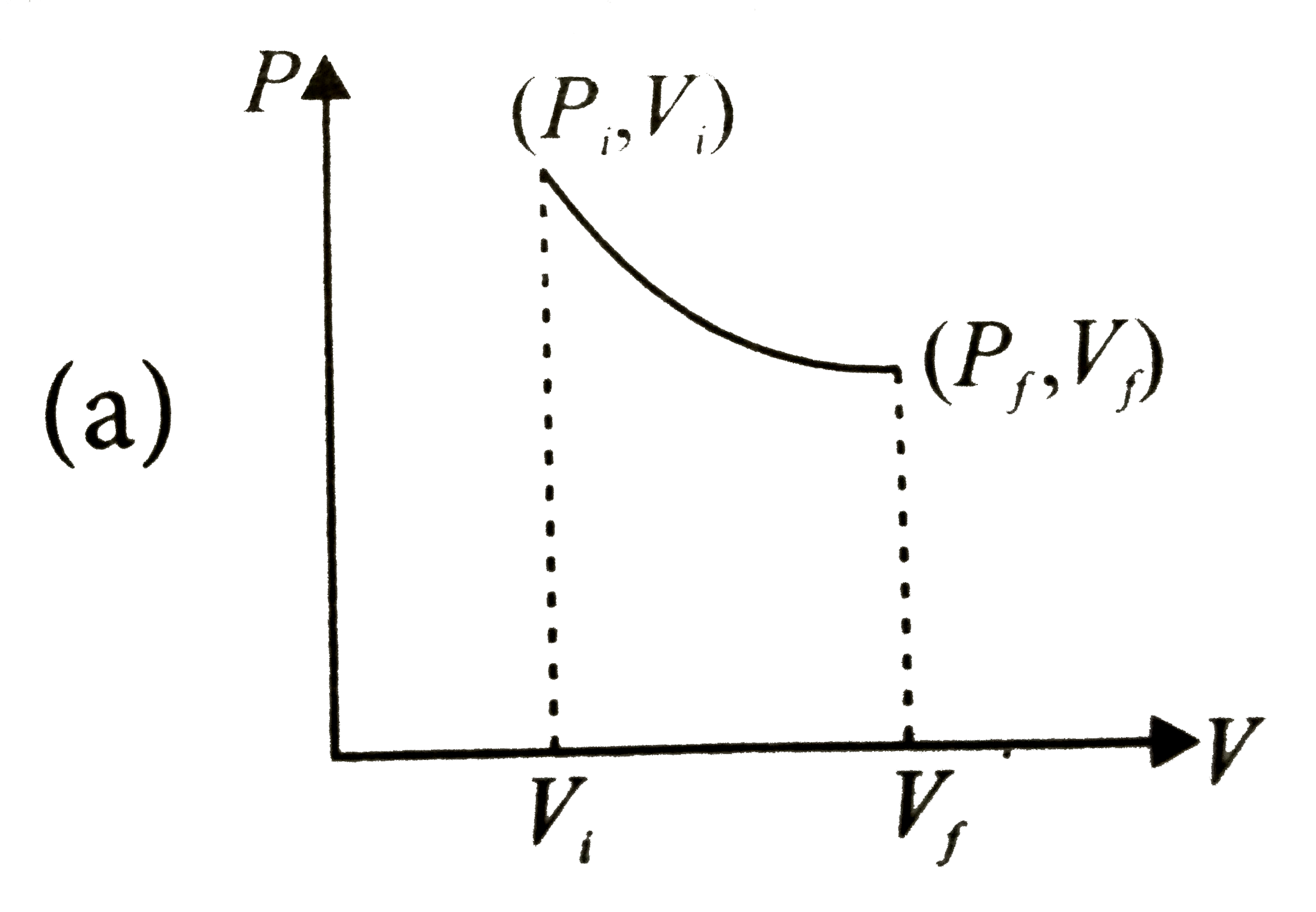 B
B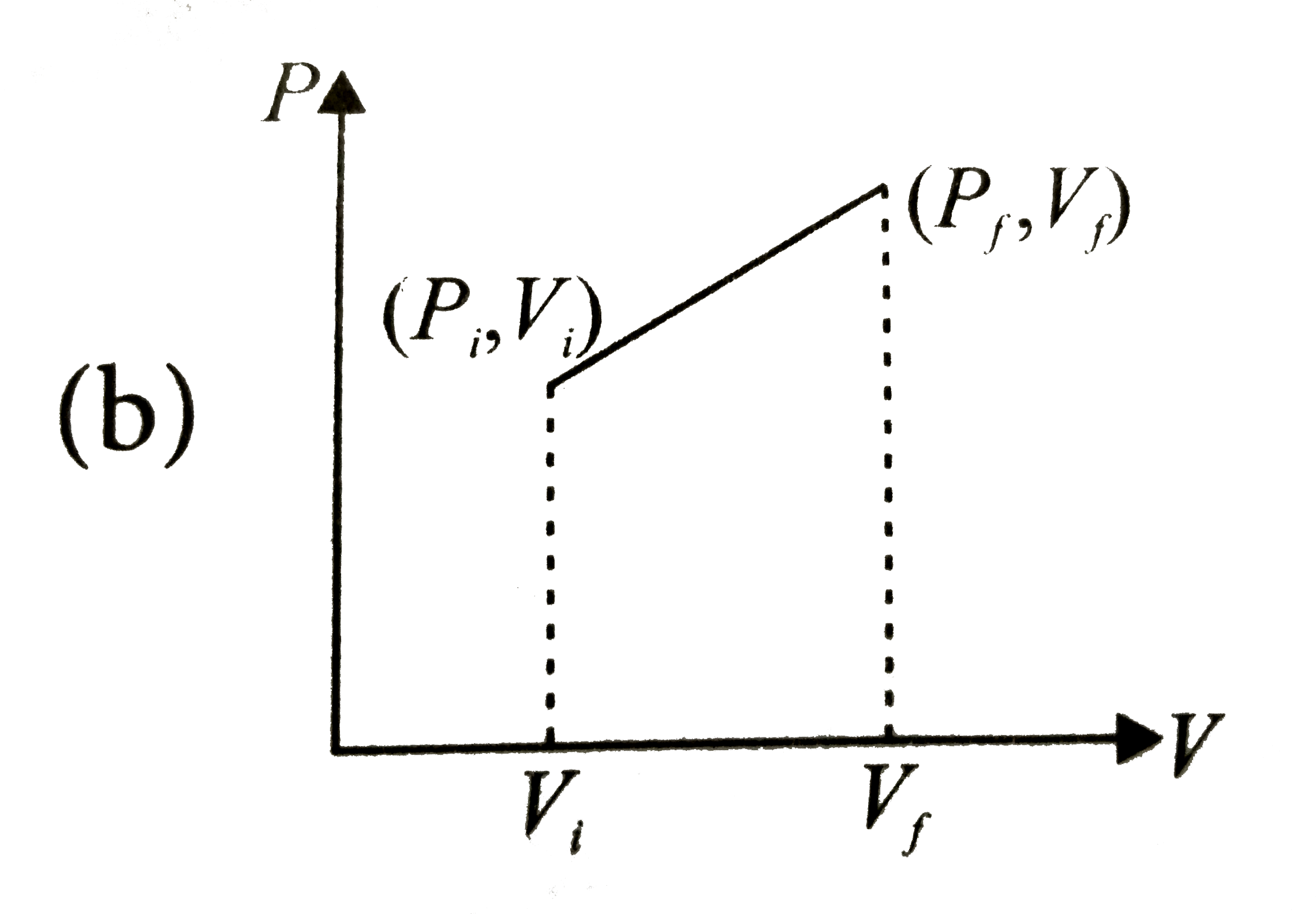 C
C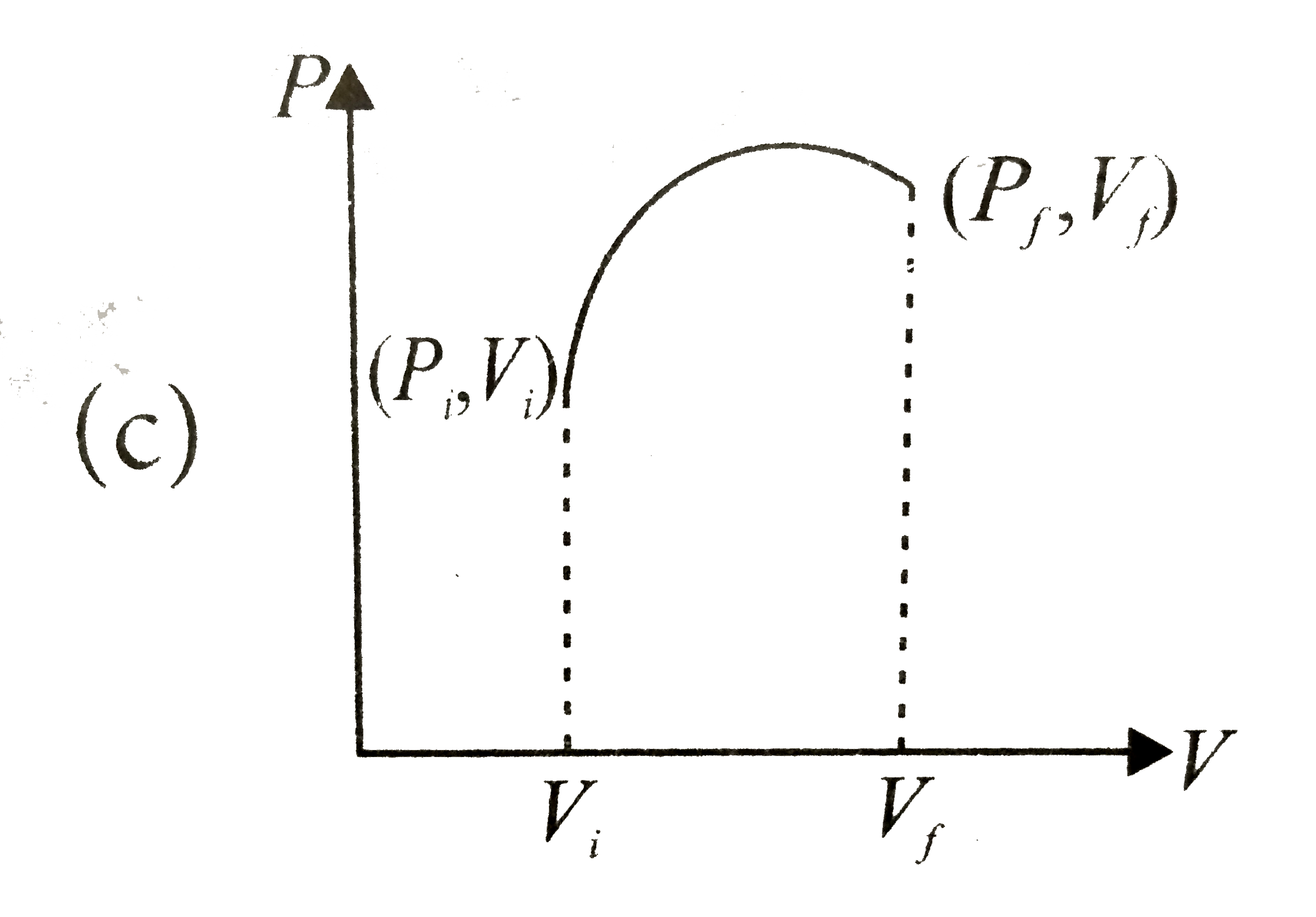 D
D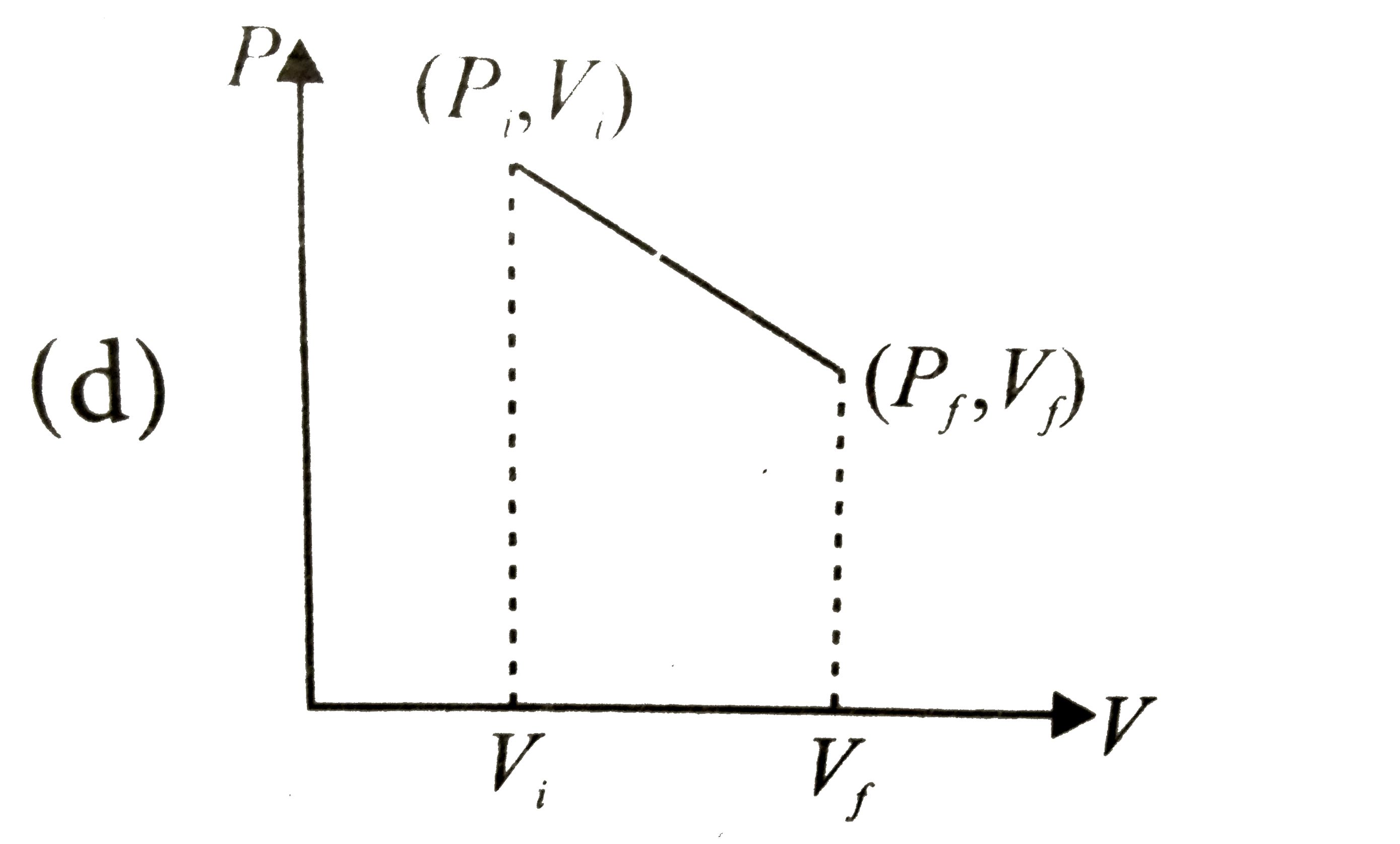
The work done, W, during an isothermal process in which the gas expands from an intial volume V1, to a final volume V2 is given by (R : gas constant, T : temperature )
AR(V2−V1)logeT1T2BR(T2−T1)loge(V1V2)CRTloge[V2V1]D2RTloge[V1V2]
One mole of an ideal gas is taken from state A to state B by three different processes (a) ACB, (b) ADB and (c ) AEB as shown in the P−V diagram. The heat absorbed by the gas is

