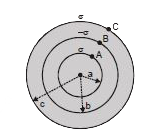
What is VA−VB in the arrangement shown in.What is the condition such that VA−VB=0
Let the charge be as shown in. We know that capacitors in series have the same charge. Considering the loop containing C1,C2 and E, we get
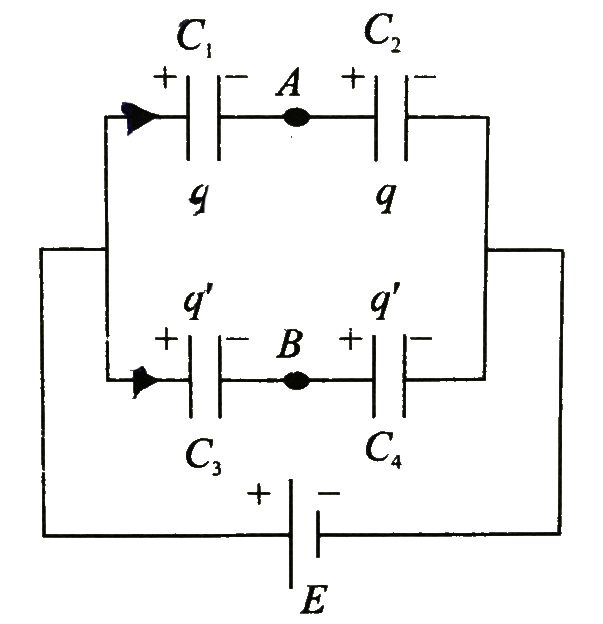
qC1+qC2−E=0
or q=E[C1C2C1+C2]
from the loop containting C3,C4, and E, we get
q'C3+q'C4−E=0 or q'=E[C3C4C3+C4]
Now
VA−VB=qC2−q'C4=E[C1C1+C2−C3C3+C4]
=E[C1C4−C3C2(C1+C2)(C3+C4)]
For VA−VB=0,C1C4=C2C3=0. If (C1/C2)=(C3/C4), the potential difference across A and B will be zero . This statement is very important is capacitor circuit solving. This type of the situation is callede balacned Wheatstone bridge.
टॉपर्स ने हल किए ये सवाल
- CAPACITOR AND CAPACITANCEBOOK - CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHCHAPTER - CAPACITOR AND CAPACITANCEEXERCISE - Solved Examples
9 Videos
- CAPACITOR AND CAPACITANCEBOOK - CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHCHAPTER - CAPACITOR AND CAPACITANCEEXERCISE - Exercise 4.1
