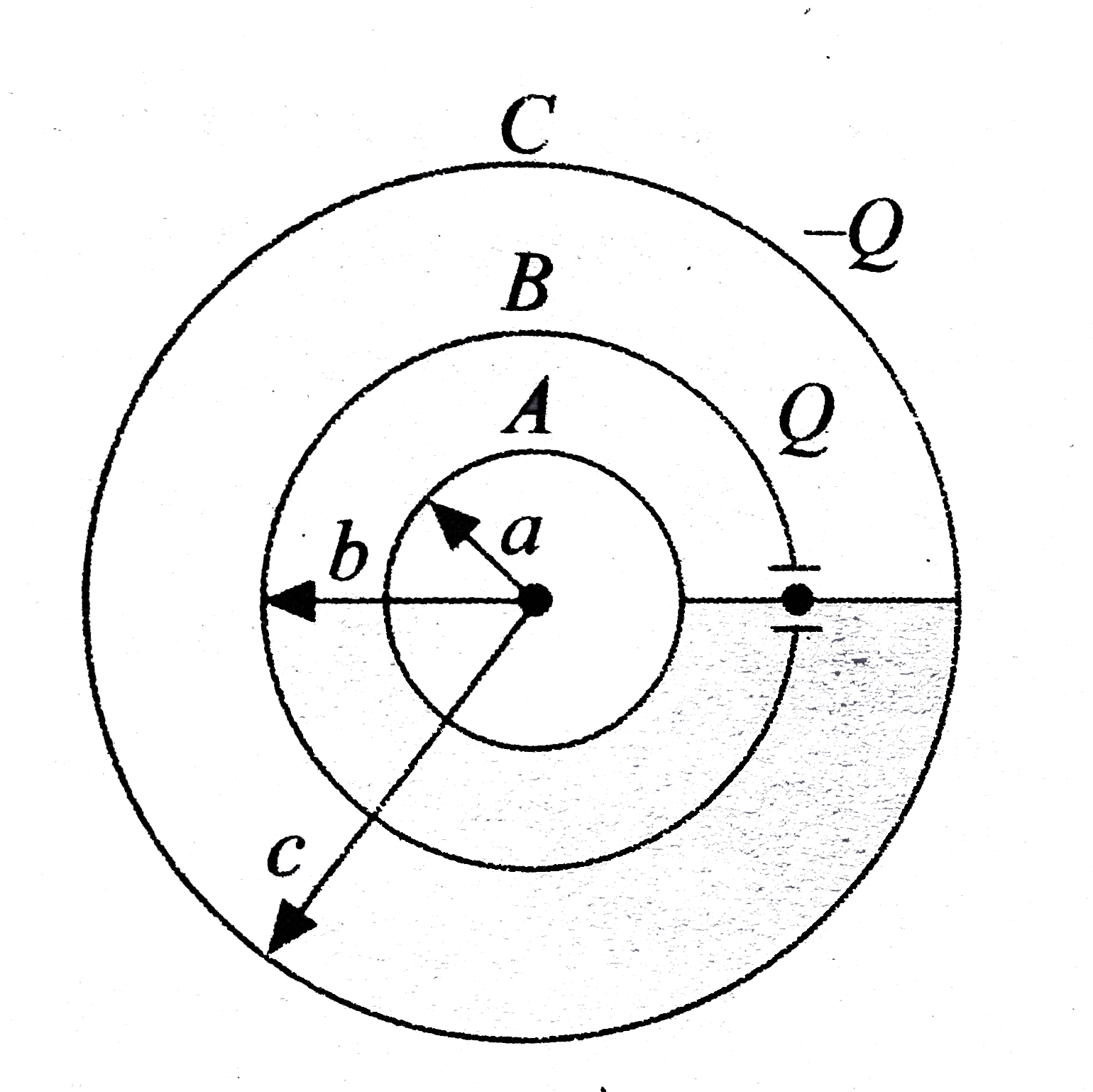
Three conducting spherical shells have radii (a, b, and c) such that a<b<c (Fig. 3.113). Initially, the inner shell is uncharged, the middle shell has a positive charge Q, and the outer shell has a negative charge −Q.
 .
.
a. Find the electric potential of the three shells.
b. If the inner and outer shells are now connected by a wire that is insulated as it passes through the middle shell, what is the electric potential of each of the three shells ? Also, what is the final charge on each shell ?
The correct Answer is:a. VA−VB=Q4πε0[c−bbc],VC=0
b. Charge on A−Qab[c−bc−a]
Charge on B,Qb=Q
Charge on C,Qcb[c−bc−a].
a. Potential of shell A
VA=Vdue to charge on A+Vdue to charge on B+Vdue to charge on C
=0+Q4πε0b−Q4πε0c
Potential of shell B
VB=Vdue to charge on A+Vdue to charge on B+Vdue to charge on C
=0+Q4πε0b−Q4πε0c
Potential of shell C
VC=Vdue to charge on A+Vdue to charge on B+Vdue to charge on C
=0+Q4πε0c−Q4πε0c=0
B After connecting inner and outer shells, we get
 .
