Two parallel long smooth conducting rails separated by a distance l are connected by a movable conducting connector of mass m. Terminals of the rails are connected by the resistor R and the capacitor C as shown in figure. A uniform magnetic field B perpendicular to the plane of the rail is switched on. The connector is dragged by a constant force F. Find the speed of the connector as a function of time if the force F is applied at t=0. Also find the terminal velocity of the connector.
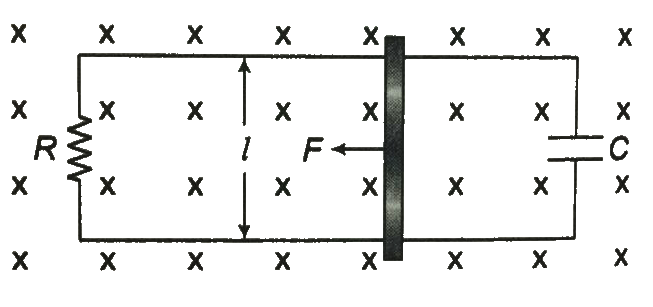
The correct Answer is:B
Let v be the veloicty of connector at some instant of time. Then,
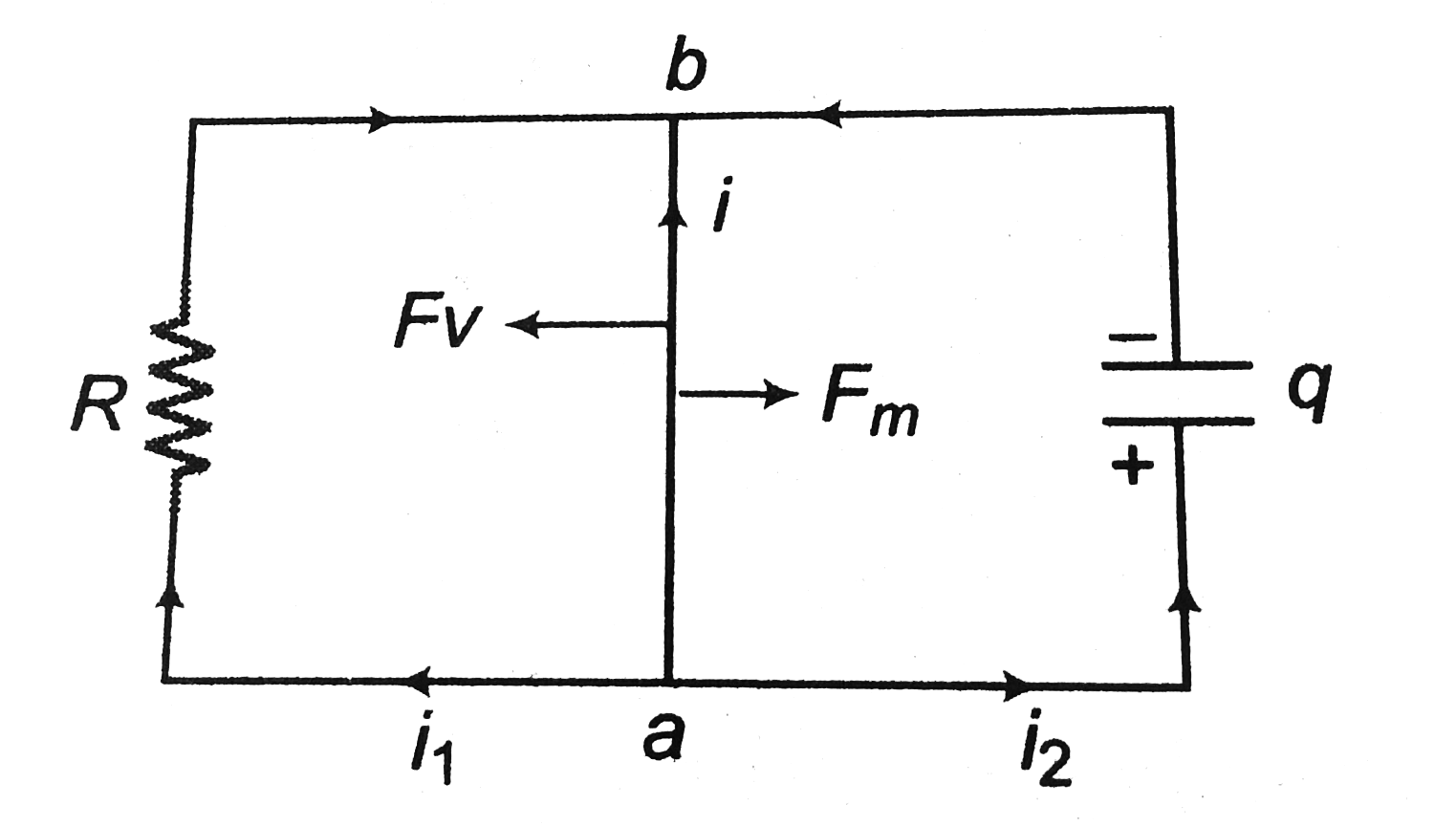
Vab=Bvl,i1=BvlR,q=C(Bvl)
∴i2=dqdt=CBIdvdt
Now, i=i1+i2=BvlR+CBIdvdt
Magnetic force Fm=ilB=B2l2R.v+B2l2C.dvdt
Further Fnet=F−Fm
or mdvdt=F−B2l2Rv−B2l2Cdvdt
∴∫v0dvF−B2l2Rv=∫10dtm+B2l2C
Integrating we get,
V=FRB2l2[1−1−(B2l2mR+RB2l2C)t]
Terminal velocity in this case is : vT=FRB2l2
Similar Questions
