
The figure shows the shape of three strings on which sinusoidal transverse waves are propagating. The arrows in the diagram indicate the direction of wave propagation. Out of the 6 particles marked (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 ) how many have their instantaneous velocity and acceleration both directed towards their mean position.
The correct Answer is:Three
Step by step video, text & image solution for The figure shows the shape of three strings on which sinusoidal transverse waves are propagating. The arrows in the diagram indicate the direction of wave propagation. Out of the 6 particles marked (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 ) how many have their instantaneous velocity and acceleration both directed towards their mean position. by Physics experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 11 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023Similar Questions
A transverse simple harmonic wave propagating to the right along a string is shown in the figure At the moment shown, out of the particles labeled as p,q,r,s and T which point has its velocity and acceleration in opposite directions ? T R
View SolutionLet A={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9). How many subsets does A have which contain 4,5and6 ?
View Solution
Knowledge Check
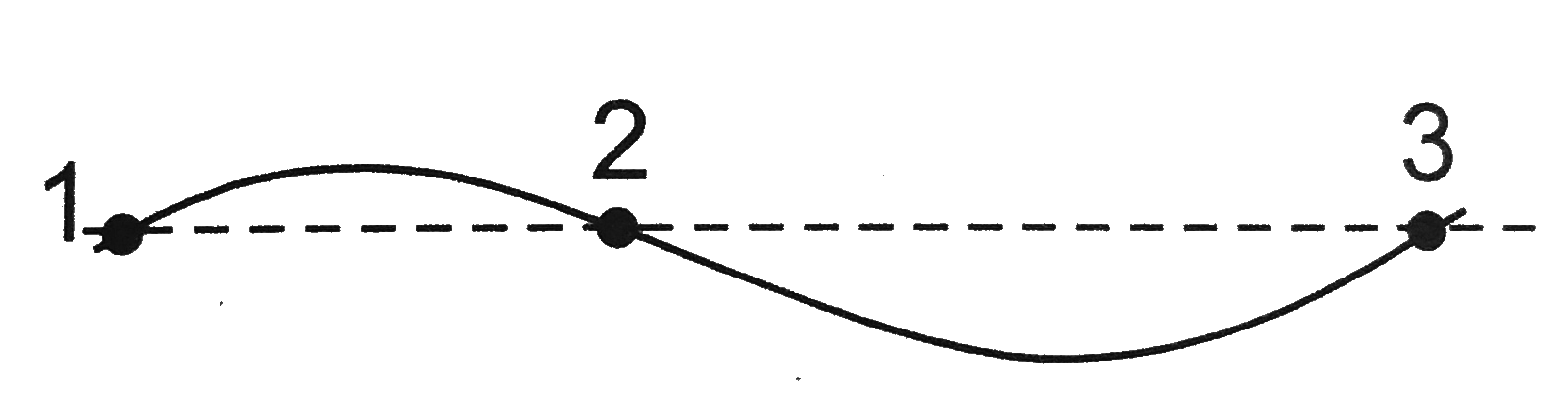
The diagram below shows an instantaneous position of a string as a transverse progressive wave travels along it from left to right Which one of the following correctly shows the direction of the velocity of the points 1,2 and 3 on the string?A→ → →B→ ← →C↓ ↓ ↓D↓ ↑ ↓A sinusoidal transverse progressive wave travelling on stretched string along x axis Choose appropriate number for direction of velocity and acceleration respectively force particle P shown in the diagram.
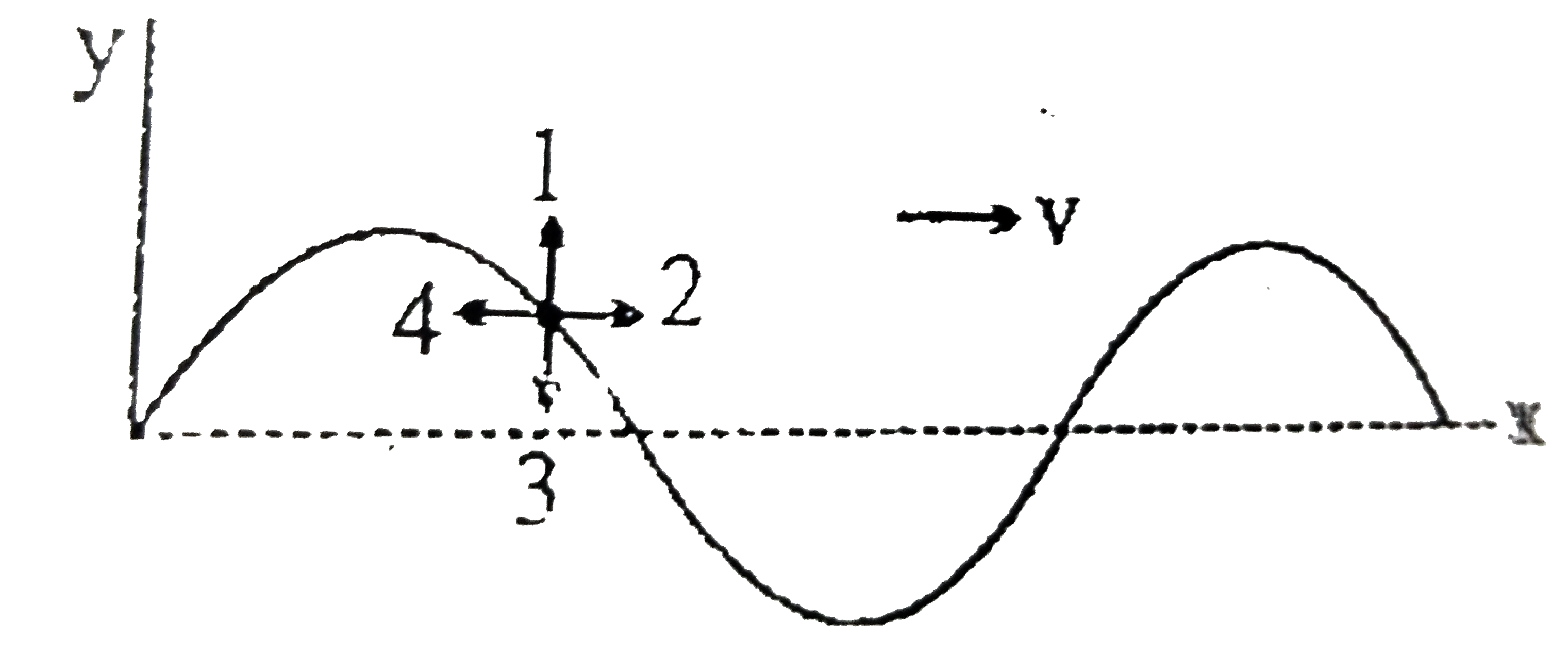 A3 and 1B1 and 3C1 and 1D2 and 4
A3 and 1B1 and 3C1 and 1D2 and 4A transverse wave of amplitude 0.5m and wavelength 1 m and frequency 2 Hz is propagating in a string in the negative x - direction. The expression for this wave is
Ay(x,t)=0.5sin(2πx−4πt)By(x,t)=0.5cos(2πx+4πt)Cy(x,t)=0.5sin(πx−2πt)Dy(x,t)=0.5cos(2πx+2πt)
Read the following passage and then answer questions (a) to (e) on the basis of your under- standing of the passage and the related studied concepts.
In accordance with Faraday.s law of electromagnetic induction a magnetic field, changing with time, gives rise to an electric field. Again as per Ampere-Maxwell.s law an electric field, changing with time, gives rise to a magnetic field. It means that if we consider a charge oscillating with some frequency, it produces an oscillating electric field in space, which produces an oscillating mag- netic field, which in turn, is a source of oscillating electric field and so on. The oscillating electric and magnetic fields thus regenerate each other and an electromagnetic wave propagates through space. The energy associated with the propagating wave comes at the expense of the energy of the oscillating charge.
