The potential difference across terminals of cell of 20 V and r=2Ω connected to 8Ω external resistance is
16
1.6
160
5
The correct Answer is:A
To find the potential difference across the terminals of a cell with an EMF of 20 V and an internal resistance of 2 Ω connected to an external resistance of 8 Ω, we can follow these steps:
Step 1: Identify the total resistance in the circuit
The total resistance (R_total) in the circuit is the sum of the internal resistance (r) and the external resistance (R_ext):
Rtotal=r+Rext=2Ω+8Ω=10Ω
Hint: Remember that in a series circuit, resistances simply add up.
Step 2: Calculate the current flowing through the circuit
Using Ohm's Law, we can find the current (I) flowing through the circuit:
I=VRtotal=20V10Ω=2A
Hint: Ohm's Law states that V=IR. Rearranging gives you the current when you know the voltage and resistance.
Step 3: Calculate the potential drop across the internal resistance
The potential drop (V_drop) across the internal resistance can be calculated using:
Vdrop=I×r=2A×2Ω=4V
Hint: The potential drop across a resistor in a circuit can be calculated using the formula V=IR.
Step 4: Calculate the potential difference across the terminals of the cell
The potential difference (V_AB) across the terminals of the cell is given by:
VAB=VEMF−Vdrop=20V−4V=16V
Hint: The potential difference across the terminals is the EMF minus the voltage drop across the internal resistance.
Final Answer:
The potential difference across the terminals of the cell is 16 V.
The total resistance (R_total) in the circuit is the sum of the internal resistance (r) and the external resistance (R_ext):
Rtotal=r+Rext=2Ω+8Ω=10Ω
Using Ohm's Law, we can find the current (I) flowing through the circuit:
I=VRtotal=20V10Ω=2A
The potential drop (V_drop) across the internal resistance can be calculated using:
Vdrop=I×r=2A×2Ω=4V
The potential difference (V_AB) across the terminals of the cell is given by:
VAB=VEMF−Vdrop=20V−4V=16V
The potential difference across the terminals of the cell is 16 V.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- SAMPLE PAPER 7BOOK - EDUCART PUBLICATIONCHAPTER - SAMPLE PAPER 7EXERCISE - SECTION-C
6 Videos
- SAMPLE PAPER 7BOOK - EDUCART PUBLICATIONCHAPTER - SAMPLE PAPER 7EXERCISE - SECTION-C
6 Videos
- SAMPLE PAPER 6BOOK - EDUCART PUBLICATIONCHAPTER - SAMPLE PAPER 6EXERCISE - Section-C
6 Videos
- SAMPLE PAPER 9 BOOK - EDUCART PUBLICATIONCHAPTER - SAMPLE PAPER 9 EXERCISE - SECTION - C
3 Videos
Similar Questions

The null point of a potentiometer is at 56 cm with standard cell of 1.02 V. If the null point is at 70 cm, the value of another cell is:
View Solution
The null point of a potentiometer is at 56 cm with standard cell of 1.02 V. If the null point is at 70 cm, the value of another cell is:
View Solution
If two conductors carry current in opposite direction, then:
View SolutionIn the given figure charge on capacitor C2 is:
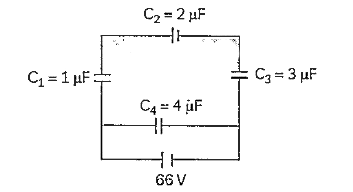
View SolutionA voltmeter having a resistance of 1800 Omega is employed to measure the potential difference across 200 Omega resistance, which is connected, to dc power supply of 50 V and internal resistance 20 Omega . What is the approximate percentage change in the potential difference across 200 Omega resistance as aresult of connecting the voltmeter across it?
View SolutionA voltmeter of resistance 995Ω is connected across a cell of emf 3V and internal resistance 5Ω. Find the potential difference across the voltmeter, that across the terminals of the cell and percentage error in the reading of voltmeter.
View SolutionWhen a resistor of 5Ω is connected across a cell, its terminal potential differnce is balanced by 140 cm of potentiometer wire and when a resistance of 8Ω is connected across the cell, the terminal potential difference is balanced by 160 cm of the potentiometer wire. Find the internal resistance of the cell.
View SolutionA voltmeter having resistance of 1800 Omega is employed to measure the potential difference across 200 Omega resistance which is connected to DC power supply of 50 V and internal resistance 20 Omega . What is the percentage change in potential difference across 200 Omega resistance as a result of connecting voltmeter across it ?
View SolutionA voltmeter having a resistance of 1800 Omega employed to measure the potential difference across a 200 Omega resistor which is connected to the terminals of a dc power supply having an emf of 50 V and an internal resistance of 20 Omega . What is the percentage decrease in the potential difference across the 200 Omega resistor as a result of connecting the voltmeter across it?
View SolutionA series combination of three resistances 1Ω,2Ω and 3Ω is connected with a cell of emf 1.5 V and of negligible internal resistance. What is the terminal potential difference across the third resistance?
View SolutionA cell of emf 2.1 V and 0.1Ω internal resistance sends 100 mA current in an external circuit. Determine the external resistance,terminal potential difference across that resistance and internal potential drop of the cell.
View SolutionThe potential difference betwee11 the terminals of a cell in an open circuit is 2.2 V. When a resistor of 5Ω is connected across the terminals of the cell, the potential difference between the terminals of the cell is found to be 1.8 V. The internal resistance of the cell is
View SolutionA cell of emf 2.0 V and internal resistance 0.1 Ω is connected with a resistance of 3.9Ω. The voltage across the cell terminals will be
View SolutionThe potential difference between the terminals or a battery is 10 V and internal resistance 1Ω drops to 8 V when connected across an external resistor . Find the resistance of the external resistor.
View SolutionA voltmeter having a resistance of 1800Ω employed to measure the potential difference across a 200Ω resistor which is connected to the terminals of a dc power supply having an emf of 50 V and an internal resistance of 20Ω. What is the percentage decrease in the potential difference across the 200Ω resistor as a result of connecting the voltmeter across it?
View SolutionThe potential difference between the terminals of a cell in open circuit is 2.2 V. With resistance of 5Ω across the terminals of a cell, the terminal potential difference is 1.8 V. The internal resistance of the cell is
View Solution

