Two containers of equal volume contain the same gas at pressure P1 and P2 and absolute temperature T1 and T2, respectively. On joining the vessels, the gas reaches a common pressure P and common temperature T. The ratio P/T is equal to
P1T1+P2T2
12[P1T1+P2T2]
P1T2+P2T1T1+T2
P1T2−P2T1T1−T2
The correct Answer is:B
For a closed system, the total mass of gas or the number of moles remains constant.
Let n1 and n2 be number of moles of gas in container 1 and container 2 respectively. Then
P1V=n1RT1orn1=P1VRT1
P2V=n2RT2orn2=P2VRT2
P(2V)=(n1+n2)RT ...(i)
Substituting the values of n1andn2 in equation (i), we get
P(2V)=(P1VRT1+P2VRT2)RTorPT=12(P1T1+P2T2)
Topper's Solved these Questions
- BEHAVIOUR OF PERFECT GAS AND KINETIC THEORYBook:MTG GUIDEChapter:BEHAVIOUR OF PERFECT GAS AND KINETIC THEORYExercise:TOPICWISE PRACTICE QUESTIONS (Kinetic Theory of Gases and Kinetic Interpretation of Temperature
Explore 11 Videos
- BEHAVIOUR OF PERFECT GAS AND KINETIC THEORYBook:MTG GUIDEChapter:BEHAVIOUR OF PERFECT GAS AND KINETIC THEORYExercise:TOPICWISE PRACTICE QUESTIONS (Law of Equipartition of Energy and Application to Specific Heat capacities)
Explore 14 Videos
- BEHAVIOUR OF PERFECT GAS AND KINETIC THEORYBook:MTG GUIDEChapter:BEHAVIOUR OF PERFECT GAS AND KINETIC THEORYExercise:AIPMT / NEET (MCQs)
Explore 11 Videos
- GRAVITATIONBook:MTG GUIDEChapter:GRAVITATIONExercise:AIPMT/NEET MCQS
Explore 32 Videos
Similar Questions
The mean translational kinetic energy of a perfect gas molecule at the temperature Tk is :
View SolutionA gas is formed of molecules each molecules possessing f degrees of freedom, then the value of γ=CPCV is equal to
View SolutionIf CpandCv denote the specific heats (per unit mass of an ideal gas of molecular weight M), then
where R is the molar gas constant.
