Two paper discs are mounted on a rotating vertical shaft. The shaft rotates with a constant angular speed ω and the separation between the discs is H. A bullet is fired vertically up so that it pierces through the two discs. It creates holes H1 and H2 in the lower and the upper discs. The angular separation between the two holes (measured with respect to the shaft axis) is θ. Find the speed (v) of the bullet. Assume that the speed of the bullet does not change while travelling through distance H and that the discs do not complete even one revolution in the interval the bullet pierces through them.
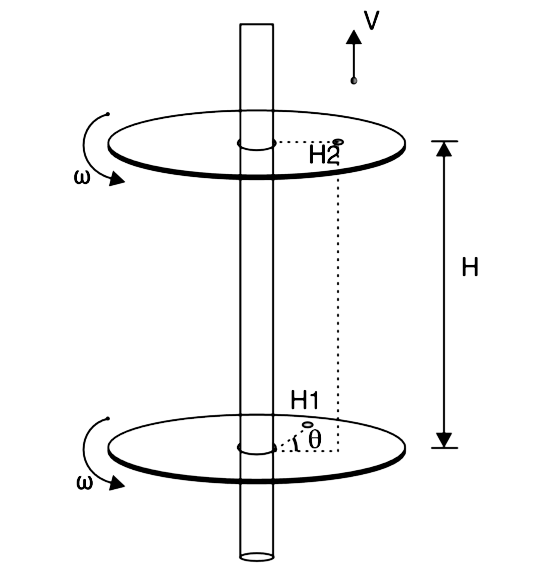
The correct Answer is:v=ωHθ
Step by step video, text & image solution for Two paper discs are mounted on a rotating vertical shaft. The shaft rotates with a constant angular speed omega and the separation between the discs is H. A bullet is fired vertically up so that it pierces through the two discs. It creates holes H1 and H2 in the lower and the upper discs. The angular separation between the two holes (measured with respect to the shaft axis) is theta. Find the speed (v) of the bullet. Assume that the speed of the bullet does not change while travelling through distance H and that the discs do not complete even one revolution in the interval the bullet pierces through them. by Physics experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 11 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023Similar Questions
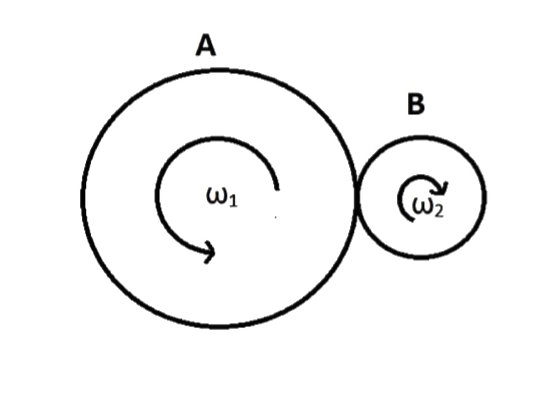
Two discs A and B are in contact and rotating with angular velocity with angular velocities ω1andω2 respectively as shown. If there is no slipping between the discs, then
View SolutionA disc of moment of inertia I1 is rotating freely with angular speed ω1 when another non-rotating disc of moment of inertia I2 is dropped on it. The two discs then rotate as one unit. Find the final angular speed.
View Solution
Knowledge Check
A disc is rotating with angular velocity ω. If a child sits on it, what is conserved?
