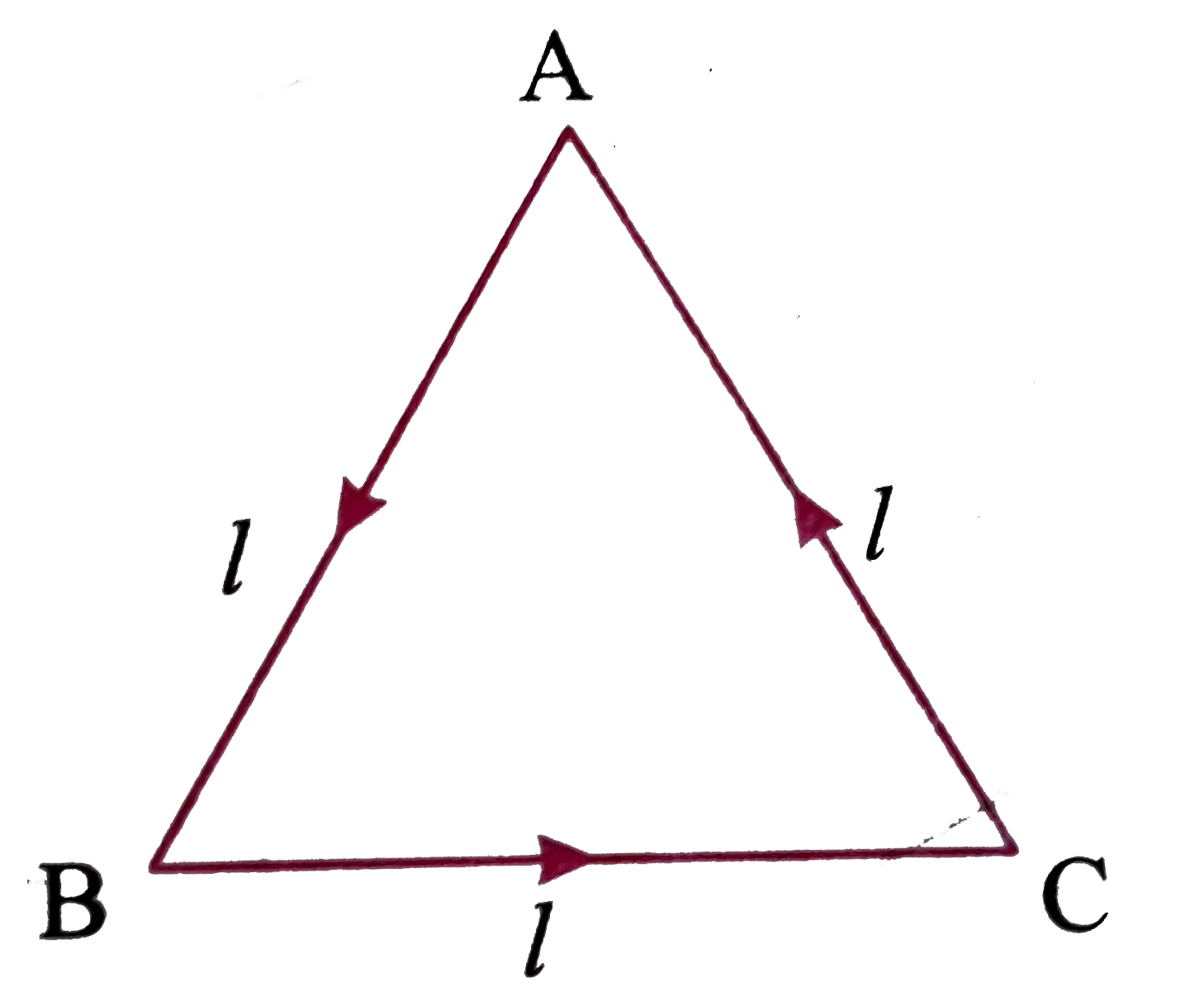
Three particles A, B and C are situated at the vertices of an equilateral triangle ABC of side d at time t=0. Each of the particles moves with constant speed v. A always has its velocity along AB, B along BC and C along CA. At what time will the particles meet each other?
Let at any instant the velocity od B makes an angle ∝ with that of x - axis and the time to collide is T.
Vapp=V−ucos∝
l=∫T0Vappdt=∫T0(V−ucos∝)dt …(i)
Now equating the displacement of AandB along x direction, we get
uT=∫Vcos∝dt ....(ii)
Now from (i) and (ii), we get
l=VT−∫T0ucos∝dt
=VT−uV∫T0Vcos∝dt=VT−vV.uT⇒T=T=lVv2−u2
Now distance travelled by AandB
=u×lVv2−u2andv×lVv2−u2
=uVlV2−u2andV2lV2−u2.