.
VA=VC
or qa−qb+Q+qb−Q+qc=q−q+Q+q−(Q+q)c
or q=Qab(b−c)(c−a)
Final potential of A and C is zero.
VB=k[qa−qb+Q+qb−(Q+q)c]=k(Q+q)[c−bbc]
=k[Q+Qa(b−c)b(c−a)][c−bbc]=kQ[(b−a)(c−b)b2(c−a)].
Topper's Solved these Questions
- ELECTRIC POTENTIALBook:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:ELECTRIC POTENTIALExercise:Single Correct
Explore 56 Videos
- ELECTRIC POTENTIALBook:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:ELECTRIC POTENTIALExercise:Multiple Correct
Explore 10 Videos
- ELECTRIC POTENTIALBook:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:ELECTRIC POTENTIALExercise:Exercise 3.3
Explore 9 Videos
- ELECTRIC FLUX AND GAUSS LAWBook:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:ELECTRIC FLUX AND GAUSS LAWExercise:MCQ s
Explore 38 Videos
- ELECTRICAL MEASURING INSTRUMENTSBook:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:ELECTRICAL MEASURING INSTRUMENTSExercise:M.C.Q
Explore 2 Videos
Similar Questions
A large insulated sphere of radius r charged with Q units of electricity is placed in contact with a small insulated uncharged sphere of radius r' and is then separated. The charge on the smaller sphere will now be.
View SolutionA wire having a uniform linear charge density λ is bent in the form of a ring of radius R. Point A as shown in (Fig. 3.145) is in the plane of the ring but not at the center. Two elements of the ring of lengths a1 and a2 subtend very small same angle at point A. they are at distances r1 and r2 from point A, respectively (r2>r1).
 .
.
View SolutionAn electric dipole of length 4 cm, when placed with its axis making an angle of 60∘ with a uniform electric field, experiences a torque of 4√3Nm. Calculate the
a. magnitude of the electric field, and
b. potential energy of the dipole, if the dipole has charges of ±8nC.
View SolutionElectric flux through a surface are 10m2 lying in the xy plane is (if→E=ˆi+√2ˆj+√3ˆkN/C)
View SolutionThe measurement of an unknown resistance R is to be carried out using Wheatstone bridge (see Fig. 2(EP).3). Two students perform an experiment in two way. The first student takes R2=10Ω and R1=5Ω. The other student takes R2=1000Ω and R1=500Ω. In the standard arm, both take R3=5Ω. Both find R=R2R1R3=10Ω within errors.
View SolutionA small conducting spherical shell with inner radius a and outer radius b is concentric with a larger conducting spherical shell with inner radius c and outer radius d ( as shown in Fig . 2.121). The inner shell has a total charge + 2 q , and the outer shell has a total charge + 4 q . Calculate the electric field in terms of q and the distance r from the common center of the two shells for a lt r lt b
View SolutionA small conducting spherical shell with inner radius a and outer radius b is concentric with a larger conducting spherical shell with inner radius c and outer radius d ( as shown in Fig . 2.121). The inner shell has a total charge +2q, and the outer shell has a total charge +4q. Calculate the electric field in terms of q and the distance r from the common center of the two shells for

