Three rods of equal length of same material are joined to form an equivalent triangle ABC as shown figure. Area of cross-section of rod AB is S of rod BC is 2S and that of AC is S , then
_E01_150_Q01.png)
Column-IColumn-II(A)Temperature of junctionB(p)Greater than50∘C(B)Heat current inAB(q)Less than50∘C(C)Heat current in BC(r)Is equal to current in BC(s)Is 23times heat current in AC(t)None
The correct Answer is:A, B, C
Thermal resistance α1Area
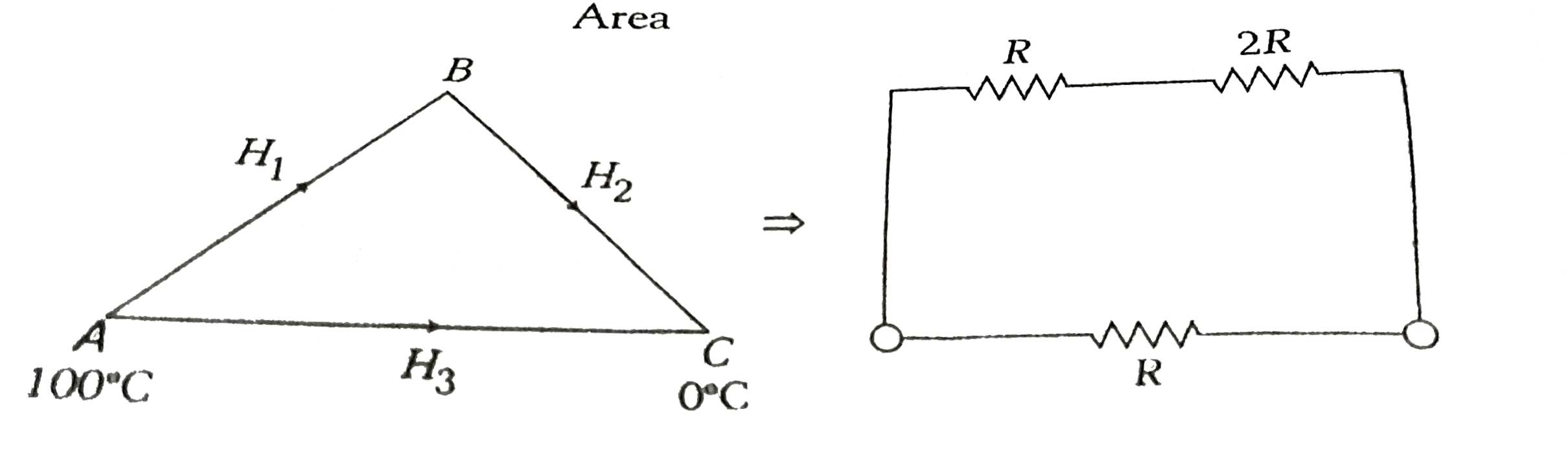
So let, RBC = R
Then RAB+RAC = 2R
H1=H2
100−θBR=θB−02R
∴ θB=66.7∘C
RABC-3R and RAC=R
H1=H2=H33
Topper's Solved these Questions
- CALORIMETRY AND HEAT TRANSFERBOOK - DC PANDEYCHAPTER - CALORIMETRY AND HEAT TRANSFEREXERCISE - Medical entrance s gallery
38 Videos
- CALORIMETRY AND HEAT TRANSFERBOOK - DC PANDEYCHAPTER - CALORIMETRY AND HEAT TRANSFEREXERCISE - Assertion and reason
17 Videos
- CALORIMETRY & HEAT TRANSFERBOOK - DC PANDEYCHAPTER - CALORIMETRY & HEAT TRANSFEREXERCISE - Level 2 Subjective
14 Videos
- CENTRE OF MASSBOOK - DC PANDEYCHAPTER - CENTRE OF MASSEXERCISE - Medical entrances gallery
27 Videos
Similar Questions
A black body is at a temperature of 5760K. The energy of radiation emitted by the body at wavelength 250nm is U1 at wavelength 500nm is U2 and that at 1000nm is U3. Wien's consant, b=2.88×106nmK. Which of the following is correct?
View SolutionAssertion : A body that is a good radiator is also a good absorber of radiation at a given wavelength.