Electromagnetic wave propagates through free space as a transverse wave in which →Eand→B are perpendicular to each other as well as perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation. Like other waves electromagnetic waves carry energy and momentum. As electromagnetic waves contains both electric and magnetic fields, it has an electrical energy density μE=12∈0E2 as well as a magnetic energy density μB=B22μ0. Both of these vary with time.
In which direction does the electric field oscillates?
View SolutionRead the following passage and then answer questions (a) to (e) on the basis of your under- standing of the passage and the related studied concepts.
In accordance with Faraday.s law of electromagnetic induction a magnetic field, changing with time, gives rise to an electric field. Again as per Ampere-Maxwell.s law an electric field, changing with time, gives rise to a magnetic field. It means that if we consider a charge oscillating with some frequency, it produces an oscillating electric field in space, which produces an oscillating mag- netic field, which in turn, is a source of oscillating electric field and so on. The oscillating electric and magnetic fields thus regenerate each other and an electromagnetic wave propagates through space. The energy associated with the propagating wave comes at the expense of the energy of the oscillating charge.
Electromagnetic wave propagates through free space as a transverse wave in which →Eand→B are perpendicular to each other as well as perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation. Like other waves electromagnetic waves carry energy and momentum. As electromagnetic waves contains both electric and magnetic fields, it has an electrical energy density μE=12∈0E2 as well as a magnetic energy density μB=B22μ0. Both of these vary with time.
What is the frequency and wavelength of the electromagnetic wave?
View SolutionA transverse wave is propagating along +x direction. At t=2 sec the particle at x=4m is at y=2 mm. With the passage of time its y coordinate increases and reaches to a maximum of 4 mm. The wave equation is (using ω and k with their usual meanings)
View SolutionStationary wave is setup in a uniform string clamped at both the ends. Length of the string is 0.3 m.Snapshot of the string is taken the two instants one at t=0 sec and another at t=0.2 sec. These is two snapshots are shown below.
