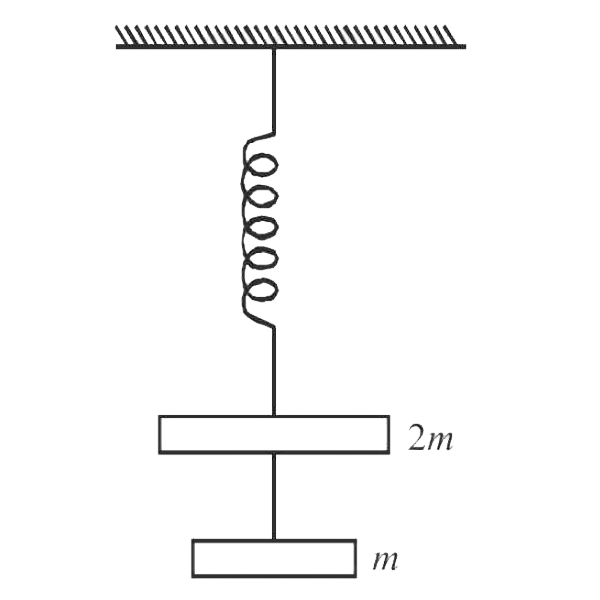
Two blocks are connected by a spring. The combination is suspended, at rest, from a string attached to the ceiling, as shown in fig. The string breaks suddenly.
Immediately after the string breaks, what is the initial downward acceleration of the upper block of mass 2m?

