Two parallel vertical metallic rails AB and CD are separated by 1m. They are connected at the two ends by resistances R1 and R2 as shown in the figure. A horizontal metallic bar l of mass 0.2kg slides without friction, vertically down the rails under the action of gravity. There is a uniform horizontal magnetic field of 0.6T perpendicular to the plane of the rails. It is observed that when the terminal velocity is attained, the powers dissipated in R1 and R2 are 0.76W and 1.2W respectively (g=9.8m/s2)
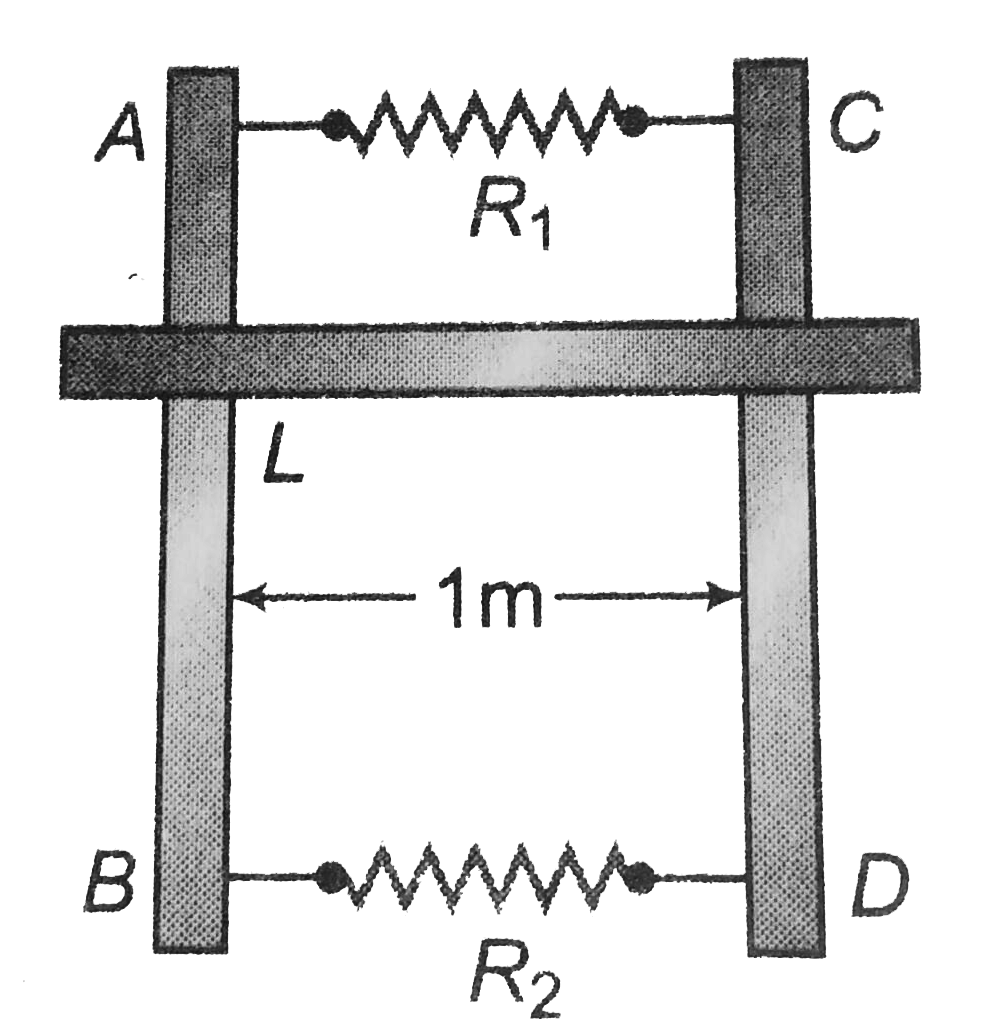
The terminal velocity fo the bar L will be
2m/s
3m/s
1m/s
None of these
The correct Answer is:C
At terminal velocity
iLB=mg
∴i=mbLB=0.2×981×0.6
i=3.27A ...(i)
e=BvL(v=terminal velocity)
=(0.6)(v)(1)
e=0.6v
PR1=e2R1
∴0.76=0.36v2R1 …..(ii)
PR2=e2R2
∴1.2=0.36v2R2 .........(iii)
R1 and R2 are in parallel
∴Rnet=R1R2R1+R2..........iv
ii=eRnet ............(v)
Solving these five equation we can get the results.
