What is the difference between r and R ?
To understand the difference between small r (r) and capital R (R), we can break it down step by step:
Step 1: Definition of r and R
- Small r (r): This represents the specific gas constant for a particular gas. It is defined as the universal gas constant (R) divided by the molar mass (M) of the gas. The units for r are typically J/(kg·K).
- Capital R (R): This is the universal gas constant. It is a constant that applies to all ideal gases and is used in the ideal gas law. The value of R is approximately 8.314 J/(mol·K) when using moles as the unit of measurement.
Step 2: Context of Use
- When to use r: The specific gas constant (r) is used when the mass of the gas is given in kilograms. It is particularly useful in thermodynamics and fluid mechanics when dealing with specific properties of gases.
- When to use R: The universal gas constant (R) is used when the amount of gas is measured in moles. It is commonly used in chemistry and physics for calculations involving ideal gases.
Step 3: Relationship between r and R
- The relationship can be expressed mathematically as:
r=RM
where M is the molar mass of the gas in kg/mol. This shows that the specific gas constant (r) is derived from the universal gas constant (R) by taking into account the molar mass of the gas.
Conclusion
In summary, the main difference between small r and capital R lies in their definitions and the context in which they are used. Small r is specific to a particular gas and is used with mass in kilograms, while capital R is a universal constant used with the amount of gas in moles.
---
- Small r (r): This represents the specific gas constant for a particular gas. It is defined as the universal gas constant (R) divided by the molar mass (M) of the gas. The units for r are typically J/(kg·K).
- Capital R (R): This is the universal gas constant. It is a constant that applies to all ideal gases and is used in the ideal gas law. The value of R is approximately 8.314 J/(mol·K) when using moles as the unit of measurement.
- When to use r: The specific gas constant (r) is used when the mass of the gas is given in kilograms. It is particularly useful in thermodynamics and fluid mechanics when dealing with specific properties of gases.
- The relationship can be expressed mathematically as:
r=RM
where M is the molar mass of the gas in kg/mol. This shows that the specific gas constant (r) is derived from the universal gas constant (R) by taking into account the molar mass of the gas.
In summary, the main difference between small r and capital R lies in their definitions and the context in which they are used. Small r is specific to a particular gas and is used with mass in kilograms, while capital R is a universal constant used with the amount of gas in moles.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- PROPERTIES OF MATTERBOOK - ICSECHAPTER - PROPERTIES OF MATTEREXERCISE - MODULE 3 (KINETIC THEORY OF GASES ) VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
11 Videos
- PROPERTIES OF MATTERBOOK - ICSECHAPTER - PROPERTIES OF MATTEREXERCISE - MODULE 3 (KINETIC THEORY OF GASES ) FROM GAS LAW AND EQUATION OF STATE
12 Videos
- PROPERTIES OF MATTERBOOK - ICSECHAPTER - PROPERTIES OF MATTEREXERCISE - MODULE 3 (KINETIC THEORY OF GASES ) LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
9 Videos
- OSCILLATIONS BOOK - ICSECHAPTER - OSCILLATIONS EXERCISE - SELECTED PROBLEMS (OSCILLATION IN A TUNNEL BORED THROUGH THE EARTH)
2 Videos
- SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER - 01 BOOK - ICSECHAPTER - SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER - 01 EXERCISE - SECTION - D
12 Videos
Similar Questions
In figure LM is a line parallel to the Y-axis at a distance of 3 units .
(i) What are the coordinates of the points P,R and Q ?
(ii) What is the difference between the abscissa of the points L and M ?