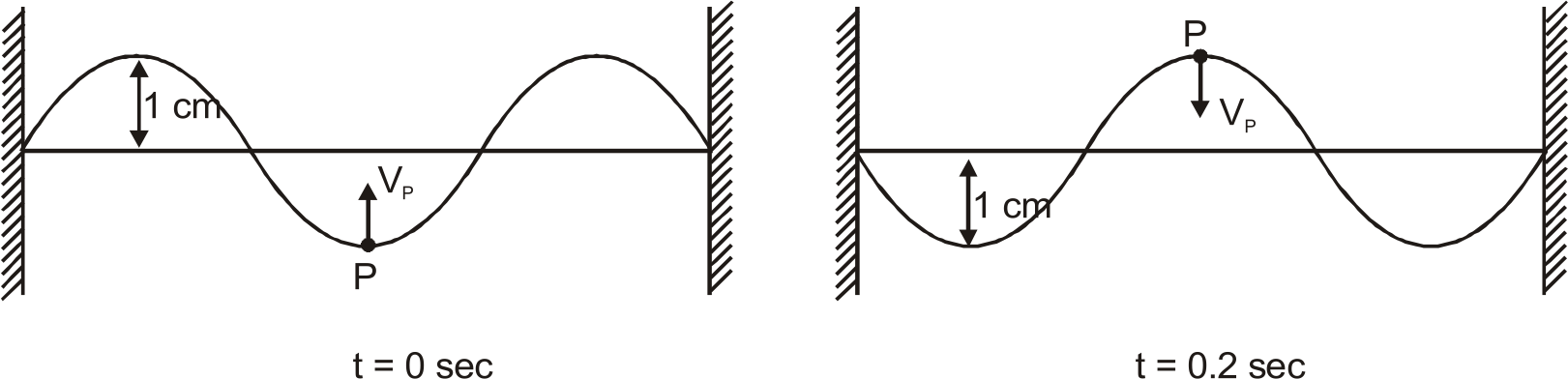
Velocity of point P (which is also the mid point of the string ) is in upward direction (take upward direction to be positive ) at t=0 sec.At the instant snapshots are taken particles are at half of their respective maximum displacement from mean position.During this time interval particles have crossed their mean position only once.Answer the following 3 questions for the qiven situation.
Velocity of travelling wave in the string is :
View SolutionStationary wave is setup in a uniform string clamped at both the ends. Length of the string is 0.3 m.Snapshot of the string is taken the two instants one at t=0 sec and another at t=0.2 sec. These is two snapshots are shown below.
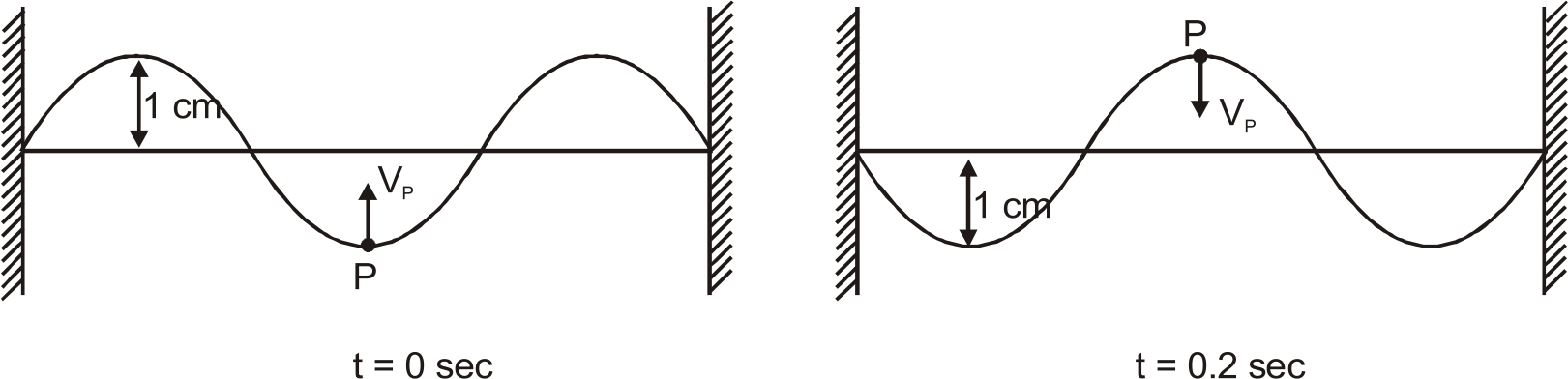
Velocity of point P (which is also the mid point of the string ) is in upward direction (take upward direction to be positive ) at t=0 sec.At the instant snapshots are taken particles are at half of their respective maximum displacement from mean position.During this time interval particles have crossed their mean position only once.Answer the following 3 questions for the qiven situation.
Acceleration time graph of the particle at mid point of the string (i.e. , particle P ) is
View Solution