AKinetic energyBPotential energyCLinear momentumDAngular momentumA constant power is suppied to a rotating disc. The relationship between the angular velocity (ω) of the disc and number of rotations (n) made by the disc is governed by
Aω∝n13Bω∝n23Cω∝n32Dω∝n2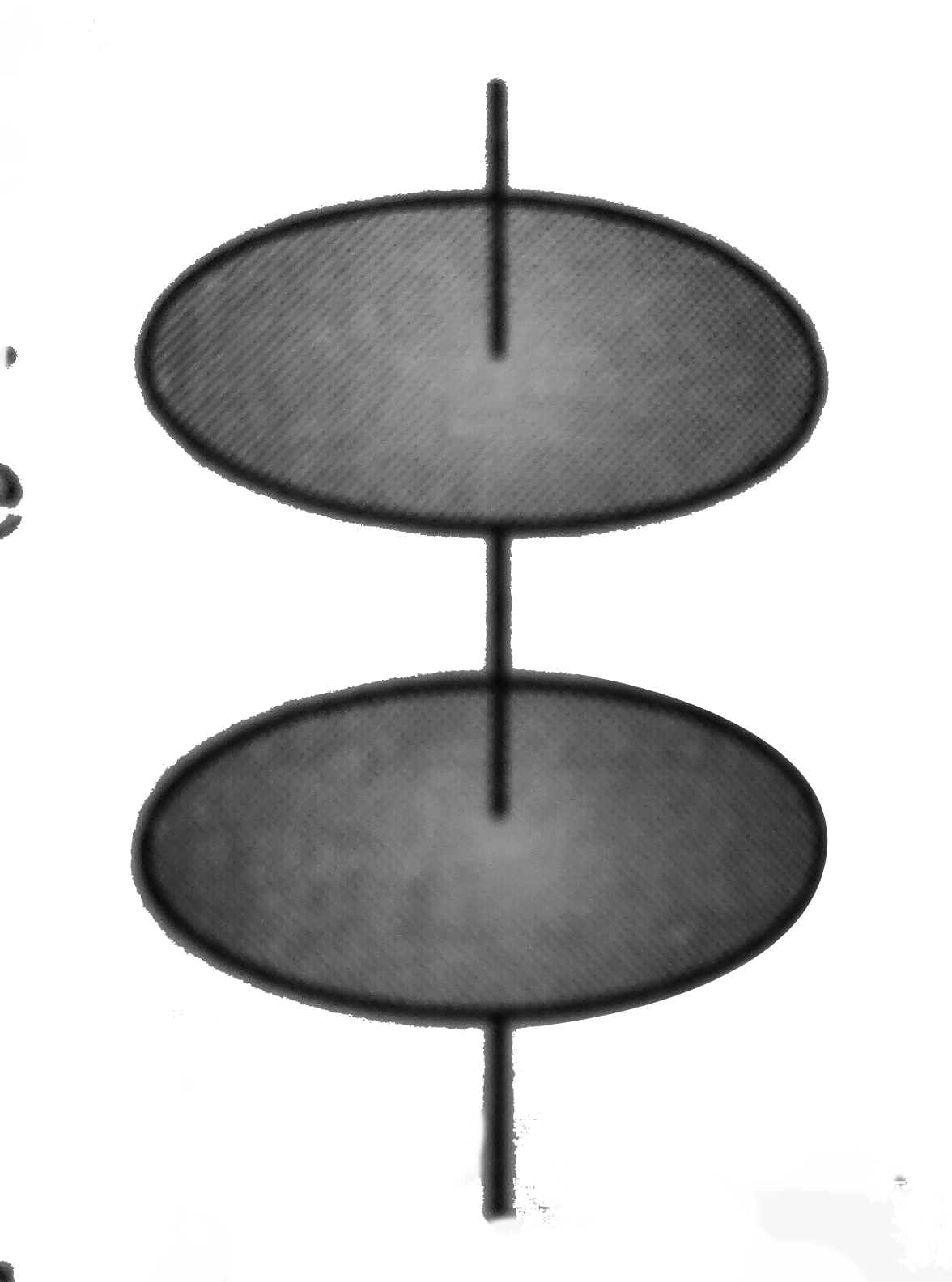
Two identical discs are positioned on a vertical axis as shown in the figure. The bottom disc is rotating at angular velocity ω0 and has rotational kinetic energy K0. Change in the rotational kinetic energy of the system isAK0/2B−K0/2C−K0/4DK0/4
A metal disc of radius a rotates with a constant angular velocity ω about its axis. The potential difference between the center and the rim of the disc is (m = mass of electron, e = charge on electro)
View SolutionA uniform disc of radius a and mass m, is rotating freely with angular speed ω in a horizontal plane. About a smooth fixed vertical axis through its centre. A particle, also of mass m, is suddently attached to the rim of the disc of the disc and rotates with it. The new angular speed is
View SolutionA disc is rotating with angular speed CD. If a child sits on it, what is conserved
View SolutionA bullet is moving horizontally with certain velocity. It pierces two paper discs rotating coaxially with angular speed ω separated by a distance l. IF the hole made by bullet on second disc is shifted by an angle θ with respect to the first, find velocity of bullet.
View SolutionA uniform disc of radius 'a' and mass 'm' is rotating freely with angular speed ω in a horizontal plane about a smooth fixed vertical axis through its centre. A particle of mass 'm' is then suddenly attached to the rim of the disc and rotates with it. The new angular speed is
View Solution