13 Videos
- ATOMIC PHYSICSBOOK - CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHCHAPTER - ATOMIC PHYSICSEXERCISE - ddp.4.3
15 Videos
- CENGAGE PHYSICS DPPBOOK - CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHCHAPTER - CENGAGE PHYSICS DPPEXERCISE - single correct type
14 Videos
समान प्रश्न
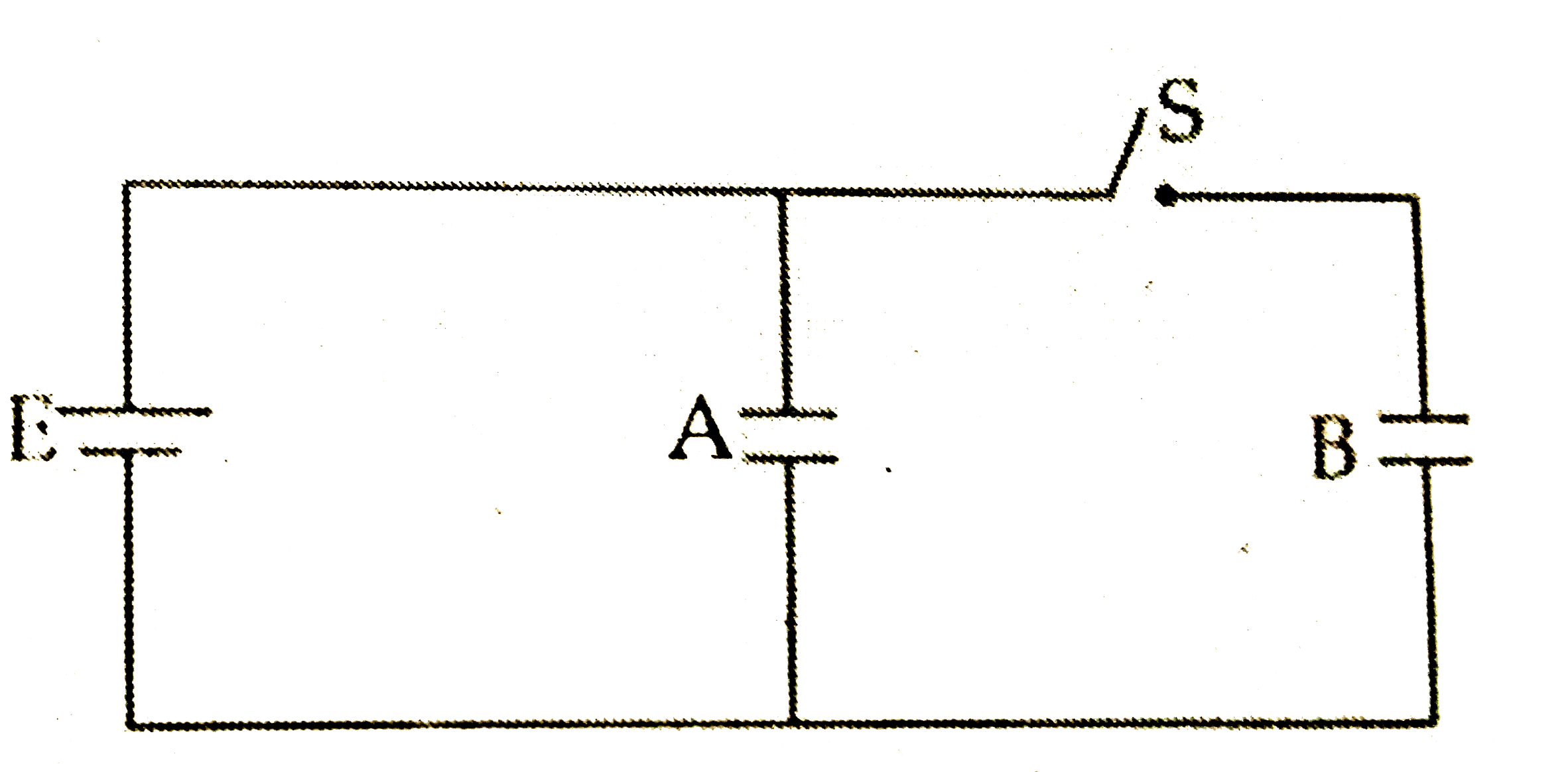
Two identical parallel plate capacitors A and B are
connected to a battery of V volts with the switch S
closed . The switch is now opend and the free
space between the plantes of the capacitors is filled
with a dielectric of dielectric constant K. Find the
rario of the total electrostatic energy stored in both
capacitors before and after the introduction of the dielectric.
View SolutionSuppose the two plates of a capacitor have different areas. When the capacitor is charged by connecting it to a battery, do the charges on the two plates have equal magnitued, or can they be differet? Explain you reasoning.