Reason : According to Kirchhoff's law the absorptivity of a body is equal to its emissivity at a given wavelength
View SolutionAs a physicist, you put heat into a 500 g solid sample at the rate of 10.0kJ/min, while recording its temperature as a function of time. You plot your data and obtain the graph shown in figure.
 .
.
(a) What is the latent heat of fusion for this solid?
(b) What is the specific heat of solid state of the material?
View SolutionA rod of weight w is supported by two parallel knife edges A and B and is in equilibrium in a horizontal position. The knives are at a distance d from each other. The centre of mass of the rod is at distance x from A. The normal reaction on A is.. And on B is......
View SolutionThree rods of lengths 20cm eac h and area of cross section 1cm2 are joined to from a triangle ABC. The conductivites of the rods are kAB=50Js−1m−1(@)C^(-1),k_(BC)=200Js^(-1)m^(-1)(∘)C−1 , and kAC=400Js−1m−1(@)C^(-1).ThejunctionA,BandCarema∫a∈edat40^(@)C,80^(@)Cand80^(@)C respectivelt. Find the rate of heat flowing through the rods AB, AC and BC .
View SolutionThree rods AB,BC and BD made of the same materical and having the same area of cross section have been joined as shown is the The ends A,C and D are held at temperatures 20∘C Cand 80∘C respectively If each rod is of same length then find the temperature at the junction B of the three rods
 .
.
View Solution(a) Three rod of lengths 20cm each and area of cross-section 1cm2 are joined to form a triangle ABC. The conductivities of the rods are KAB=50J/m−s−.∘C,KBC=200J/m−s−.∘C and KAC=400J/m−s−.∘C. The junctions A,B and C are maintained at 40∘C, 80∘C and 80∘C respectively. Find the rate of heat flowing through the rods AB,AC and BC.
(b) A semicircular rod is joineted as its end to a straight rod of the same material and the same cross-sectional area. The straight rod forms a diameter of the other rod. The junctions are maintained at different temperatures. Find the ratio of the heat transferred through a cross-section of the simicircular rod to the heat transferred through a cross-section of the straight rod in a given time.
View SolutionThree rods A, B and C of the same length and cross- sectional area are joined in series as shown. The temperature at the junction of A and B , in equilibriu, is
