Two blocks A and H. each of mass m, are connected by a massless spring of natural length I. and spring constant K. The blocks are initially resting in a smooth horizontal floor with the spring at its natural length, as shown in Fig. A third identical block C, also of mass m, moves on the floor with a speed v along the line joining A and B. and collides elastically with A. Then
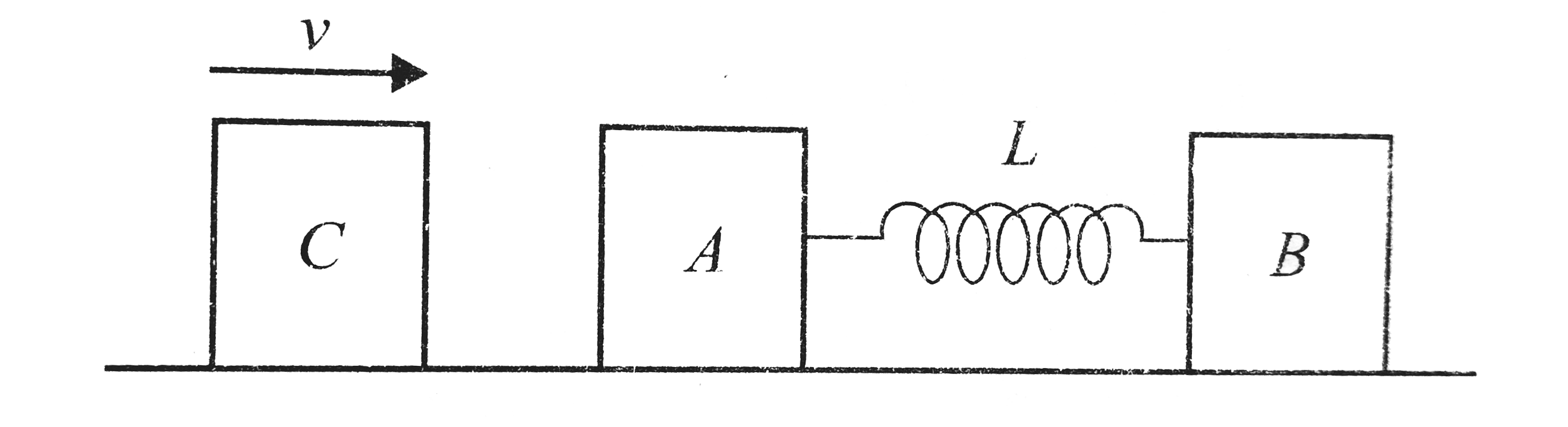
the kinetic energy of the A−B system, at maximum compression of the spring, is zero.
the kinetic energy of the A−B system, at maximum compression of the spring, is
the maximum compression of the spring is √(mK)
the maximum compression of the spring is v√(m2K)
The correct Answer is:B, D
In situation i mass C is moving towards right with velocity v,A and B are at rest. In situation ii, which is just after the collision of C with A,C stops and A acquires a velocity v. when A starts moving towards right, the spring suffers a compression due ot which B also starts moving towards right. The compression of the spring continues till there is a relative velocity between A and B. Once this relative velocity becomes zero, both A and B move with the same velocity v' and the spring is in a state of maximum compression.

Applying momentum conservation in situations ii and iii
mv=mv'+mv'⇒v'=v2
Therefore, KE of the system in situation iii is
12mv'2+12mv'2=mv'2=mv24
Applying energy conservation we get
12mv2=12mv'2+12Kx2
solve to get x=v√m2K
Topper's Solved these Questions
- CENTRE OF MASSBOOK - CENGAGE PHYSICSCHAPTER - CENTRE OF MASSEXERCISE - AR_TYPE
1 Video
- CENTRE OF MASSBOOK - CENGAGE PHYSICSCHAPTER - CENTRE OF MASSEXERCISE - LC_TYPE
3 Videos
- CENTRE OF MASSBOOK - CENGAGE PHYSICSCHAPTER - CENTRE OF MASSEXERCISE - SCQ_TYPE
12 Videos
- CALORIMETRYBOOK - CENGAGE PHYSICSCHAPTER - CALORIMETRYEXERCISE - Solved Example
13 Videos
- DIMENSIONS & MEASUREMENTBOOK - CENGAGE PHYSICSCHAPTER - DIMENSIONS & MEASUREMENTEXERCISE - Integer
2 Videos
Similar Questions
Two blocks A and B of masses m and 2m are connected by a massless spring of natural length L and spring constant k. The blocks are intially resting on a smooth horizontal floor with the spring at its natural length , as shown . A third identical block C of mass m moves on the floor with a speed v0 along the line joining A and B and collides elastically with A. FInd (a) the velocity of c.m. of system (blockA+B+spring) and (b) the minimum compression of spring.