When blocks A and B are I equilibrium position
When string is cut, tension T becomes zero. But spring does not change its shape just after cutting. So spring force acts on mass B, again draw FBD of blocks A and B as shown in fig.
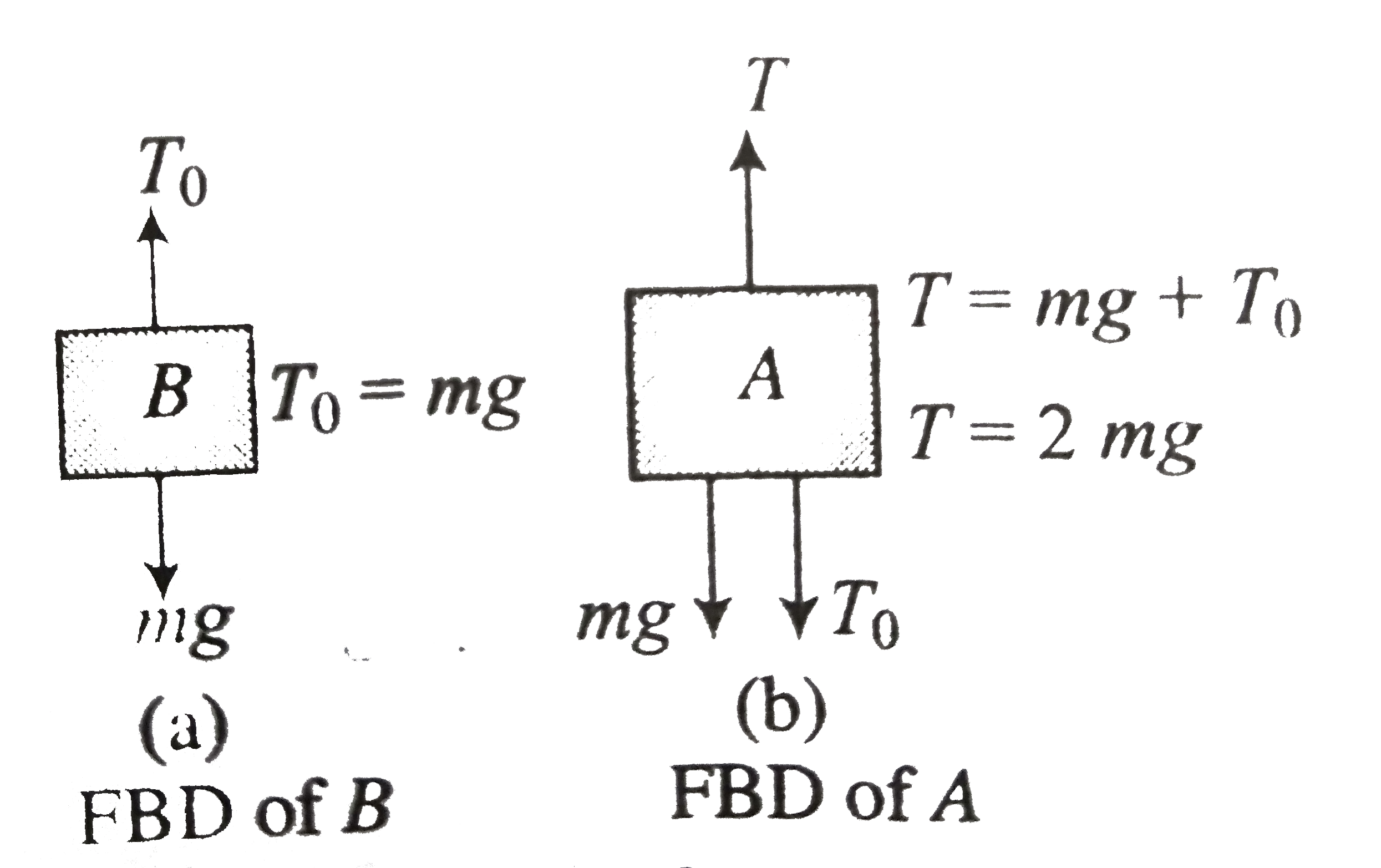
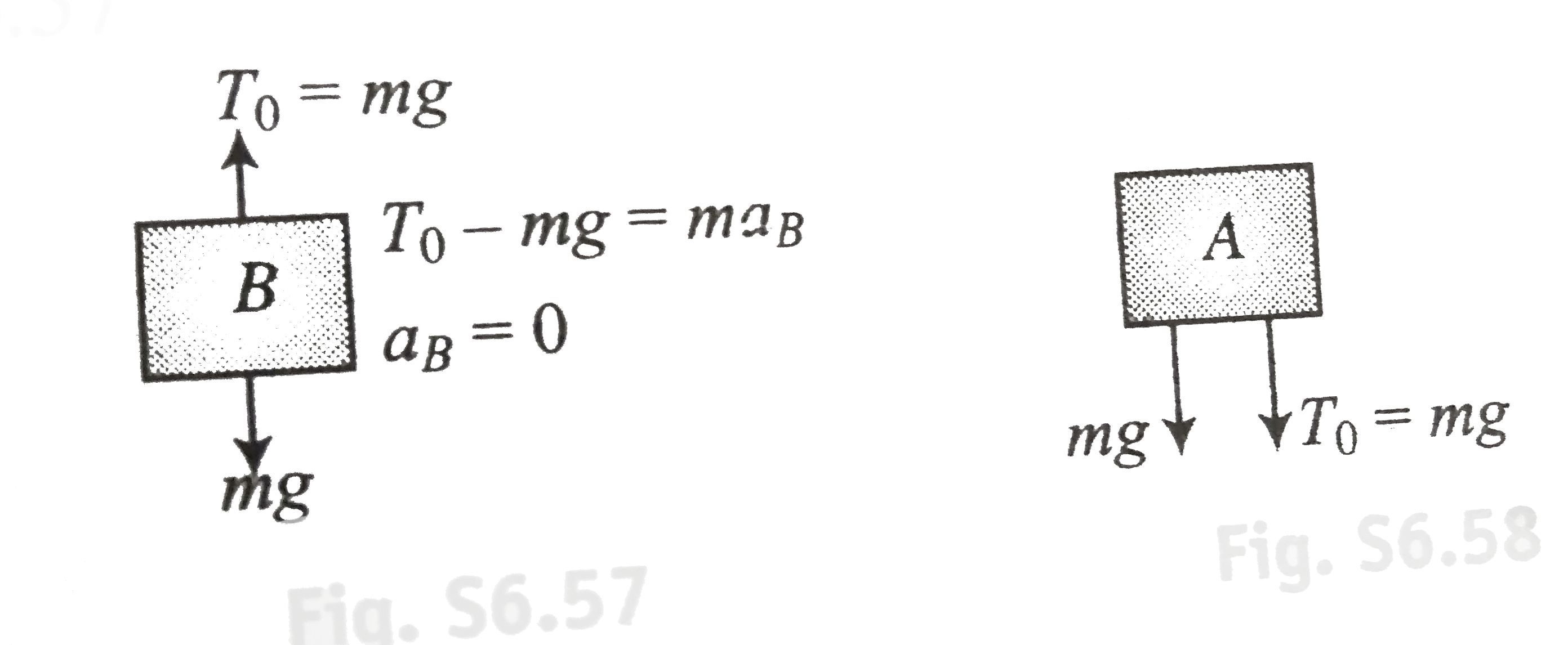 ,
,
mg+T0=maA
2mg=maA
aA=2g (downwards).