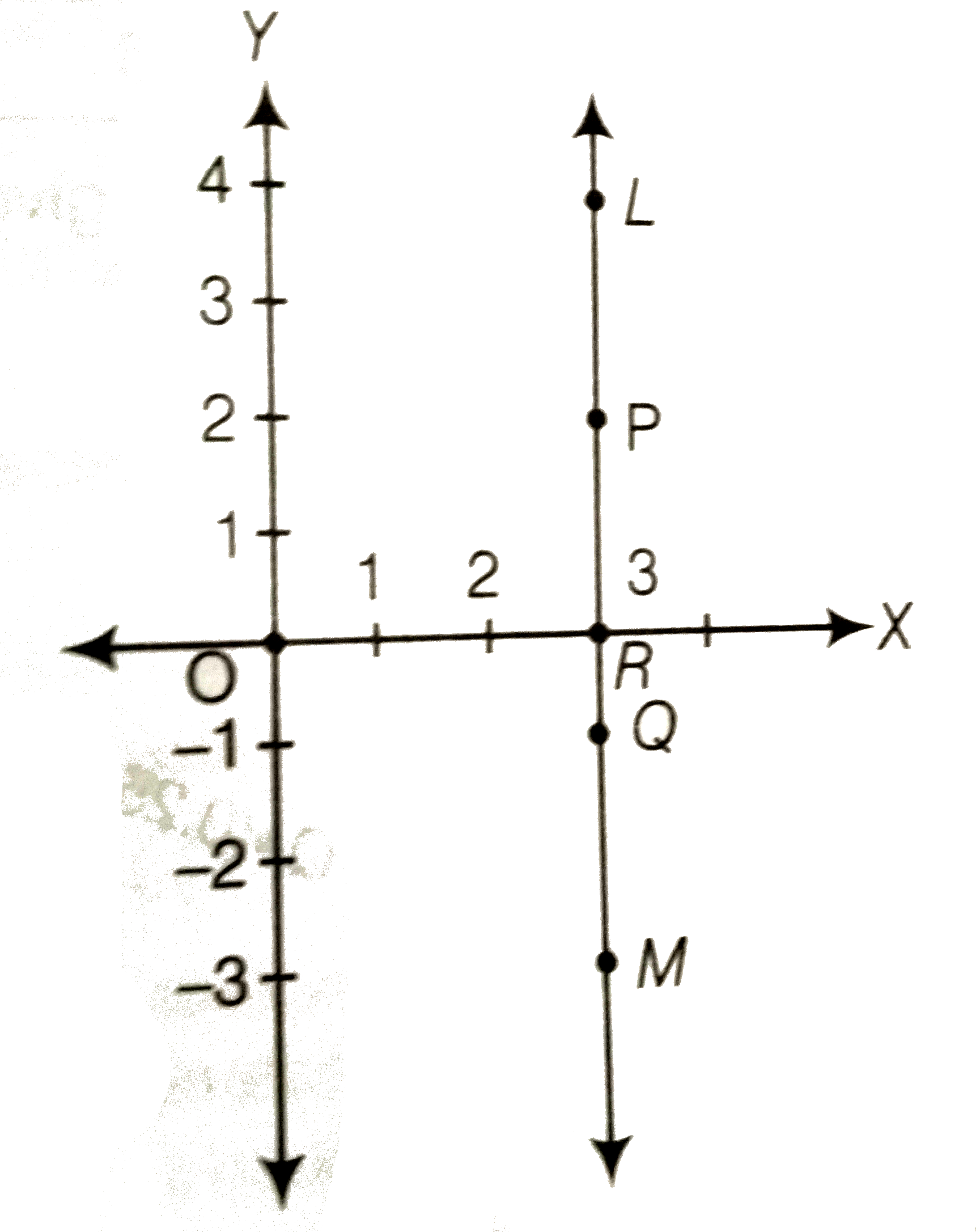
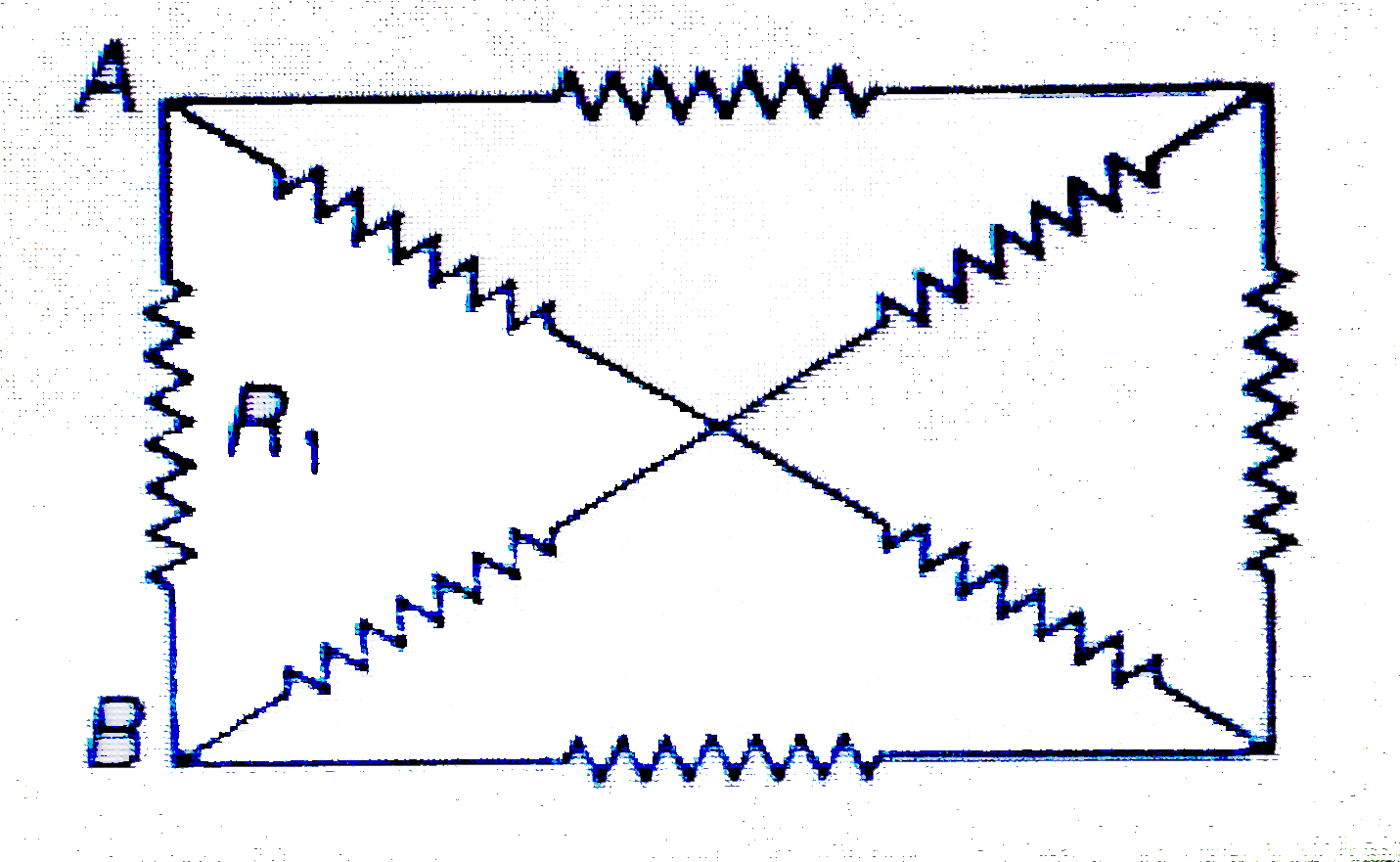
View SolutionAs shown, the circuit is made of 8 different resistance. It is found that when R1=4Ω, the resistance between A and B is 2Ω. Now replace R1 by a 6Ω resistor, what is the resistance between A and B ?
View Solution(a) If the radius of octahedral void is 'r' and the radius of the atoms in close packing is 'R' what is the relation between 'r' and 'R' ?
(b) A metal crystallises in body centred cubic structure. If 'a' is the edge length of its unit cell, 'r' is the radius of the sphere, what is the relation between 'r' and 'a' ?
View SolutionThe incircle of ΔABC touches side BC at D. The difference between BD and CD (R is circumradius of ΔABC) is
View SolutionA={1,2,3.5} and B={4,6,9}. Define a relation R from A to B by R = {(x, y): the difference between x and y is odd: x∈A,y∈B}. Write R in roster form.
View SolutionAssertion (A): Lithium chloride is predominantly covalent compound.
Reason (R ): electronegativity difference between Li and CI is small.
View SolutionTwo small metallic balls of radii R1&R2 are kept in vacuum at a large distance compared to the radii. Find the ratio between the charges on the two balls at which electrostatic energy of the system is minimum. What is the potential difference between the two balls ? total charge of balls is constant.