Two parallel long smooth conducting rails separated by a distance l=10cm are connected by a movable conducting connector of mass m = 4mg. Terminal of the rails are connected by the resistor R=2Ω & the capacitor C=1μF as shown. A uniform magnetic field B=20T perpendicular to the plane of the rails is switched on. The connector is dragged by a constant force F=10 N. The speed of the connector as function of time if the force F is applied at t=0 is equal to v=5(1−e−x×104×t)m/s. Find the value of x.
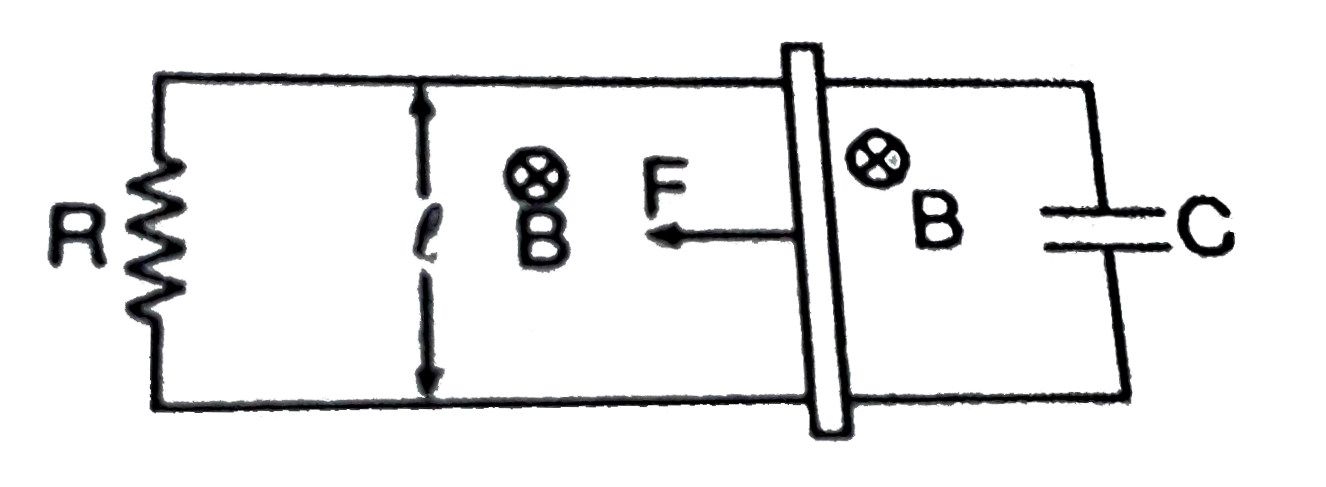
View SolutionTwo parallel long smooth conducting rails separated by a distance l=10cm are connected by a movable conducting connector of mass m=4mg.Terminals of the rails are connected by the resistor R=2Ω & the capacitor C=1μF as shown.A uniform magnetic field B=20T perpendicular to the plane of the rails is swiched on.The connector is dragged by a constant force F=10N.The speed of the connector as function of time if the force F is applied at t=0 is equal to v−5(1−e−x×104×tm/s).Find the value of x.