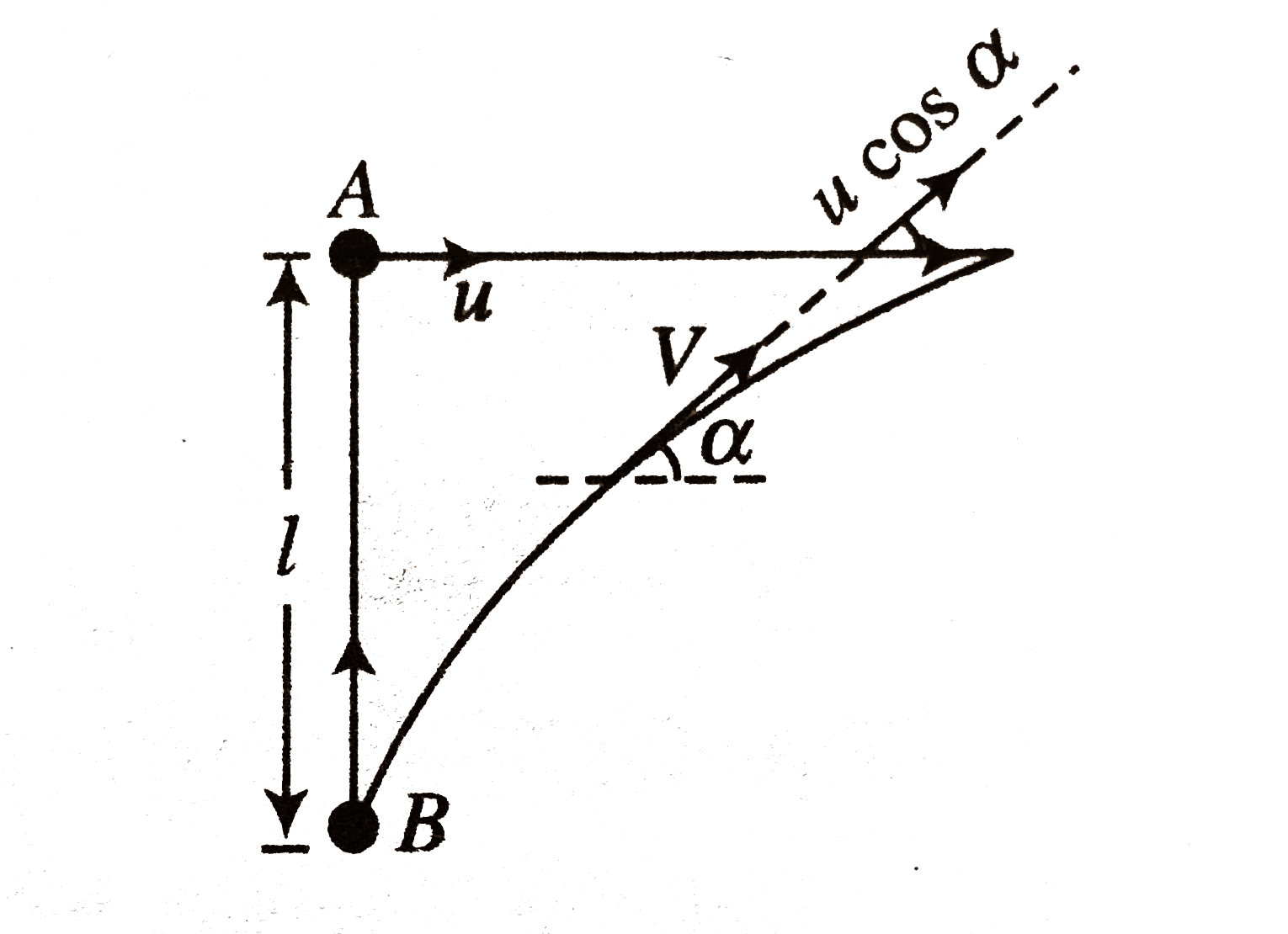 .
.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- KINEMATICS-2Book:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:KINEMATICS-2Exercise:Exercise 5.1
Explore 15 Videos
- KINEMATICS-2Book:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:KINEMATICS-2Exercise:Exercise 5.2
Explore 24 Videos
- KINEMATICS-2Book:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:KINEMATICS-2Exercise:Exercise Integer
Explore 9 Videos
- KINEMATICS-1Book:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:KINEMATICS-1Exercise:Integer
Explore 9 Videos
- KINETIC THEORY OF GASESBook:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:KINETIC THEORY OF GASESExercise:Compression
Explore 2 Videos
Similar Questions
The equation of projectile is y=16x−5x24. Find the horizontal range.