View SolutionThe radii of circular orbits of two satellite A and B of the earth are 4R and R, respectively. If the speed of satellite A is 3v, then the speed of satellite B will be
View SolutionTwo containers of equal volume contain the same gas at pressure P1 and P2 and absolute temperature T1 and T2, respectively. On joining the vessels, the gas reaches a common pressure P and common temperature T. The ratio P/T is equal to
View SolutionTwo identical vessels contain the same gas at pressure P_(1) and P_(2) at absolute temperature T_(1) and T_(2) , respectively. On joining the vessels with a small tube as shown in the figure. The gas reaches a common temperature T and a common pressure P. Determine the ratio P//T
View Solutionshows two vessels A and B with rigid walls containing ideal gas. The pressure volume and temperature in vessel A are PA,V and TA whereas in vessel B,PBV and TB The vessel are now connected through small tube of negligible volume Show that the final pressure P and temperature T satisfy the equation
PT=12[PATA+PBTB]
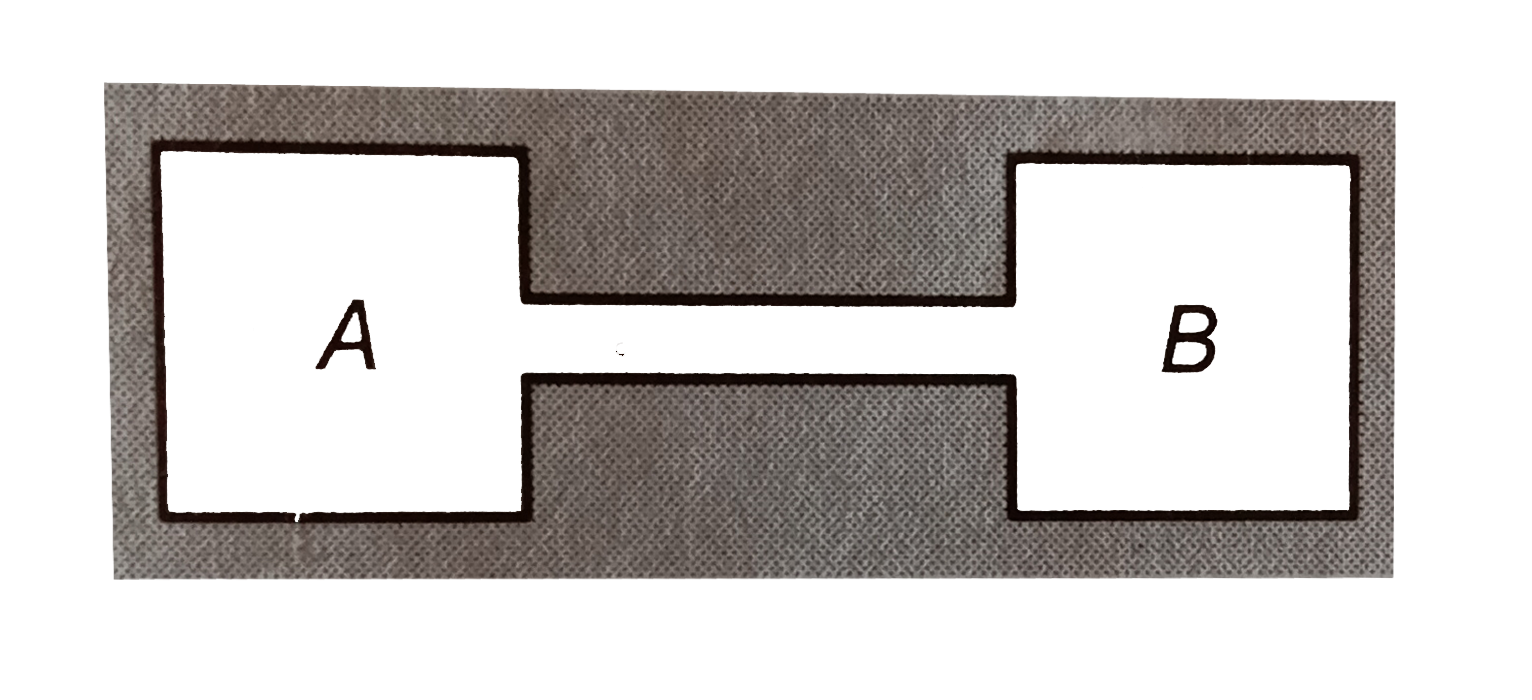 .
.
View SolutionAn ideal gas in thermally insulated vessel at internal (pressure)=P_(1), (volume)=V_(1) and absolute temperature = T_(1) expands irreversiby against zero external, pressure , as shown in the diagram, The final internal pressure, volume and absolute temperature of the gas are p_(2), V_(2) and T_(2) , respectively . For this expansion
View SolutionAn ideal gas in a thermally insulated vessel at internal pressure =P1, volume =V1 and absolute temperature =T1 expands irreversibly against zero external pressure, as shown in the diagram. The final internal pressure, volume and absolute temperature of the gas are P2,V2 and T2 respectively. For this expansion.