Topper's Solved these Questions
- NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 1Book:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 1Exercise:Subjective
Explore 15 Videos
- NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 1Book:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 1Exercise:Single Correct
Explore 73 Videos
- NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 1Book:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 1Exercise:Exercise 6.3
Explore 19 Videos
- MISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 2Book:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:MISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 2Exercise:INTEGER_TYPE
Explore 10 Videos
- NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 2Book:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 2Exercise:Integer type
Explore 1 Video
Similar Questions
A hot- air balloon consists of a basket, one passenger, and some carge. Let the total mass be M. Even though there is an upward lift force on the balloon, the balloon is initially acceleration downwards at a rate of g/3.
(a) Draw a free-body diagram for the descending balloon.
(b) Find the upward lift force in terms of the initial total weight Mg.
(c ) The passenger notices that he is heading straight for a waterfall and decides he needs to go up. What fraction of the total weight must he drop overboard so that the balloon accelerates upward at a rate of g/2? Assume that the upward lift force remains the same.
View SolutionTwo skaters have weight in the ratio 4:5 and are 9m apart, on a smooth frictionless surface. They pull on a rope stretched between them. The ratio of the distance covered by them when they meet each other will be
View SolutionBlock A is given an acceleration 12ms−2 towards left as shown in fig. Assuming block B always remains horizontal, find the acceleration (in ms−2) of B.
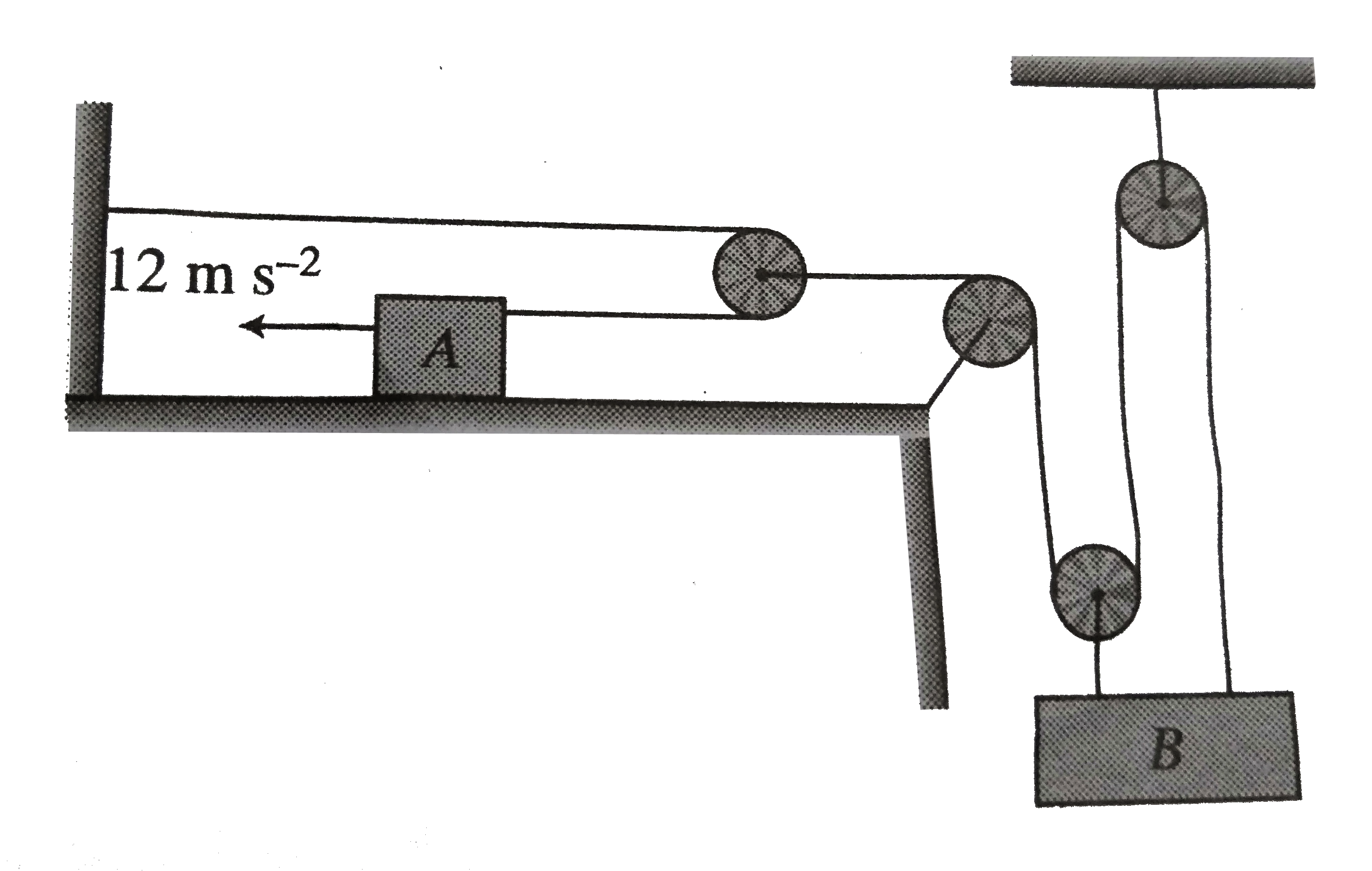
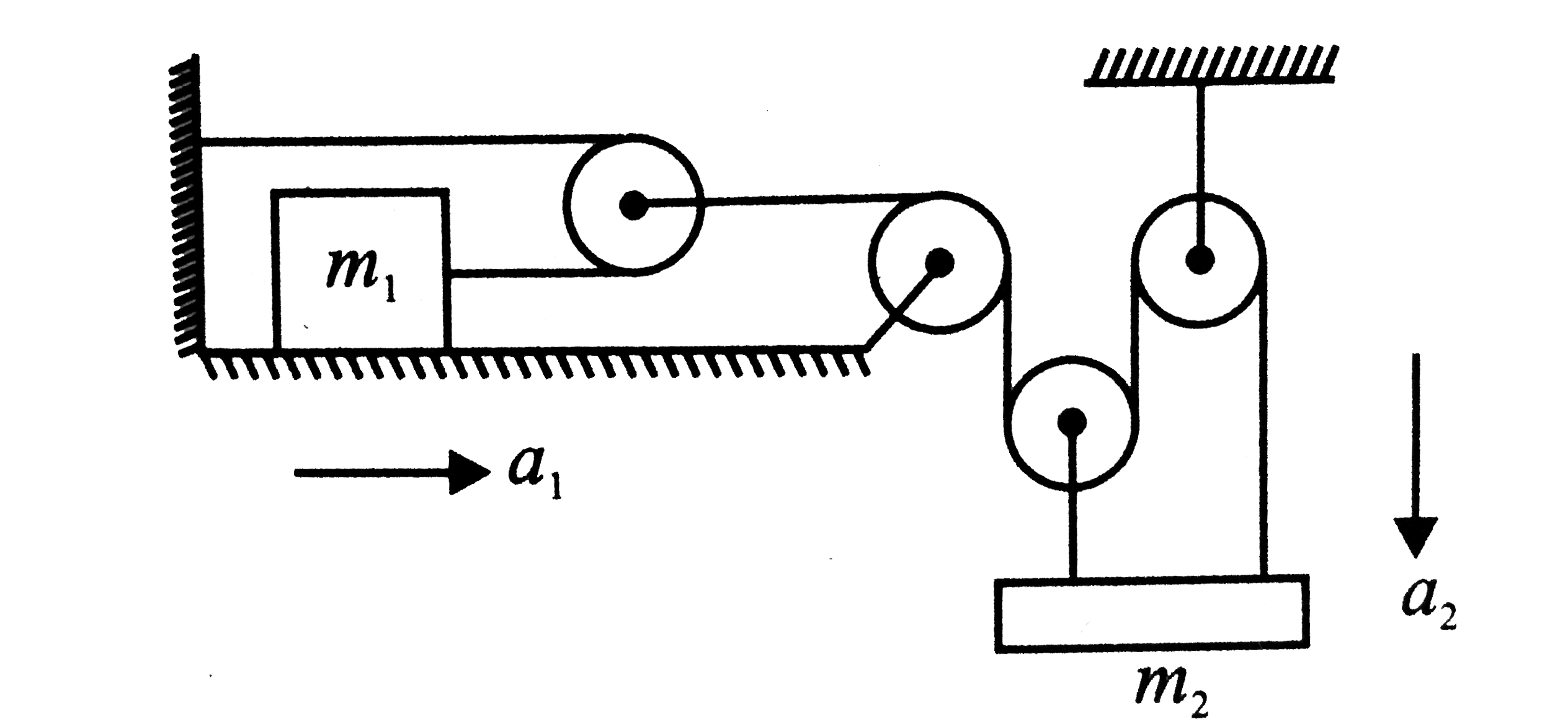
View SolutionTwo blocks are arranged as shown in figure. Find the ratio of a1/a2. (a1 is acceleration of m1 and a2 that of m2)
View SolutionA block is moving on an inclined plane making an angle 45∘ with the horizontal and the coefficient of friction is μ. The force required to just push it up the inclined plane is 3 times the force required to just prevent it from sliding down. If we define N=10μ, then N is
View SolutionThe string between blocks of mass m and 2m is massless and inextensible. The system is suspended by a massless spring as shown. If the string is cut find the magnitudes of accelerations of mass 2m and m (immediately after cutting)
View SolutionTwo blocks A and B of same mass m attached with a light spring are suspended by a string as shown in fig. Find the acceleration of block A and B just after the string is cut.
