What happens to the image distance in the eye when we increase the distance of an object from the eye ?
To answer the question of what happens to the image distance in the eye when we increase the distance of an object from the eye, we can follow these steps:
1. Understanding the Structure of the Eye:
- The human eye consists of several parts, including the cornea, lens, and retina. The distance between the lens and the retina is fixed and does not change.
2. Image Formation in the Eye:
- When light from an object enters the eye, it passes through the lens, which focuses the light onto the retina. The retina is where the image is formed.
3. Constant Image Distance:
- Since the distance from the lens to the retina is constant, the image distance (denoted as 'V' in lens formula) remains constant regardless of how far the object is from the eye.
4. Accommodation of the Eye:
- The eye has the ability to adjust its focal length (denoted as 'F') through a process called accommodation. This adjustment allows the eye to focus on objects at different distances.
5. Effect of Increasing Object Distance:
- When the distance of the object (denoted as 'U') increases, the eye lens changes its focal length to maintain a clear image on the retina. Although the object distance increases, the image distance remains constant due to the fixed distance between the lens and the retina.
6. Lens Formula:
- The lens formula is given by:
1V−1U=1F
- In this formula, as 'U' increases (object moves away), 'F' (focal length) changes to keep 'V' constant.
Conclusion:
When we increase the distance of an object from the eye, the image distance does not change because the distance from the lens to the retina is constant. Instead, the eye adjusts its focal length to ensure that the image remains clear.
- The human eye consists of several parts, including the cornea, lens, and retina. The distance between the lens and the retina is fixed and does not change.
- When light from an object enters the eye, it passes through the lens, which focuses the light onto the retina. The retina is where the image is formed.
- Since the distance from the lens to the retina is constant, the image distance (denoted as 'V' in lens formula) remains constant regardless of how far the object is from the eye.
- The eye has the ability to adjust its focal length (denoted as 'F') through a process called accommodation. This adjustment allows the eye to focus on objects at different distances.