View SolutionThe equation of a state of a gas is given by p(V−b)=nRT. If 1 mole of a gas is isothermally expanded from volume V and 2V, the work done during the process is
View SolutionWhen a sample of ideal gas is changed from an initial state to a final state, various curves can be plotted for the process like P-V curve, V-T curve,P-T curve etc.
For example, P-V curve for a fixed amount of an ideal gas at constant temperature is a rectangular hyperbola, V-T curve for a fixed amount of an ideal gas at constant volume is again a straight line. However, the shapes may vary if the constant parameters are also changed.
Now, answer the following questions :
Which of the following graphs is not possible for a fixed amount of ideal gas upon moving from initial state A to final state B :
View SolutionWhen a sample of ideal gas is changed from an initial state to a final state, various curves can be plotted for the process like P-V curve, V-T curve,P-T curve etc.
For example, P-V curve for a fixed amount of an ideal gas at constant temperature is a rectangular hyperbola, V-T curve for a fixed amount of an ideal gas at constant volume is again a straight line. However, the shapes may vary if the constant parameters are also changed.
Now, answer the following questions :
Two moles of an ideal gas is changed from its initial state (16 atm, 6L) to final state (4 atm, 15L) in such a way that this change can be represented by a straight line in P-V curve.The maximum temperature attained by the gas during the above change is :(Take : R=112LatmK−1mol−1)
View SolutionThe pressure p and volume V of an ideal gas both increase in a process.
View Solution