View Solution
Knowledge Check
A conducting wire xy of lentgh l and mass m is sliding without friction on vertical conduction rails ab and cd as shown in figure. A uniform magnetic field B exists perpendicular to the plane of the rails, x moves with a constant velocity of
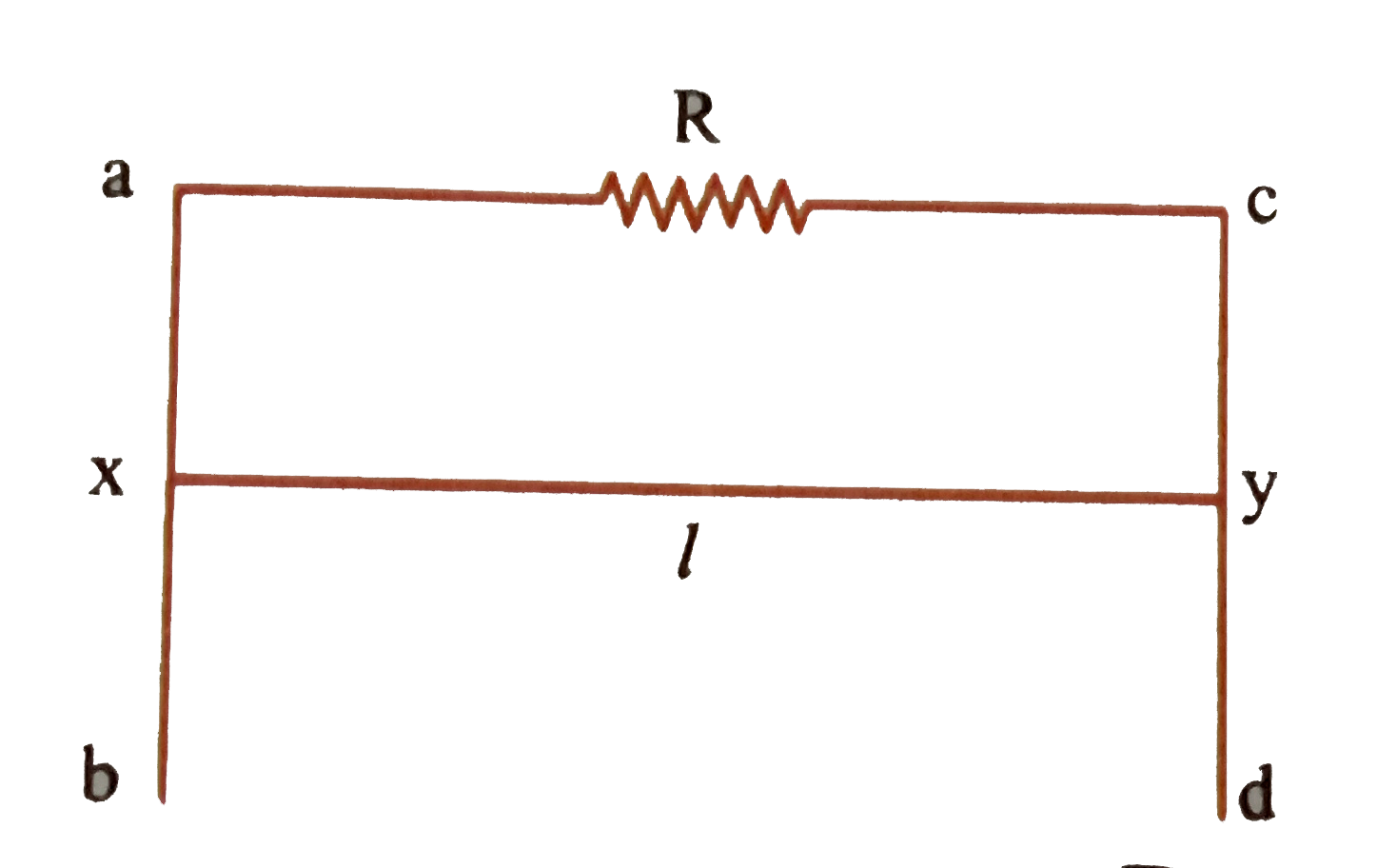 AmgRBlBmgRBl2CmgRB2l2DmgRB2l
AmgRBlBmgRBl2CmgRB2l2DmgRB2lA copper wire ab of length l, resistance r and mass m start sliding at t=0 down a smooth, vertical, thick pair of connected conducting rails as shown in figure. A uniform magnetic field B exists in the space in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the rails which options are correct .