View SolutionTwo blocks A and B each of mass m are connected by a light spring of natural length L and spring constant k. The blocks are initially resting on a smooth horizontal floor with the spring at its natural length, as shown. A third identical block C, also of mass m, moves on the floor with a speed v along the line joining A to B and collides with A. Collision is elastic and head on. Then -

View Solution
Knowledge Check
Two blocks A and B, each of mass m, are connected by a masslesss spring of natural length L and spring constant K. The blocks are initially resting on a smooth horizontal floor with the spring at its natural length, as shown in fig. A third identical block C, also of mass m, moves on the floor with a speed v along the line joining A and B, and collides elastically with A. Then
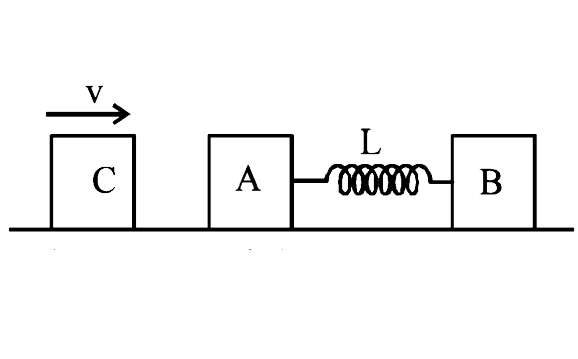 Athe kinetic energy of the A-B system, at maximum compression of the spring, is zero.Bthe kinetic energy of the A-B system, at maximum compression of the spring, is mv2/4.Cthe maximum compression of the spring is v√(m/K)Dthe maximum compression of the spring is v√(m/2K)
Athe kinetic energy of the A-B system, at maximum compression of the spring, is zero.Bthe kinetic energy of the A-B system, at maximum compression of the spring, is mv2/4.Cthe maximum compression of the spring is v√(m/K)Dthe maximum compression of the spring is v√(m/2K)Two identical blocks A and B , each of mass m resting on smooth floor are connected by a light spring of natural length L and spring constant k, with the spring at its natural length. A third identical block C (mass m) moving with a speed v along the line joining A and B collides with A. The maximum compression in the spring is
Av√m2kBm√m2kC√mvkDmv2kTwo identical blocks A and B , each of mass m resting on smooth floor are connected by a light spring of natural length L and spring constant k, with the spring at its natural length. A third identical block C (mass m) moving with a speed v along the line joining A and B collides with A. The maximum compression in the spring is
Av√m2kBv√v2kC√mvkDmv2k
Two blocks A and B each of mass m are connected by a massless spring of natural length L and spring constant k. The blocks are initially resting on a smooth horizontal floor with the spring at its natural length. A third identical block C also of mass m moves on the floor with a speed v along the line joining A and B and collides with A. Then
The kinetic energy of the A-B system at maximum compression of the spring is mv2/4
The maximum compression of the spring v√m/3k<br>Thek∈etice≠rgyoftheA−Bsystematmaxiμmcompression<br>Themaxiμmcoppressionofthespr∈gisvsqrt(m//k)
View SolutionTwo identical blocks A and B each of mass m resting on the smooth horizontal floor are connected by a light spring of natural length L and spring constant K. A third block Cof mass m moving with a speed v along the line joining A and B collides with A. The maximum compression in the spring is
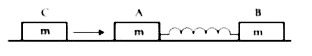
View SolutionA block of mass m is connected to another block of mass M by a massless spring of spring constant k. the blocks are kept of a smooth horizontal plane and are at rest. The spring is unstretched when a constant force F starts acting on the block of mass M of pull it. Find the maximum extension of the spring
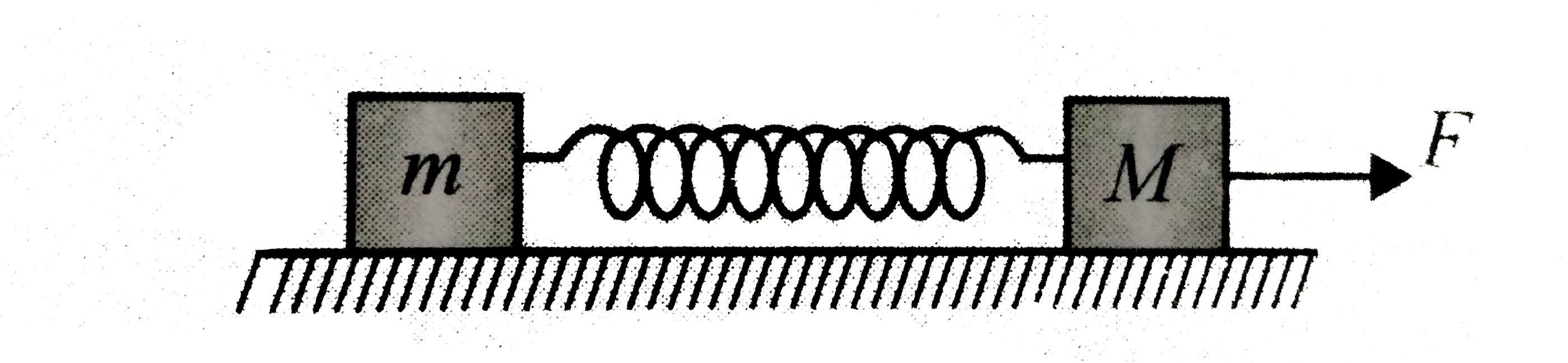
View SolutionTwo blocks A and B, each of mass m, are connected by a spring of force constant K. Initially, the spring is in its natural length. A horizontal constant force F starts acting on block A at time t=0 and at time t , the extension in the spring is seen to be l. What is the displacement of the block A in time t ?
View SolutionTwo blocks of masses m1 and m2 are connected by a massless spring and placed on smooth surface. The spring initially stretched and released. Then :
View Solution