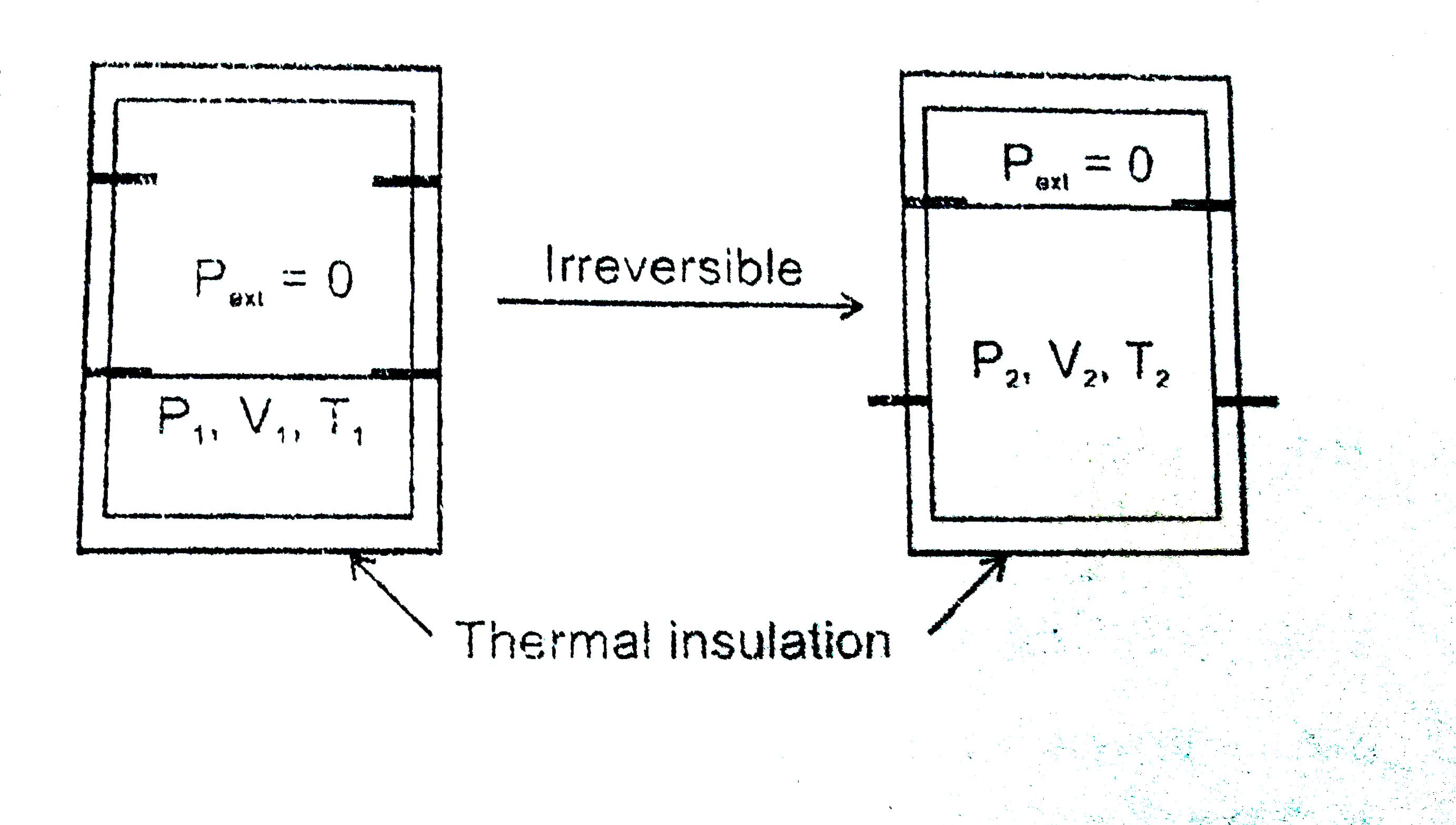
View SolutionThe pressure and temperature of a gas are P and T respectively. If the critcal pressure and critical temperature of the gas be PcandTc respectively, then liquefacction will be possible when-
View SolutionTwo containers of equal volume contain the same gas at pressure P1 and P2 and absolute temperature T1 and T2, respectively. On joining the vessels, the gas reaches a common pressure P and common temperature T. The ratio P/T is equal to
View Solutionसमान आयतन के दो बर्तनों में दो समान गैसें दाब p1 तथा p2 पर हैं तथा ताप क्रमशः T1 तथा T2 हैं। बर्तनों को जोड़ने पर गैस का उभयनिष्ठ दाब p तथा उभयनिष्ठ ताप T हो जाता है। अनुपात pT समतुल्य है
View SolutionAn ideal gas in a thermally insulated vessel at internal pressure = P4, volume =V1 and absolute temperature =T1 expands irreversibly against zero external pressure, as shown in the diagram. The final internal pressure, volume and absolute temperature of the gas are P2,V2andT2, respectively. For this expansion.
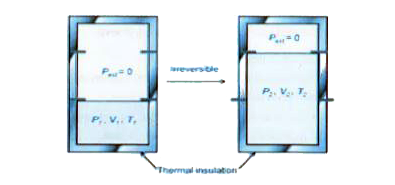
View SolutionTwo containers of equal volume contain the same gas at pressures P1andP2 and absolute temperatures T1andT2 respectively. On joining the vessels, the gas reaches a common pressure P and a common temperature T. Find the value P/T.
View SolutionTwo containers of equal volume contain the same gas at pressures P1andP2 and absolute temperatures T1andT2 respectively. On joining the vessels, the gas reaches a common pressure Panda common temperature T. Find the value P/T.
View SolutionTwo containers of equal volume contain the same gas at pressure P1 and P2 and absolute temperature T1 and T2, respectively. On joining the vessels, the gas reaches a common pressure P and common temperature T. The ratio P/T is equal to
View Solution