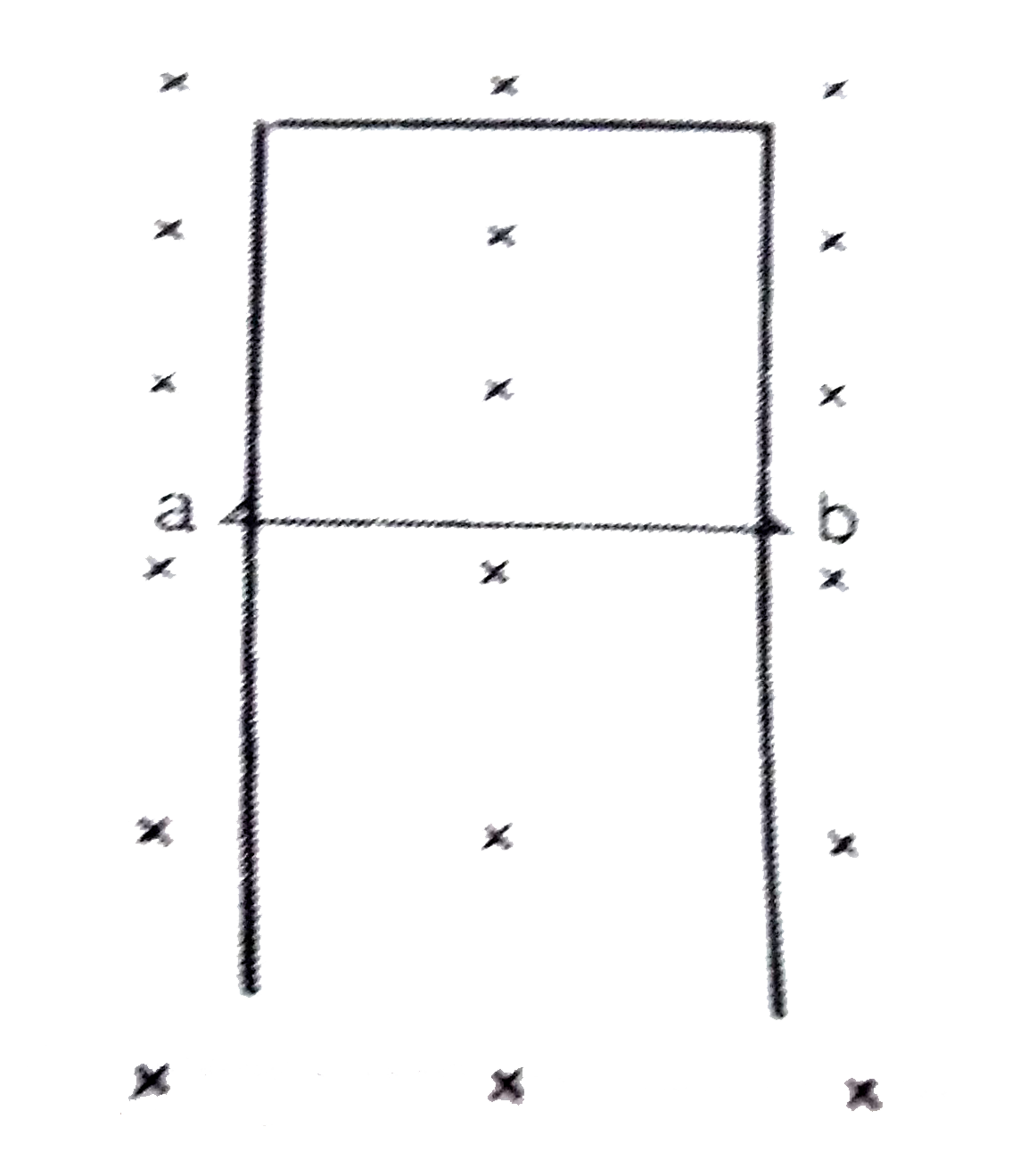 AThe magnitude and direction of the induced current in the wire when speed of the wire v is vBlr, a to bBThe downward acceleration of the wire at this instant g−B2l2mrvCThe velocity of the wire as a function of time vm(1−e−gt/vm),(wherevm=mgrB2l2)DThe displacement of the wire as a function of time vmt−v2mg(1−e−gt/vm),(wherevm=mgrB2l2)
AThe magnitude and direction of the induced current in the wire when speed of the wire v is vBlr, a to bBThe downward acceleration of the wire at this instant g−B2l2mrvCThe velocity of the wire as a function of time vm(1−e−gt/vm),(wherevm=mgrB2l2)DThe displacement of the wire as a function of time vmt−v2mg(1−e−gt/vm),(wherevm=mgrB2l2)A copper rod of mass m slides under gravity on two smooth parallel rails l distance apart set at an angle θ to the horizontal. At the bottom, the rails are joined by a resistance R.