Similar Questions
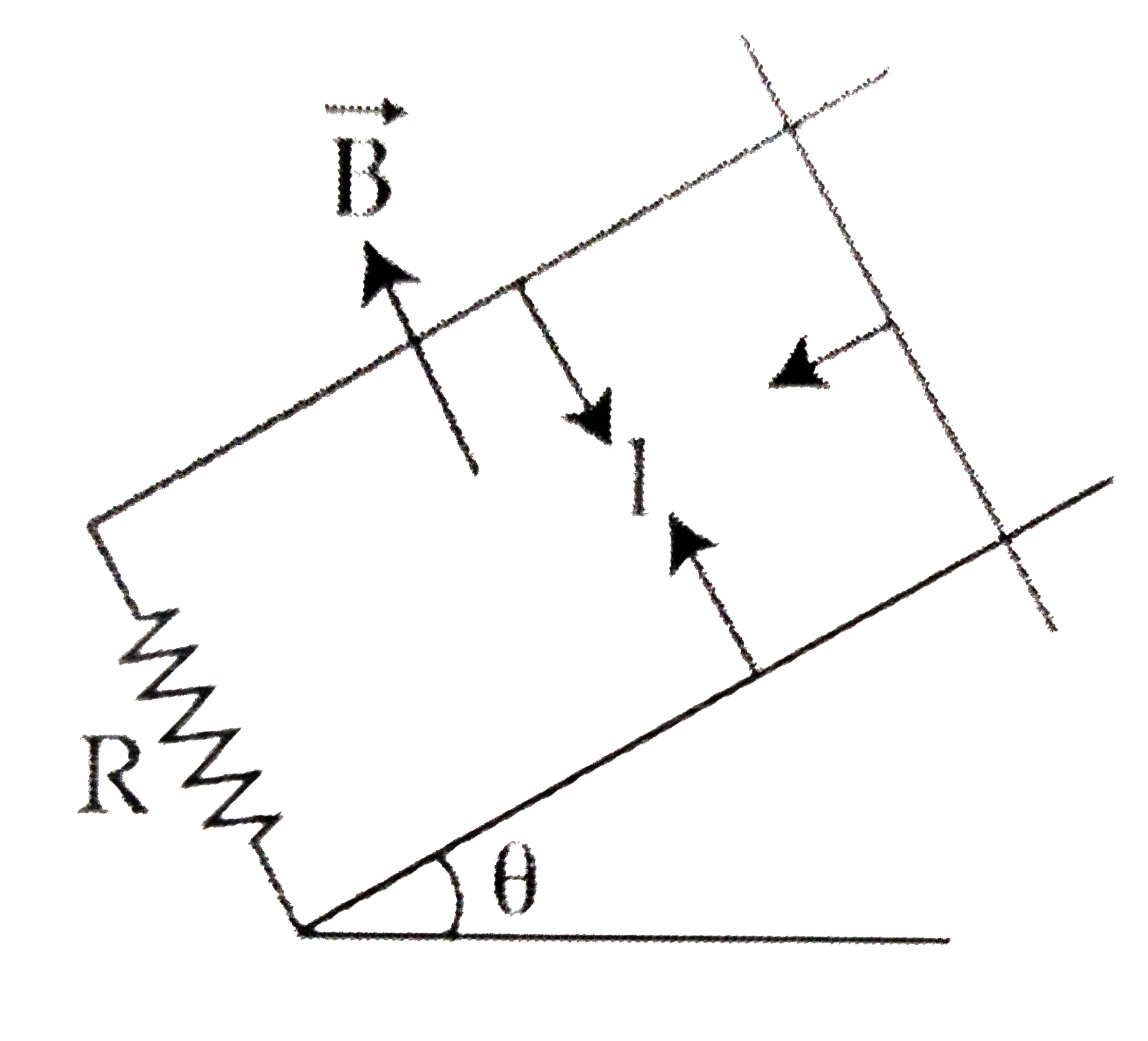
a copper rod of mass m slides under gravity on two smooth parallel rails with separation I and set at an angle of θ with the horiziontal at the bottom rails are joined by resistance R. There is a uniform magnetic field B normal to the plane of the rails as shown in the figure The terminal speed of the copper rod is :
View SolutionA wire ab of length l, mass m and resistance R slides on a smooth thick pair of metallic rails joined at the bottom as shown in fig. The plane of the rails makes an angle theta with the horizontal. A vertical magnetic field B exist in the region. If the wire slides on the rails at a constant speed v, then the value of B is -
View Solutionएक कॉपर की छड़ का द्रव्यमान m है। यह दो क्षैतिज समान्तर चिकनी पटरियों (rails) जिनके बीच की दूरी । है तथा क्षैतिज के साथ θ कोण बनाती है, पर गुरुत्व के अन्तर्गत फिसलती है। तली में पटरियाँ एक प्रतिरोध R के द्वारा चित्रानुसार जुड़ी हैं। यहाँ एकसमान चुम्बकीय क्षेत्र B पटरियों (rails) के तल के लम्बवत् है। छड़ का क्रान्तिक वेग है

View Solutiona copper rod of mass m slides under gravity on two smooth parallel rails with separation I and set at an angle of theta with the horiziontal at the bottom rails are joined by resistance R. There is a uniform magnetic field B normal to the plane of the rails as shown in the figure The terminal speed of the copper rod is :