View SolutionA body of mass 2kg has an initial velocity of 3ms−1 along OE and it is subjected to a force of 4N in OF direction perpendicular to OE. Find the distance of the body from O after 4s.
 .
.
View SolutionA particle is projected with velocity u at angle θ with horizontal. Find the time when velocity vector is perpendicular to initial velocity vector.
View SolutionA man in a lift ascending with an upward acceleration a throws a ball vertically upwards with a velocity v with respect to himself and catches it after t1 seconds. After wards when the lift is descending with the same acceleration a acting downwards the man again throws the ball vertically upwards with the same velocity with respect to him and catches it after t2 seconds?
View SolutionOne mole of an ideal monatomic gas undergoes a linear process from A to B , in which is pressure P and its volume V change as shown in figure .
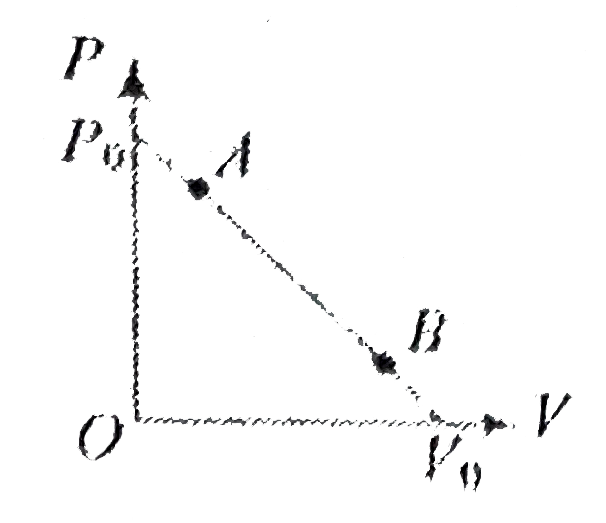
The absolute temperature T versus volume V for the given process is
View SolutionSix particles situated at the corners of a regular hexagon of side a move at a constant speed v. Each particle maintains a direction towards the particle at the next corner. Calculate the time the particles will take to meet each other.
View SolutionThree particles A, B and C are situated at the vertices of an equilateral triangle ABC of side d at time t=0. Each of the particles moves with constant speed v. A always has its velocity along AB, B along BC and C along CA. At what time will the particles meet each other?
View SolutionThree identical particles are located at the vertices of an equilateral triangle. Each particle moves along a meridian with equal speed towards the centroid and collides inelastically.
View SolutionThree particles A,B,andC are situated at the vertices of an equilateral triangle of side r at t=0. The particle A heads towards B, B towards C, C towards A with constant speeds v. Find the time of their meeting.
View SolutionFour particles A, B, C and D are situated at the cornerst of a square ABCD of side a at t-0 . Each of particles moves with constant speed (v). A always has its velocity along AB, B along BC, C along CB~ and D along DA . At what time will these particles meet each other ?
View SolutionThree particles A,B and C and situated at the vertices of an equilateral triangle ABC of side of length l at time t=0,Each of the particles move with constant speed u. A always has its velocity along AB,B along BC and C along CA.
View SolutionThree particles each of mass m are located at the vertices of an equilateral triangle ABC. They start moving with equal speeds each along the medians of the triangle and collide at its centroid G. If after collision, A comes to rest and B retraces its path along GB, then C (A) also comes
View SolutionTwo particles A and B separated by 10 m at time t=0 are moving uniformly. A is moving along line AB at a constant velocity of 4m/s and B is moving perpendicular to the velocity of A at a constant velocity of 5m/s. After what time the two particles will be nearest to each other?

View SolutionThree boys A,B and C are situated at the vertices of an equilateral triangle of side d at t=0. Each of the boys moves with constant speed v. A always moves towards C and C towards A, At what time and where they meet each other?
View Solutionतीन कण A , B और C किसी समय t = 0 पर d भुजा वाले समबाहु ABE के शीर्ष बिंदुओ पर है । सभी कण हर समय v चल से चलते है ।A के वेग की दिशा सदा BC की और तथा C के वेग की दिशा सदा CA की और रहती है । किस समय सभी कण एक-दूसरे से मिलेंगे ?
View SolutionThree particles A, B and C are situated at the vertices of an equilateral triangle ABC of side d at time t=0. Each of the particles moves with constant speed v. A always has its velocity along AB, B along BC and C along CA. At what time will the particles meet each other?
View Solution
