The device shown in Fig. rotates on the vertical axle as shown. The frame has negligible mass as compared to the four masses each of mass m. Initial angular velocity of the system is ω0. Due to an internal mechanism the spokes in the frame lengthen so that the radii of the masses become 2a. Initially, it was a. What will be the new angular velocity of the system?
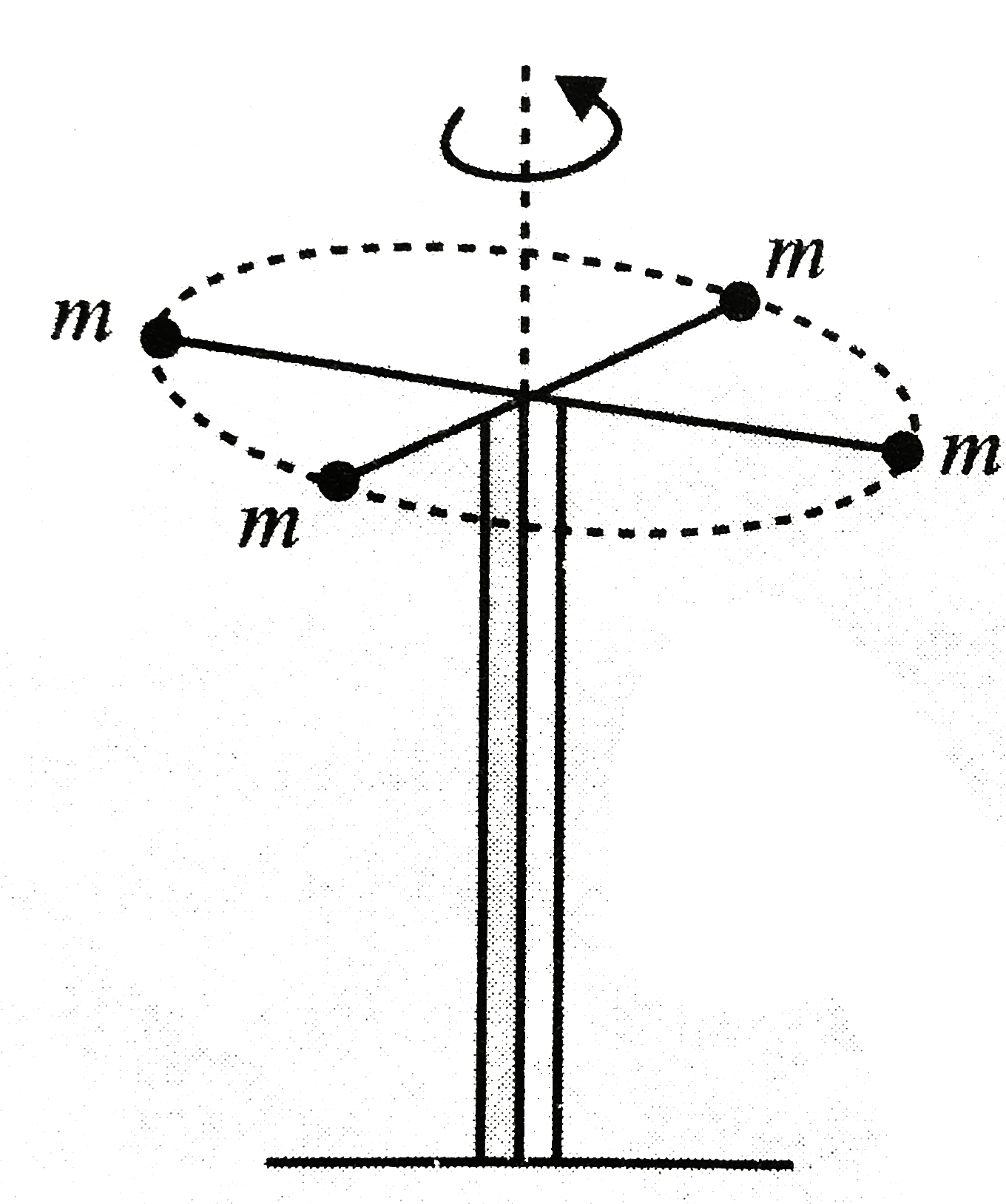
The will be no torque on the system if we ignore frictional torque at the axle. Therefore, the angular momentum of the system is conserved.