View SolutionIn a series C−R circuit shown in figureure, the applied voltage is 10V and the voltage across capacitor is found to8V. The voltage across R, and the phase difference between current and the applied voltage will respectively be
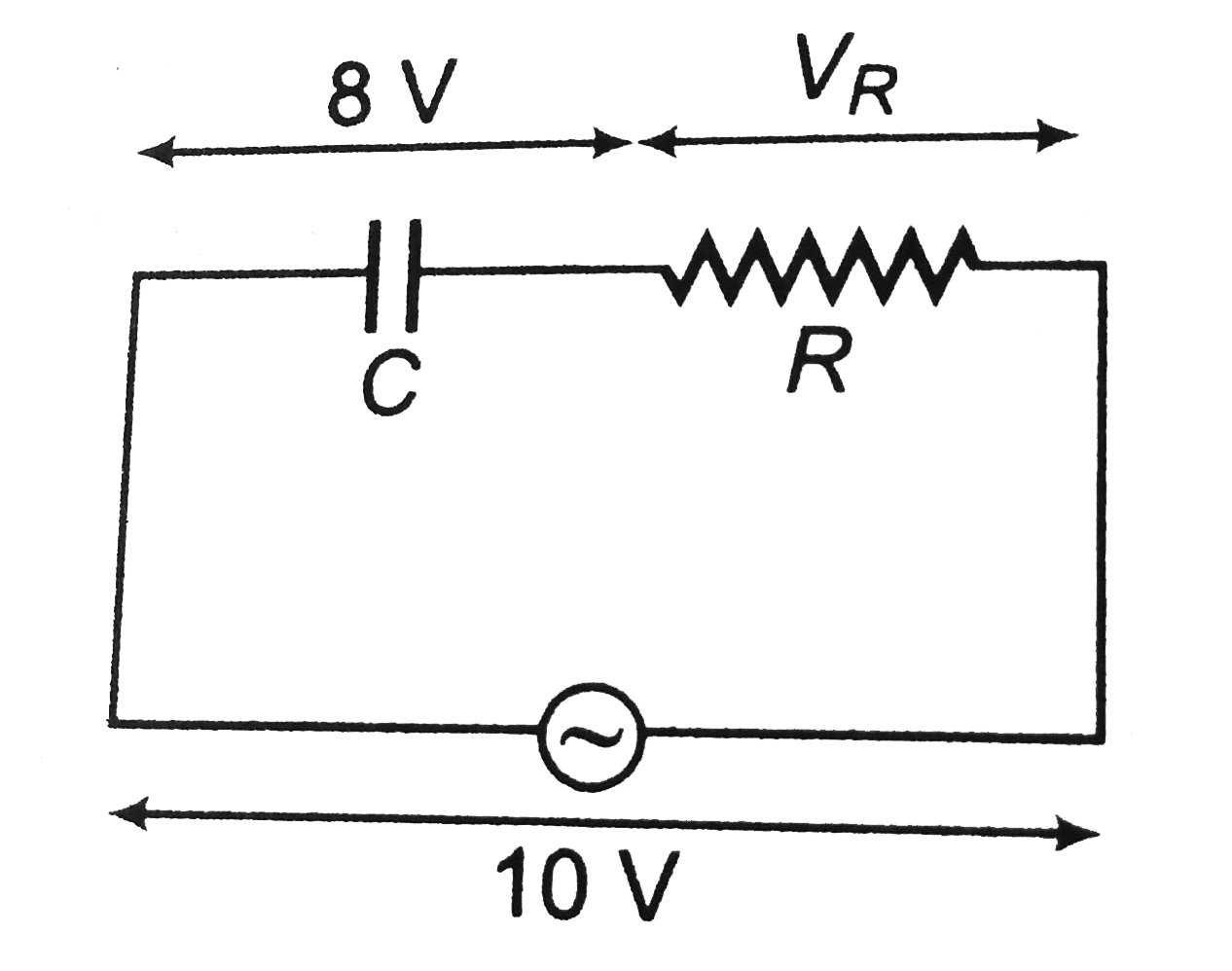 .
.