b<r<c
View SolutionA small conducting spherical shell with inner radius a and outer radius b is concentric with a larger conducting spherical shell with inner radius c and outer radius d ( as shown in Fig . 2.121). The inner shell has a total charge + 2 q , and the outer shell has a total charge + 4 q . Calculate the electric field in terms of q and the distance r from the common center of the two shells for c lt r ltd
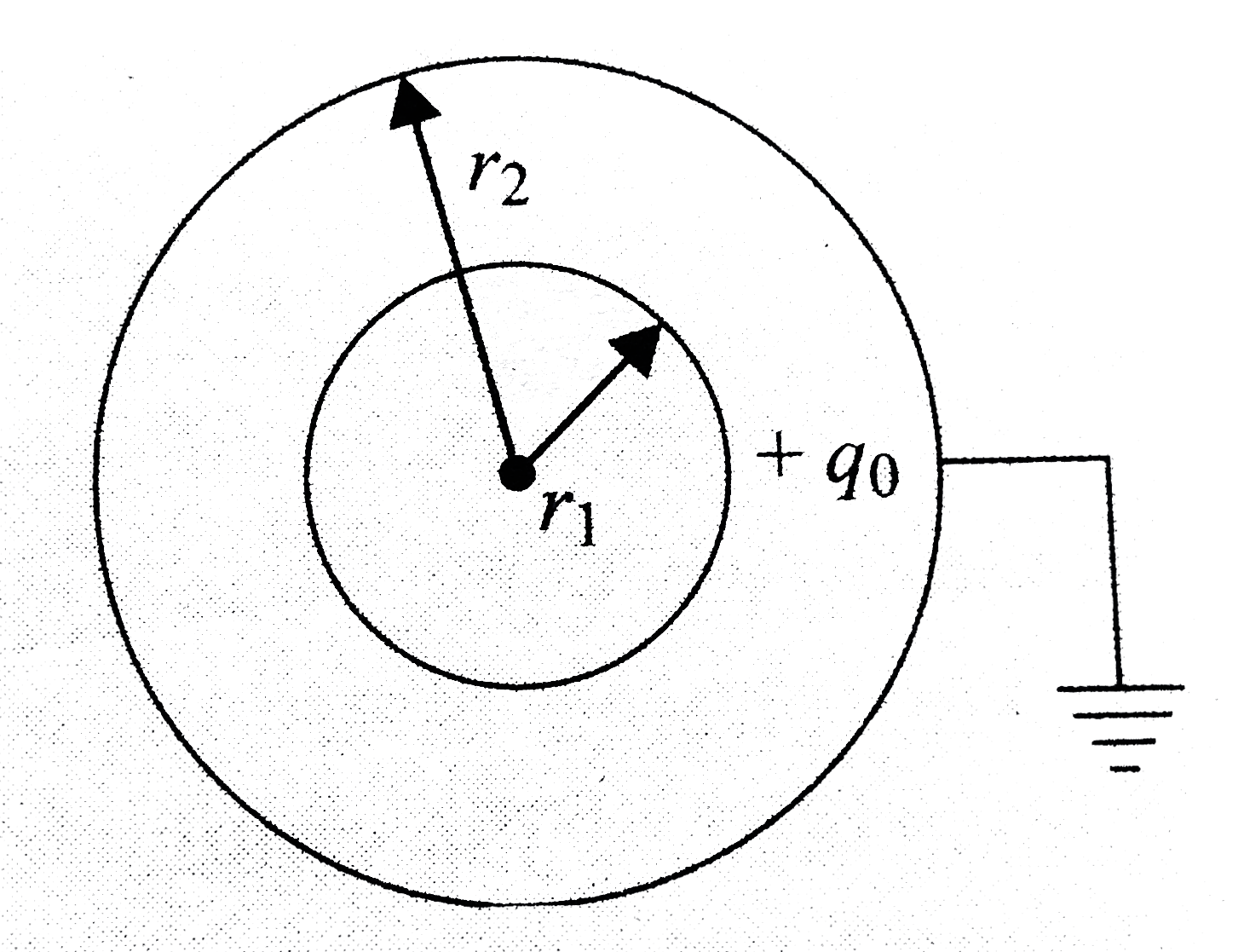
View SolutionIn (Fig. 3.73), if the inner shell has charge +q0 and the outer shell is earthed, then
 .
.
i. determine the charge on the outer shell, and
ii. find the potential of the inner shell.
View SolutionThree conducting spherical shells have radii (a, b, and c) such that a<b<c (Fig. 3.113). Initially, the inner shell is uncharged, the middle shell has a positive charge Q, and the outer shell has a negative charge −Q.
 .
.
a. Find the electric potential of the three shells.
b. If the inner and outer shells are now connected by a wire that is insulated as it passes through the middle shell, what is the electric potential of each of the three shells ? Also, what is the final charge on each shell ?
View SolutionFigure shows three concentric conducting spherical shells with inner and outer shells earthed and the middle shell is given a charge q. Find the charge distribution of sphere

View SolutionThree concentric conducting spherical shells carry charges as : +4Q on the inner shell, −2Q on the middle shell and −5Q on the outer shell. The charge on the inner surface of the outer shell is
View SolutionA point charge +q is placed at the centre of a conducting spherical shell of inner radius a and outer radius b. Find the charge appearing on the inner and outer surface of the shell.
View SolutionThere are two concentric spherical shells with inner shell having positive charge q and outer shell having a charge -q. Now outer shell is supplied a charge -2g and inner shell is earthed, Calculate the ratio of initial and final capacities of the system. (If a = 3R, b= 5 R)
View SolutionA small conducting spherical shell with inner radius a and outer radius b is concentric with a larger conducting spherical shell with inner radius c and outer radius d. The inner shell has total charge +2q, and the outer shell has charge +4q. (K=(1)/(4piepsilon_(0)))

Find the electric field in terms of q and the distance r from the common centre of the two shells for (i) r<a (ii) a<r<b
View SolutionA small conducting spherical shell with inner radius a and outer radius b is concentric with a larger conducting spherical shell with inner radius c and outer radius d. The inner shell has total charge +2q, and the outer shell has charge +4q. (K=(1)/(4piepsilon_(0)))

Find the electric field in terms of q and the distance r from the common centre of the two shells for (i) b<r<c (ii) c<r<d
View Solution