→Linitial=→Lfinal
Iinitialω0=Ifinalω
4ma2ω0=4m(2a)2ω
from which we have ω=ω04
Topper's Solved these Questions
- RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2BOOK - CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHCHAPTER - RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2EXERCISE - Exercise 3.3
21 Videos
- RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2BOOK - CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHCHAPTER - RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2EXERCISE - Exercise 3.4
13 Videos
- RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2BOOK - CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHCHAPTER - RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2EXERCISE - Exercise 3.1
11 Videos
- RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 1BOOK - CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHCHAPTER - RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 1EXERCISE - Integer
11 Videos
- SOUND WAVES AND DOPPLER EFFECTBOOK - CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHCHAPTER - SOUND WAVES AND DOPPLER EFFECTEXERCISE - Integer
16 Videos
Similar Questions
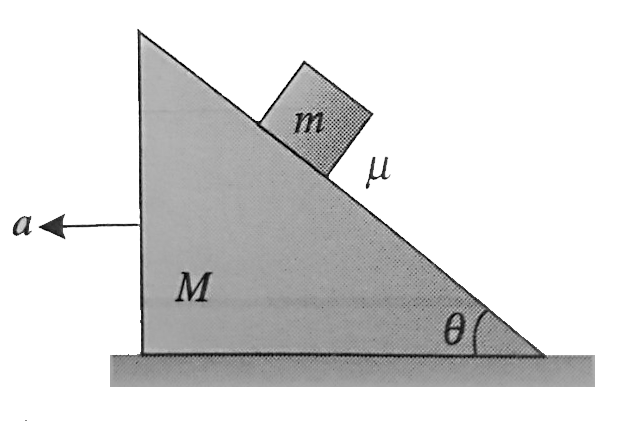
A block of mass m is at rest relative to the stationary wedge of mass M. The coefficient of friction between block and wedge is μ. The wedge is now pulled horizontally with acceleration a as shown in figure. Then the minimum magnitude of a for the friction between block and wedge to be zero is:
View SolutionA sphere rolling on a horizontal rough surface Collides elastically with a smooth vertical wall, as shown in Fig. State which of the following statements is true or false.
 a. After collision, the velocity of the centre of mass gets reversed.
a. After collision, the velocity of the centre of mass gets reversed.
b. Angular momentum of the sphere about the point of contact with the wall is conserved.
c. Angular momentum of the sphere about a stationary point on the horizontal surface is conserved.
d. Just after collision the point of contact with the horizontal surface is moving towards the wall.
e. After collision the friction force acts on the sphere such that it decreases the linear speed and increases the angular speed.
f. Finally, when the sphere starts rolling, it is moving away from the wall.
View SolutionA uniform spherical shell of mass M and radius R rotates, about a vertical axis on frictionless bearing. A massless cord passes around the equator of the shell., over a pulley of rotational inertia I and radius r and is attached to small object of mass m that is otherwise free to fall under the influence of gravity. There is no friction of pulley's axle, the cord does not slip on the pulley. What is the speed of the object after it has fallen a distance h. from rest? Use work-energy considerations.

View SolutionA solid cylinder with r=0.1m and mass M=2kg is placed such that it is in contact with the vertical and a horizontal surface as shown in Fig. The coefficient of friction is μ=(1/3) for both the surfaces. Find the distance (in CM) from the centre of the cylinder at .which a force F=40N should be applied vertically so that the cylinder just starts rotating in anticlockwise direction.
View SolutionThe average power transmitted across a cross section by two sound waves moving in the same direction are equal. The wavelength of two sound waves are in the ratio of 1:2, then find the ratio of their pressure amplitudes.
View SolutionThe device shown in Fig. rotates on the vertical axle as shown. The frame has negligible mass as compared to the four masses each of mass m . Initial angular velocity of the system is omega_(0) . Due to an internal mechanism the spokes in the frame lengthen so that the radii of the masses become 2a . Initially, it was a. What will be the new angular velocity of the system?
View SolutionA spherical ball of mass M moving with initial velocity V collides elastically with another ball of mass M , which is fixed at one end of L shaped rigid massless frame as shown in Fig. (a). The L shaped frame contains another mass M connected at the other end. The speed of the striking mass after collision is
View SolutionA disc of mass M and radius r is rotating with an angular velocity omega . If gently, two masses m each are placed at a distance r//2 on either side of the axis of rotation, what will be the new angular velocity ?
View SolutionInitial angular velocity of a circular disc of mass M is omega_(1) . Then two small spheres of mass m are attached gently to two diametrically opposite points on the edge of the disc. What is the final angular velocity of the disc -
View SolutionTwo beads of mass 2m and m , connected by a rod of length l and of negligible mass are free to move in a smooth vertical circular wire frame of radius l as shown. Initially the system is held in horizontal position ( Refer figure ) The minimum velocity that should be given to the mass 2m in clockwise direction to make it vertical is :
View SolutionA mass m is attached to a rigid rod of negligible mass as shown in figure. The system is pivoted at point O and rotates about the indicated z -axis with angular velocity vec(omega) , maintaining a fixed angle theta with the axis.
View Solutionद्रव्यमान m का एक कण एक जड़त्वीय फ्रेम में कोणीय वेग ω से त्रिज्या a के एक वृत्त में घूम रहा है। इसे एक ऐसे फ्रेम से देखा जाता है, जो स्वयं वृत्त के अक्ष के परितः कोणीय वेग ω0 से घूम रहा है। इस फ्रेम में कण पर लगता अपकेंद्र बल होगा
View SolutionA large disc has mass 2kg and radius 0.2 m and initial angular velocity 50 rad/s and small disc has mass 4kg and radius 0.1 m and initial angular velocity 200 rad/s both rotating about their common axis. Then the common final angular velocity after discs are in contact is,
View SolutionFour point masses are fastened to the corners of a frame of negligible mass lying in the xy plane. Let w be the angular speed of rotation. Then
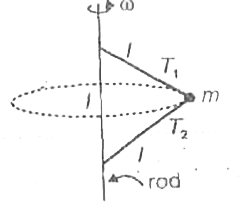
View SolutionIn the figure, a ball of mass m is tied with two strings of equal as shown. If the rod is rotated with angular velocity ω1 when
View Solution