- When the distance of the object (denoted as 'U') increases, the eye lens changes its focal length to maintain a clear image on the retina. Although the object distance increases, the image distance remains constant due to the fixed distance between the lens and the retina.
- The lens formula is given by:
1V−1U=1F
- In this formula, as 'U' increases (object moves away), 'F' (focal length) changes to keep 'V' constant.
When we increase the distance of an object from the eye, the image distance does not change because the distance from the lens to the retina is constant. Instead, the eye adjusts its focal length to ensure that the image remains clear.
Similar Questions
What happens to the image distance in the normal human eye when we decrease the
distance of an object, say 10 m to 1 m? Justify your answer.
View SolutionFor a normal eye, distance of near point from the eye is.
View SolutionThe human eye forms the image of an object at its
View SolutionA convex lens produces a real image m times the size of the object. What will be the distance of the object from the lens ?
View SolutionThe image formed on the eye retina is
View SolutionApposition image is fomred in the eye of insect
View SolutionA compound microscope has an objective of focal length 2.0cm and an eye-piece of focal length 6.25cm and distance between the objective and eye-piece is 15cm. If the final image is formed at the least distance vision (25cm), the distance of the object form the objective is
View SolutionIn a compound microscope, the objective and eye piece have focal lengths 0.95cmand5cm respectively, and are kept at a distance of 20cm. The final image is formed at a distance of 25cm from the eye piece. Calculate the position of the object and the total magnification.
View SolutionIf the eye is kept very close to a coverging lens (focal length =10cm) and at the optical centre of the lens and an object is kept at distance 'd' of the object from the lebs so that its image can be seen clearly by the defect free eye is :
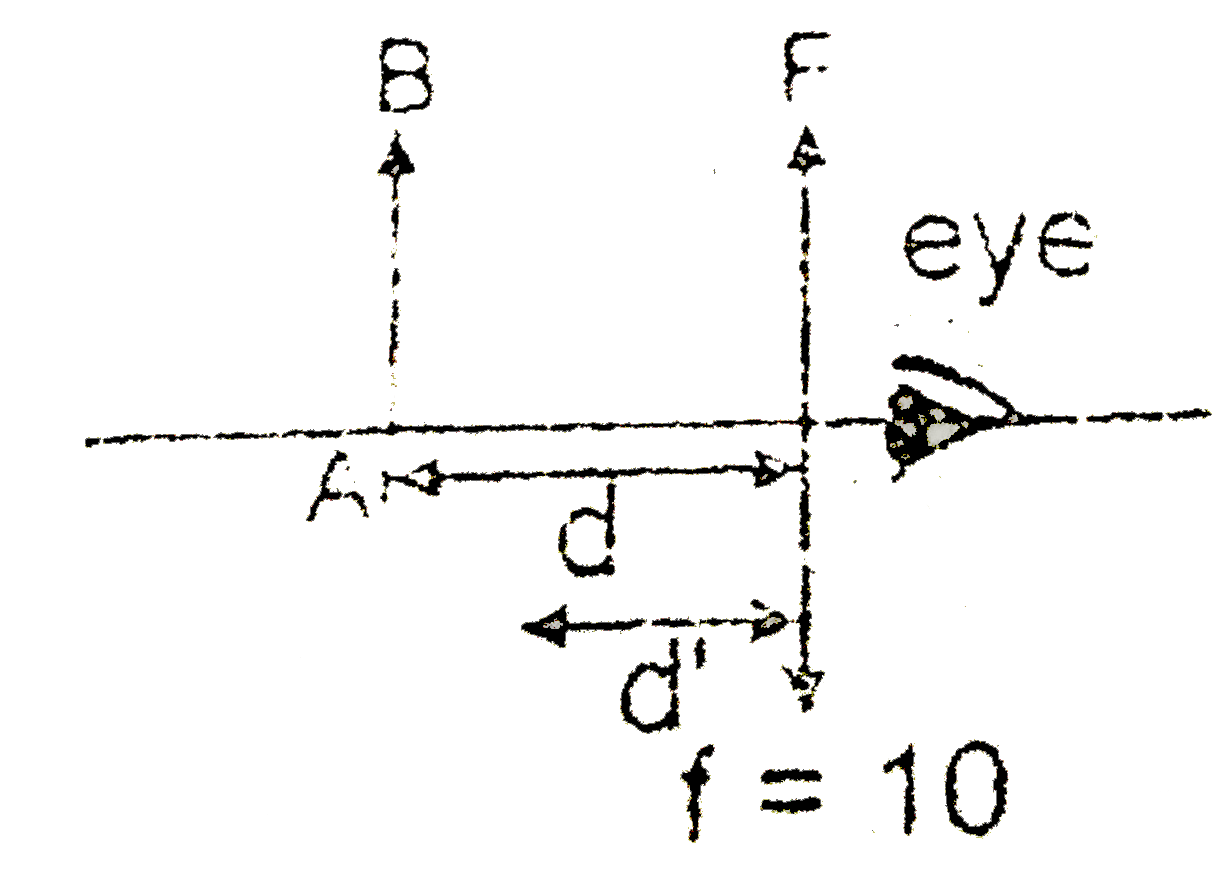 .
.
View SolutionIf the eye is kept very close to a coverging lens (focal length =10cm) and at the optical centre of the lens and an object is kept at distance 'd' of the object from the lebs so that its image can be seen clearly by the defect free eye is :
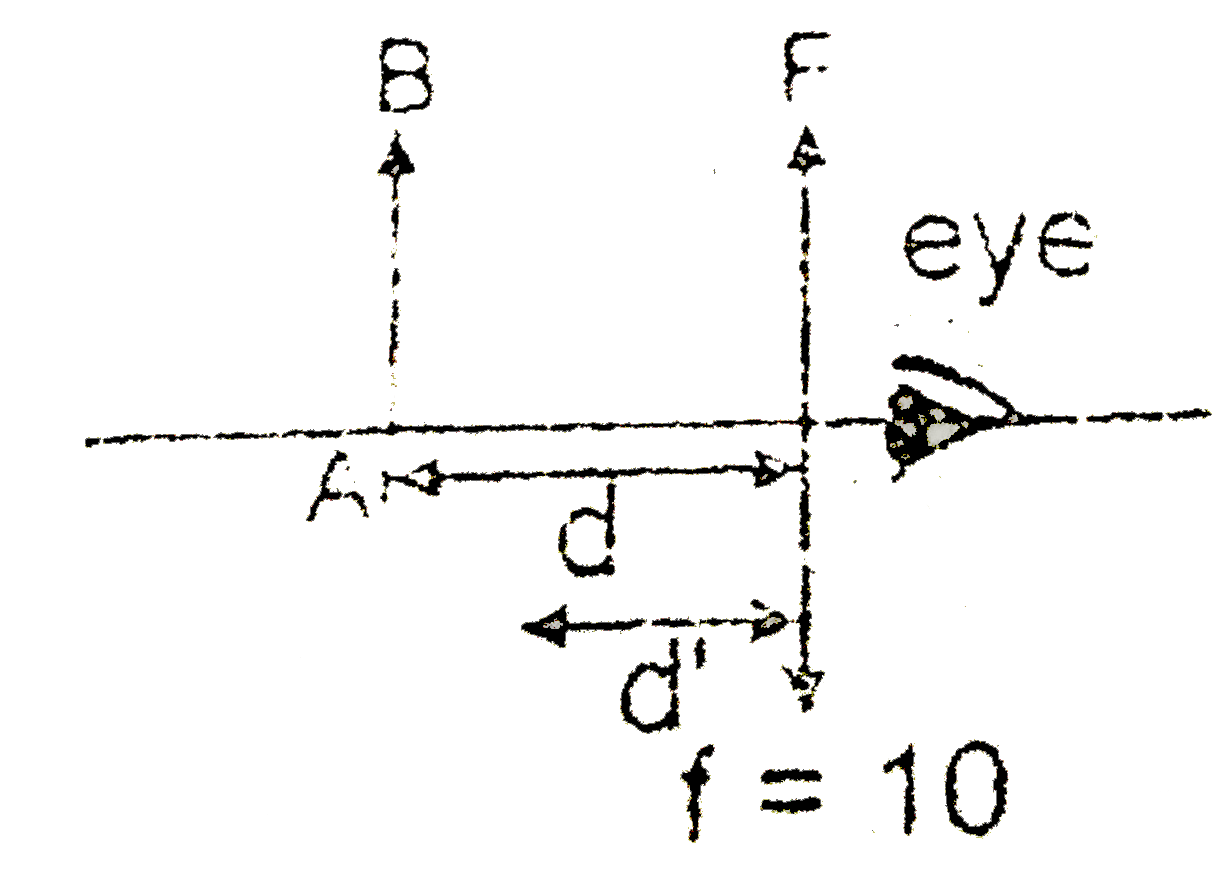 .
.
View Solution