View SolutionIn a series C−R circuit shown in figureure, the applied voltage is 10V and the voltage across capacitor is found to8V. The voltage across R, and the phase difference between current and the applied voltage will respectively be
 .
.
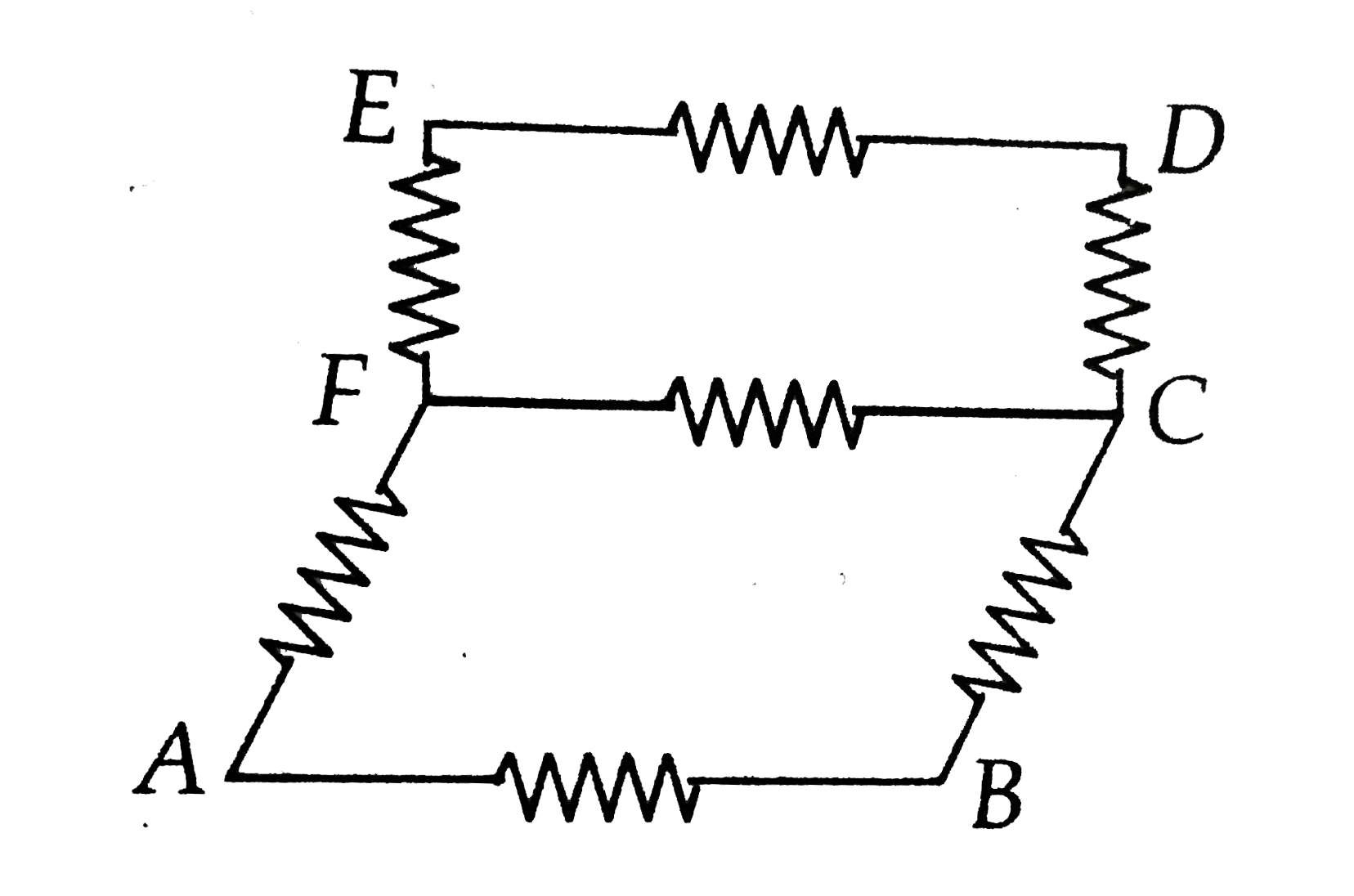
View SolutionIf the potential difference between A and D is V, what will be potential difference between F and C. each of the resistance is R.
View Solution