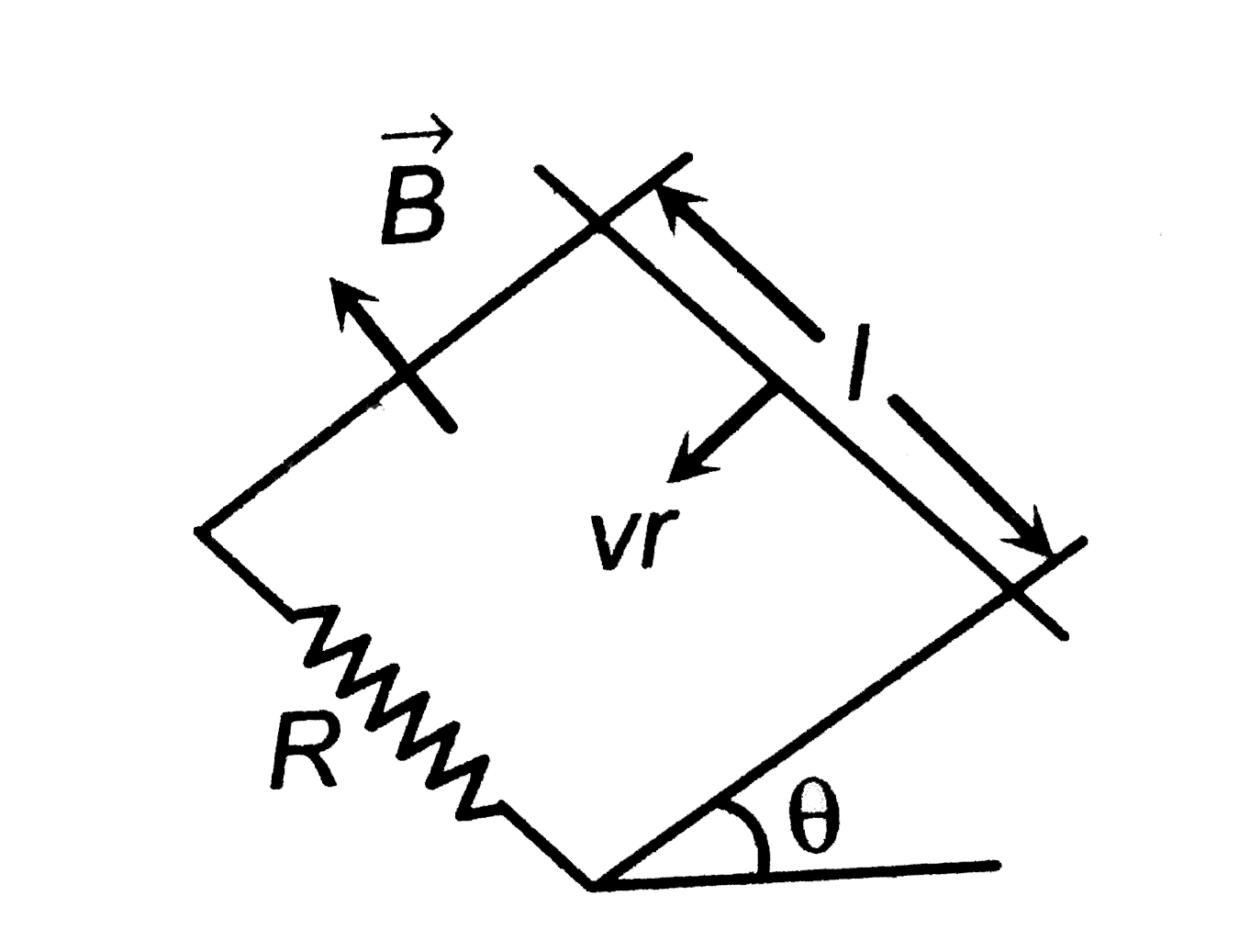
There is a uniform magnetic field perpendicular to the plane of the rails. the terminal valocity of the rod isAmgRtanθB2l2BmgRcotθB2l2CmgRsinθB2l2DmgRcosθB2l2
Two parallel long smooth conducting rails separated by a distance l are connected by a movable conducting connector of mass m. Terminals of the rails are connected by the resistor R and the capacitor C as shown in figure. A uniform magnetic field B perpendicular to the plane of the rail is switched on. The connector is dragged by a constant force F. Find the speed of the connector as a function of time if the force F is applied at t=0. Also find the terminal velocity of the connector.

