There is a fixed positive charges Q at O, and A and B are points equidistant from O. A positive charge +q is taken slowly by an external agent from A to B along the line AC and then along the line CB.

The total work done on the charge is zero.
The work done by the electrostatic force from A to C is negative.
The work done by the electrostatic force from C to B is positive.
The work done by electrostatic force in taking the charge from A to B is dependent on the actual path.
The correct Answer is:A, B, C
a.,b.,c.
(a) is correc because potential of A and B is same. (b) is correct because charge is going from low potential to high potential. Electric potential energy increases and electrostatic forces do negative work. Similarly (c) is also correct.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- MISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 3Book:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:MISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 3Exercise:Assertion and Reason Type
Explore 8 Videos
- MISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 3Book:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:MISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 3Exercise:Comprehension Type
Explore 92 Videos
- MISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 3Book:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:MISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 3Exercise:True and False
Explore 3 Videos
- MAGNETIC FIELD AND MAGNETIC FORCESBook:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:MAGNETIC FIELD AND MAGNETIC FORCESExercise:Multiple Correct Answer type
Explore 2 Videos
- MISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 5Book:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:MISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 5Exercise:Integer
Explore 11 Videos
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
The work done in bringing a unit positive charge from infinite distance to a point at distance x from a positive charge Q is W. Then the potential ϕ at that point is
AWQxBWCWxDWQWhen a positive q charge is taken from lower potential to a higher potential point, then its potential energy will
Aremin the sameBincreaseCdecreaseDbecome zeroThe work done to move a unit charge along an equipotential from P to Q
Amust be defined as −Q∫P→E.→dlBis zeroCcan have a non-zero valueDboth (a) and (b)are correct
Two equal positive charges Q are fixed at points (a, 0) and (−a,0) on the x-axis. An opposite charge -q at rest is relased from point (0, a) on the y-axis. The charge -q will
View SolutionTwo identical positive charges are fixed on the y-axis, at equal distances from the origin O. A particle with a negative charges starts on the x-axis at a large distance from O. moves along the x-axis passes through O, and moves far away from O on the other side. Its acceleration a is taken as positive along its direction of motion. Plot acceleration a of the particle against its x-coordinate.
View SolutionTwo fixed, equal, positive charges, each of magnitude 5×10−5 coul are located at points A and B separated by a distance of 6m. An equal and opposite charge moves towards them along the line COD, the perpendicular bisector of the line AB.
The moving charge, when it reaches the point C at a distance of 4m from O, has a kinetic energy of 4 joules. Calculate the distance of the farthest point D which the negative charge will reach before returning towards C.
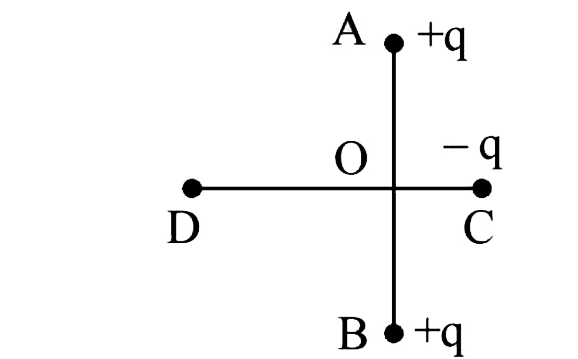
View SolutionFour similar (+q) are placed at origin O, B, C and D as shown. The angles are as shown. Charges at B, C and D are equidistant from O at a distance of a. The forces of repulsion experienced by charge at O due to charges at B and D along CO are equal, given by q2√38πε0a2. Find the relation between θ1,θ2 and θ3:

View SolutionTwo charges each having magnitude q and same polarity are fixed some distance apart.A point charge Q is kept on exactly middle of the line joining the two charges.Then equilibrium of Q is
View Solution