View SolutionFive rods of same material and same cross-section are joined as shown. Lengths of rods ab, ad and bc are l, 2l and 3l respectively. Ends a and c are maintained at temperatures 200∘C and 0∘C respectivelly.
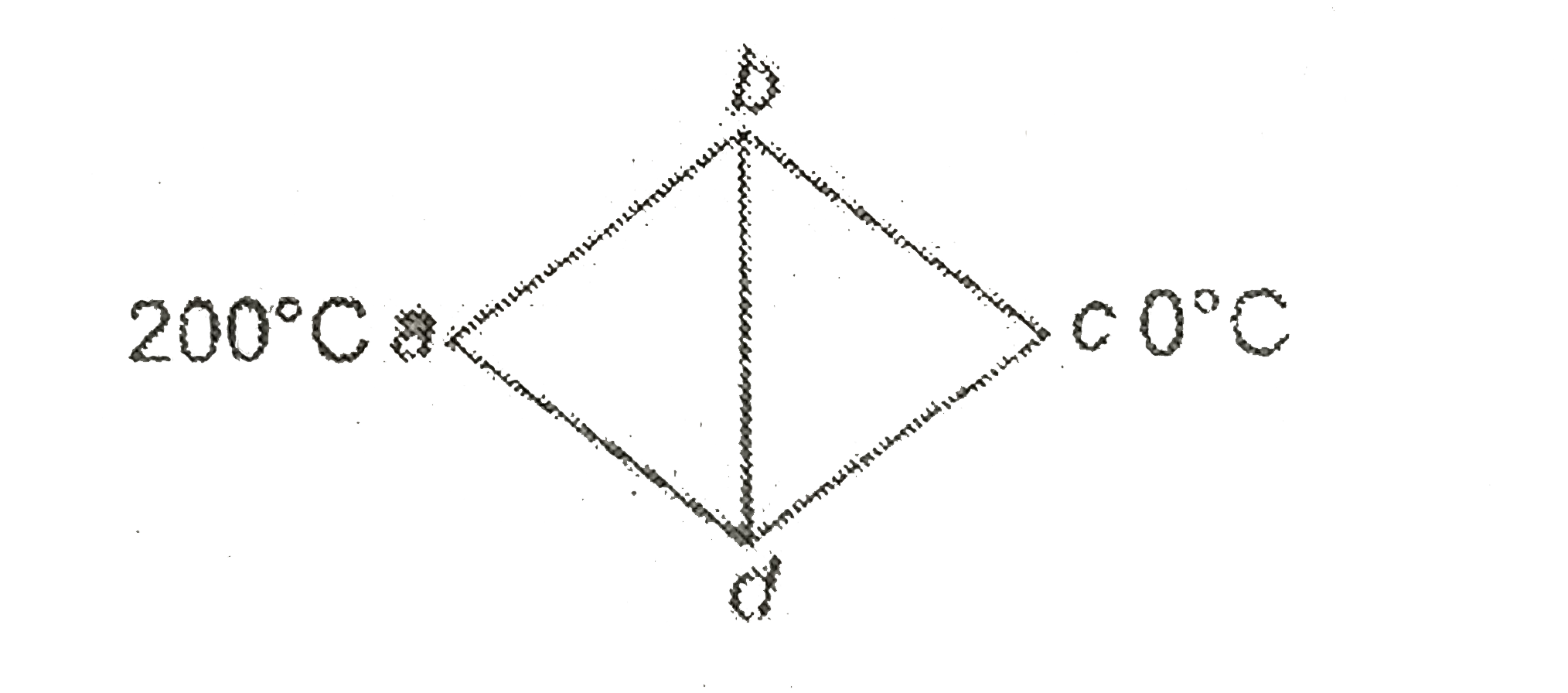
For what length x of rod dc there will be no heat flow through rod bd ?
View SolutionThree rods of equal length of same material are joined to form an equilateral triangle ABC as shown in figure. Area of cross-section of rod AB is S, of rod BC is 2S and that of AC is S. Then match the following.
View SolutionThree conducting rods of same material and cross-section are shown in figure. Temperatures of A,D and C are maintained at 20^(@)C, 90^(@)C and 0^(@)C . The ratio of lengths BD and BC if there is no heat flow in AB is
View SolutionThree rods of equal length of same material are joined to form an equivalent triangle ABC as shown figure. Area of cross-section of rod AB is S of rod BC is 2S and that of AC is S , then {:(,"Column-I",,"Column-II"),((A),"Temperature of junction" B,(p),"Greater than" 50^(@)C),((B),"Heat current in" AB,(q),"Less than" 50^(@)C),((C),"Heat current in BC",(r),"Is equal to current in BC"),(,,(s),"Is " 2/3 "times heat current in AC"),(,,(t),"None"):}
View Solutionयदि a,b,c में से कोई शून्य नहीं है तो दिखाएँ कि
Δ=∣∣ ∣ ∣∣−bcb2+bcc2+bca2+ac−acc2+aca2+abb2+ab−ab∣∣ ∣ ∣∣=(bc+ca+ab)3
View SolutionThree rods of lengths 20cm each and area of cross section 1cm2 are joined to from a triangle ABC. The conductivities of the rods are kAB=50Js−1m−1C−1 , kBC=200Js−1m−1C−1 , and kAC=400Js−1m−1C−1 . The junction A,B and C are maintained at 40∘C , 80∘C and 80∘C respectively. Find the rate of heat flowing through the rods AB, AC and BC .
View SolutionThree rods of lengths 20cm each and area of cross-section 1cm^(2) are joined to form a triangle ABC. The conductivities of the rods are K_(AB)=50J//m-s-^(0)C,K_(BC)=200J//m-s-""^(0)C and K_(AC)=400J//m-s-""^(0)C . The junctions A, B and C are maintained at 40^(@)C,80^(@)C and 80oC respectively. The rate of heat flowing through the rod AB is __________ W
View SolutionThree rods A, B and C form an equilateral triangle at 0°C. Rods AB and BC have same coefficient of expansion alpha_(1) and rod AC has alpha_2 . If change in angle between AB and BC is d theta then temperature through which system is heated.
View Solution