View SolutionA copper rod of mass m slides under gravity on two smooth parallel rails l distance apart set at an angle theta to the horizontal. At the bottom, the rails are joined by a resistance R . There is a uniform magnetic field perpendicular to the plane of the rails. the terminal valocity of the rod is
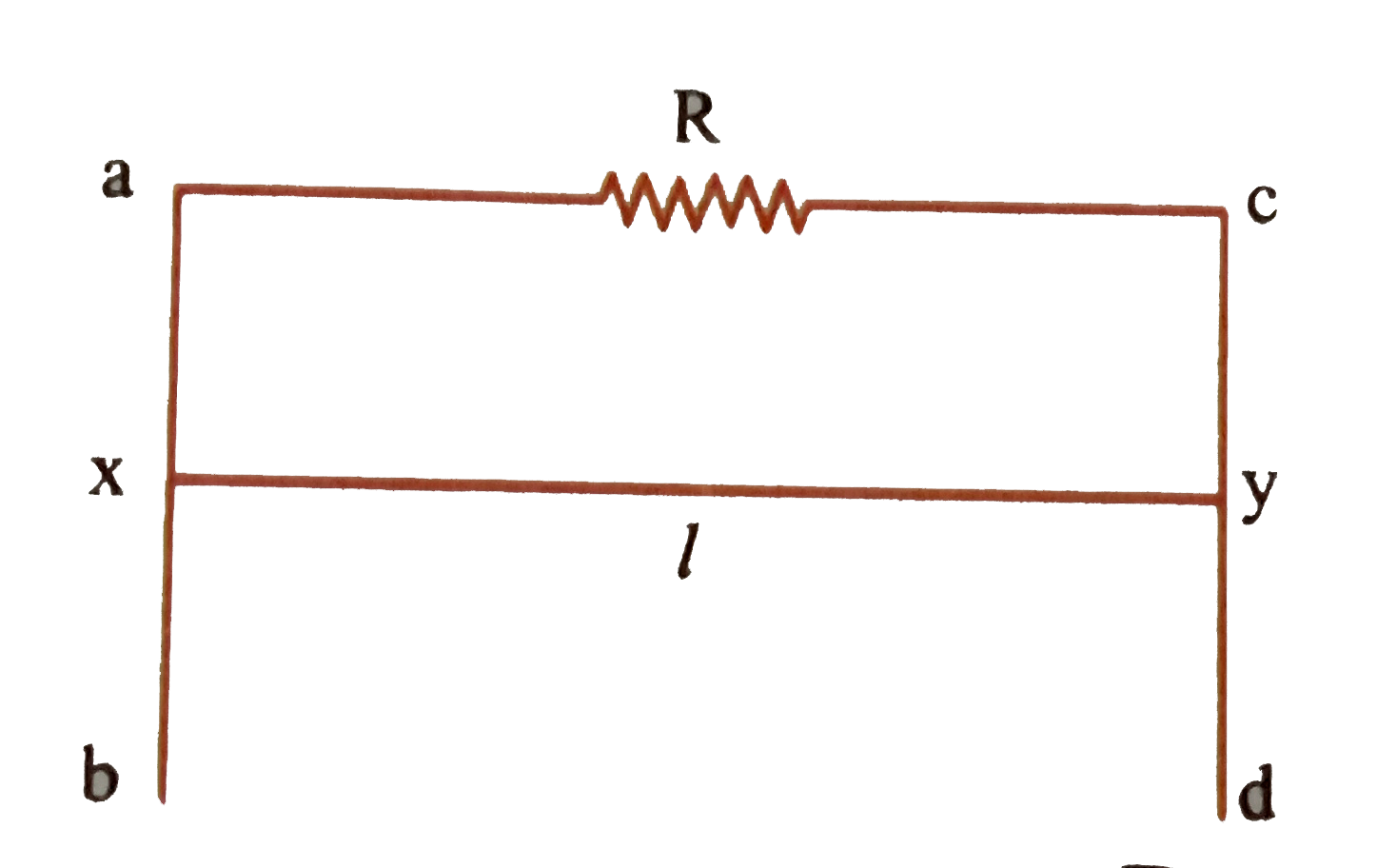
View SolutionA conducting wire xy of lentgh l and mass m is sliding without friction on vertical conduction rails ab and cd as shown in figure. A uniform magnetic field B exists perpendicular to the plane of the rails, x moves with a constant velocity of
View SolutionA vertical ring of radius r and resistance on R falls vertically. It is in contact with two vertical rails which are joined at the top. The rails are without friction and resistance. There is a horizontal uniform, magnetic field of magnitude B perpendicular to the plane of the ring and the rails. When the speed of the ring is v , the current in the section PQ is
View SolutionA conducting wire xy of lentgh l and mass m is sliding without friction on vertical conduction rails ab and cd as shown in figure. A uniform magnetic field B exists perpendicular to the plane of the rails, x moves with a constant velocity of
View Solution

