The frequency of sound produced by a bell is 500 Hz the velocity of the source relative to still air is 60 m/s. An observer moves at 30 m/s along the same line as the source. Calculate the frequency of sound wave measured by the observer. Consider all possible cases (speed of sound v=340ms.)
CASE I. Let the be at right of the source. Both source and observer are moving in right direction. There will be apparent increase in frequency because Vsource>Vobserver
f'=f0[VS−VobserverVS−Vsource]Hz=500[340−30340−60]Hz=553Hz
CASE II. Source is moving right and observer is moving left.
There will be apparent increase in frequency since both are moving towards each other.
f'=f0[VS+VobserverVS−Vsource]Hz=500[340+30340−60]Hz
CASE III. Both source and observer are receding from each other.
There will be an apparent decrease in frequency.
f'=f0[VS−VobserverVS−Vsource]Hz=500[340−30340+60]Hz=387.5Hz
CASE IV. Both source and observer are moving towards left.
f'=f0[VS+VobserverVS+Vsource]=500[340+30340+60]Hz=462.5Hz
You should repeat the example assuming that the observer is to the left of the source. What conclusions can be derived from this example? Do you get a different set of four apparent frequencies.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- SOUND WAVES AND DOPPLER EFFECTBook:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:SOUND WAVES AND DOPPLER EFFECTExercise:Exercise 6.1
Explore 56 Videos
- SOUND WAVES AND DOPPLER EFFECTBook:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:SOUND WAVES AND DOPPLER EFFECTExercise:Exercise 6.2
Explore 72 Videos
- SOUND WAVES AND DOPPLER EFFECTBook:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:SOUND WAVES AND DOPPLER EFFECTExercise:Integer
Explore 16 Videos
- RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2Book:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2Exercise:Interger
Explore 2 Videos
- SUPERPOSITION AND STANDING WAVESBook:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:SUPERPOSITION AND STANDING WAVESExercise:Comprehension Type
Explore 5 Videos
Similar Questions
Do displacement particle velocity and pressure variation in a longitudinal wave vary with the same phase?
View SolutionA person riding on a merry go round emits a sound wave of a certain frequency Does a person at the centre observe the Doppler effect?
View SolutionThe average power transmitted across a cross section by two sound waves moving in the same direction are equal. The wavelength of two sound waves are in the ratio of 1:2, then find the ratio of their pressure amplitudes.
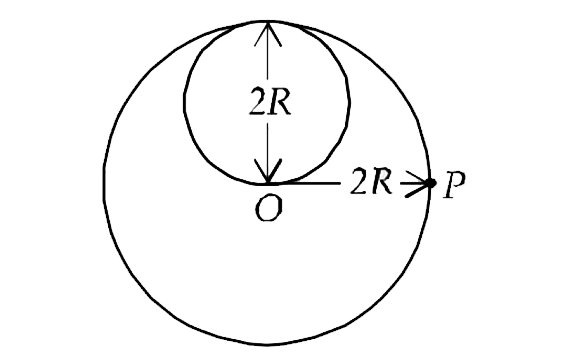
View SolutionA lamina is made by removing a small disc of diameter 2R from a bigger disc of uniform mass density and radius 2R, as shown in the figure. The moment of inertia of this lamina about axes passing though O and P is IOandIP respectively. Both these axes are perpendicular to the plane of the lamina. The ratio IPIO is
View SolutionA string of length L, fixed at its both ends is vibrating in its 1st overtone mode. Consider two elements of the string of the same small length at positions l1=0.2Landl2=0.45L from one end.
If K1andK2 are their respective maximum kinetic energies,then
View SolutionThe frequency of sound produced by a bell is 500 Hz the velocity of the source relative to still air is 60 m/s. An observer moves at 30 m/s along the same line as the source. Calculate the frequency of sound wave measured by the observer. Consider all possible cases (speed of sound v=340ms.)
View SolutionA source of sound is travelling with a velocity of 30(m)/(s) towards a stationary observer. If actual frequency of source is 1000 Hz and the wind is blowing with velocity 20(m)/(s) in a direction at 60^@C with the direction of motion of source, then the apparent frequency heard by observer is (speed of sound is 340(m)/(s) )
View SolutionThe source producing sound and an observer both are moving along the direction of propagation of sound waves. If the respective velocities of sound, source and an observer are v,vs and v0, then the apparent frequency heard by the observer will be (n = frequency of sound)
View SolutionA source of sound of frequency 500 Hz is moving towards an observer with velocity 30 m/s . The speed of sound is 330 m/s . the frequency heard by the observer will be
View SolutionA source of sound is moving away from an observer at rest with a velocity of 50 m s^(-1) . If the frequency of sound is 200 Hz , find the apparent frequency observed by the observer. (Take velocity of sound = 300 m s^(-1))
View SolutionA source of sound is moving towards a high wall with a speed of 20 m/s. The frequency of the sound produced by the source is 400 Hz. If the speed of the sound is 340 m/s, then the beat frequency heard by a person standing near the wall will be
View SolutionA source of sound is approaching an observer with speed of 30 m/s and the observer is approaching the source with a speed 60 m/s. Then the fractional change in the frequency of sound in air (330 m/s) is
View SolutionA source emits sound with a frequency of 1000 Hz. It is moving at 20 m/s toward a stationary reflecting wall. If the speed of sound is 340 m/s an observer at rest directly behind the source hears a beat frequency of
View SolutionA sound source and a listener are moving away from each other and the velocity of the symbol relative to the earth 10 m//s Is if the listener's observed frequency of the sound source 1950 Hz Is then the actual frequency of the source (velocity of sound in air = 340 m//s )
View Solution500 हर्ट्ज की आवृत्ति वाला एक ध्वनि का स्रोत एक प्रेक्षक की तरफ 30 मीटर/सेकण्ड के वेग से जा रहा है। ध्वनि की चाल 330 मीटर/सेकण्ड है। प्रेक्षक द्वारा सुनी हुई आवृत्ति होगी
View Solutionएक ध्वनि स्त्रोत जिसकी आवृत्ति 680 Hz है, 1 m/s की चाल से एक दीवार से दूर, एक प्रेक्षक की ओर गतिशील है, तो प्रेक्षक को महसूस होने वाले विस्पंदों की संख्या होगी :-
(वायु में ध्वनि का वेग = 340 m/s)
View Solution