View SolutionA copper bar of mass m sides under gravity on two smooth parallel rails l distance apart and set at angle α to the horizontal . At the lop , the rails are joined by a resistor R. Calculate the steady velocity of the bar the n when there is a unifrom magnetic field B perpedicular to the plane of the rails .
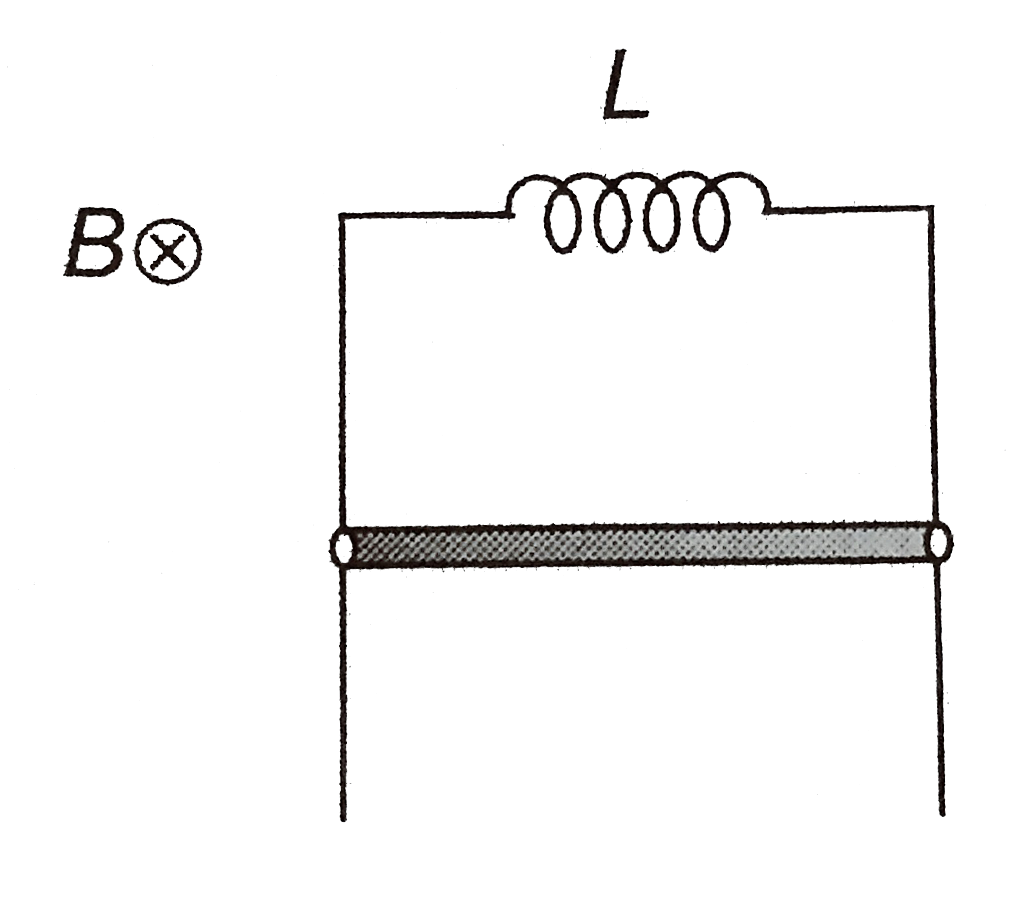
View SolutionA coil of inductance L connects the upper ends of two vertical copper bars separated by a distance l . A horizontal conducting connector of mass m starts falling with zero initial velocity along the bars without losing contact with them. The whole system is located in a uniform magnetic field B perpendicular to the plane of the bars. Find the law of motion x(t) of the connector.
View SolutionA copper wire ab of length l, resistance r and mass m starts sliding at t=0 down a smooth, vertical, thick pair of connected condcuting rails as shown in figure.A uniform magnetic field B exists in the space in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the rails which options are correct.
View SolutionA copper rod of mass m slides under gravity on two smooth parallel rails l distance apart set at an angle θ to the horizontal. At the bottom, the rails are joined by a resistance R.

There is a uniform magnetic field perpendicular to the plane of the rails. the terminal valocity of the rod is
View Solution