View SolutionTwo blocks A and B of same mass m attached with a light string are suspended by a spring as shown in fig. Find the acceleration of block A and B just after the string is cut.

View SolutionTwo block of mass 2kg are connected by a massless ideal spring of spring contant K=10N/m . The upper block is suspended from roof by a light string A . The system shown is in equilibrium. The string A is now cut, the acceleration of upper block just after the string A is cut will be (g=10m/s2 .

View SolutionA block is attached with an ideal spring and string, and is in equilibrkum as shown in Figure. The acceleration of the block just after breaking the string is a_(1) and just after breaking the spring is a_(2) . Then
View SolutionTwo identical blocks are connected by a light spring. The combination is suspended at rest from a string attached to the ceiling, as shown in the figure-2.190 below. The string breaks suddenly. Immediately after the string breaks:
View SolutionA block of mass M is suspended by a corf A from the ceiling and another cord B is attached to the bottom of the block as shown in Which string will break if we pull the string B (a) with a sudden jerk, (b) steadily ?
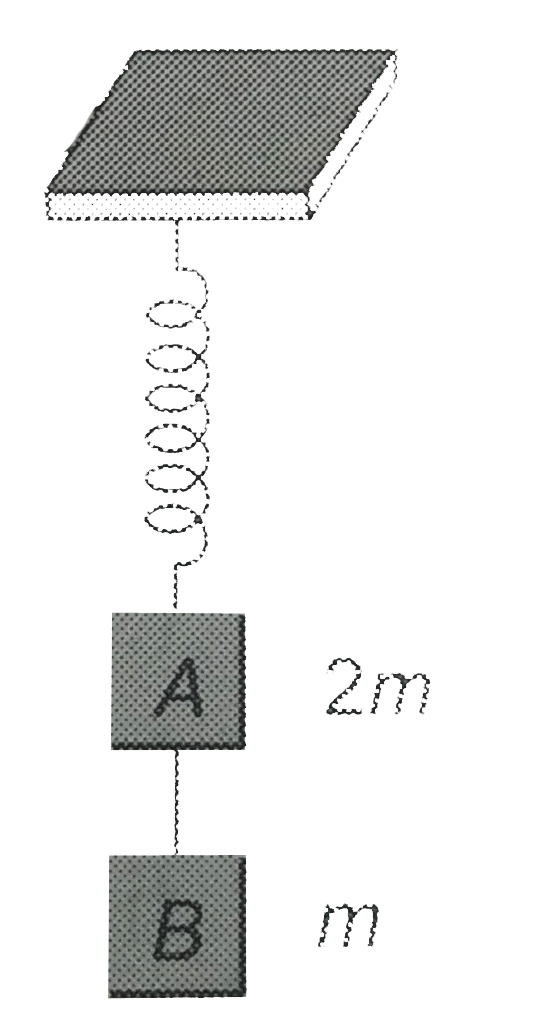
View SolutionTwo blocks A and B of masses 2m and respectively, are connected by a massless and inextensible string. The whole system is suspended by a masslessspring as shown in the figure. The magnitude of acceleration of A and B, immediately after the string is cut, are respectively
View SolutionTwo blocks are connected by a spring. The combination is suspended, at rest, from a string attatched to the ceiling, as shown in the figure. The string breaks suddenly. Immediately after the string breaks, what is the initial downward acceleration of the upeer block of mass 2m ?
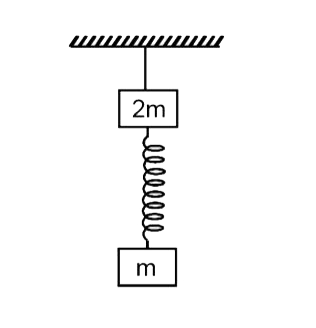
View SolutionThe string between blocks of masses 'm' and '2m' is massless and inextensible.The system is suspended by a massless spring as shown. If the string is cut, the magnitudes of accelerations of masses 2m and m (immediately after cutting)
View SolutionThe string beween blocks of mass m and 2m is massless and inextensible. The system is suspended by a massless spring as shown. If the string is cut find the magnitudes of accelerations of mass 2m and m (immediately after cutting):
View Solution