View SolutionThe continuous x - ray spectrum obtained from a Coolidge tube is of the form
View Solutionddx(√x+1√x)2=
View SolutionWhat is V_(A)-V_(B) in the arrangement shown in.What is the condition such that V_(A)-V_(B)=0
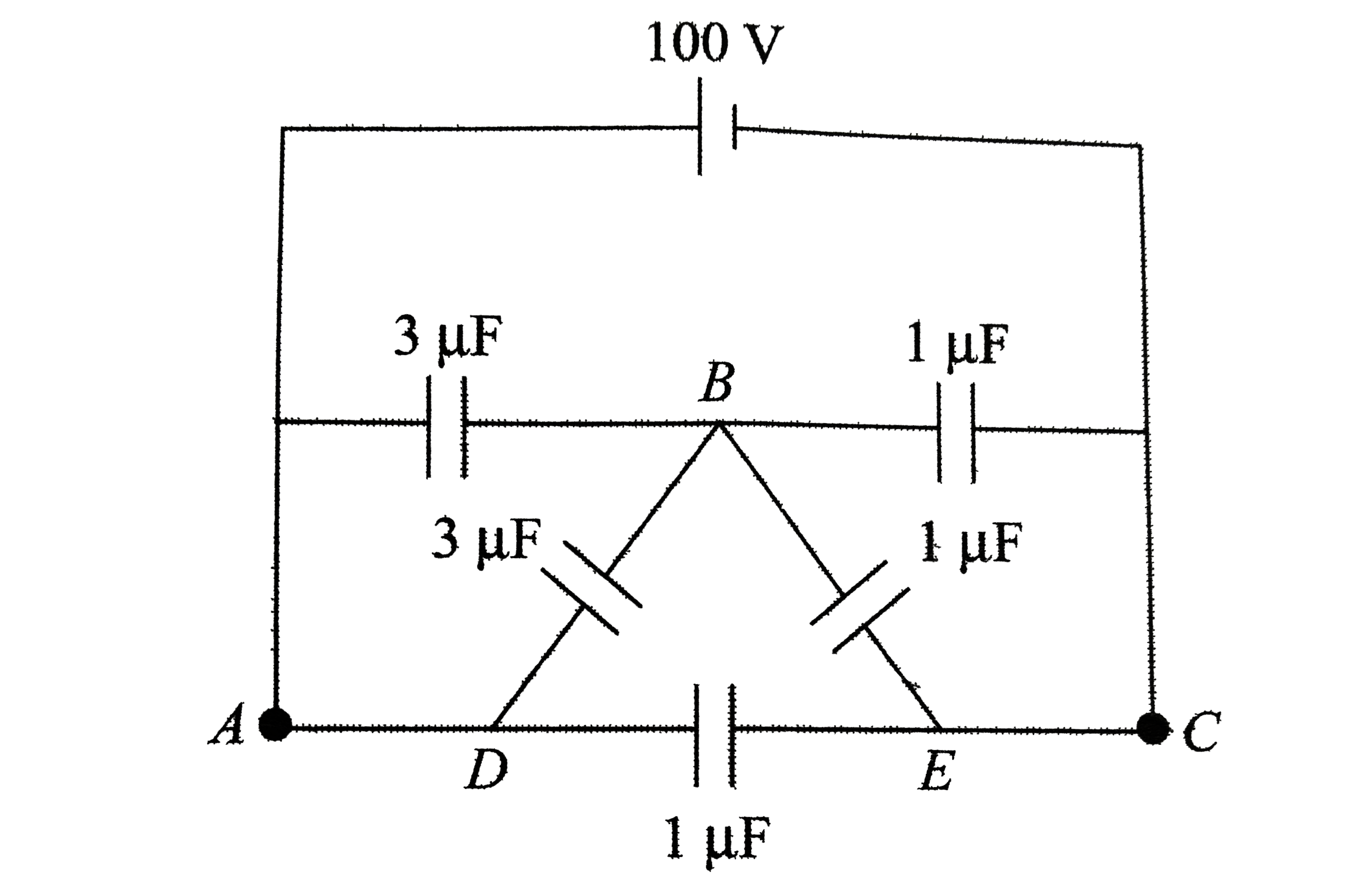
View SolutionIn the system is in steady state. Then
a. VA−VB=_______
b. VB−VC=______
c. VD−Ve=______
d. The energy stored in the circuit is "________"
 .
.
View SolutionThree block 1, 2 and 3 are arranged as shown in the figure. The velocities of the blockes v_(1) , v_(2) and v_(3) are shown in the figure. What is the relationship between v_(1) , v_(2) and v_(3) ?
View SolutionFind out following (i) V_(A)-V_(B) (ii) V_(B)-V_(C) (iii) V_(C)-V_(A) (iv) V_(D)-V_(C) (v) V_(A)-V_(D) (vi) Arrange the order of potential for points A, B, C and D.
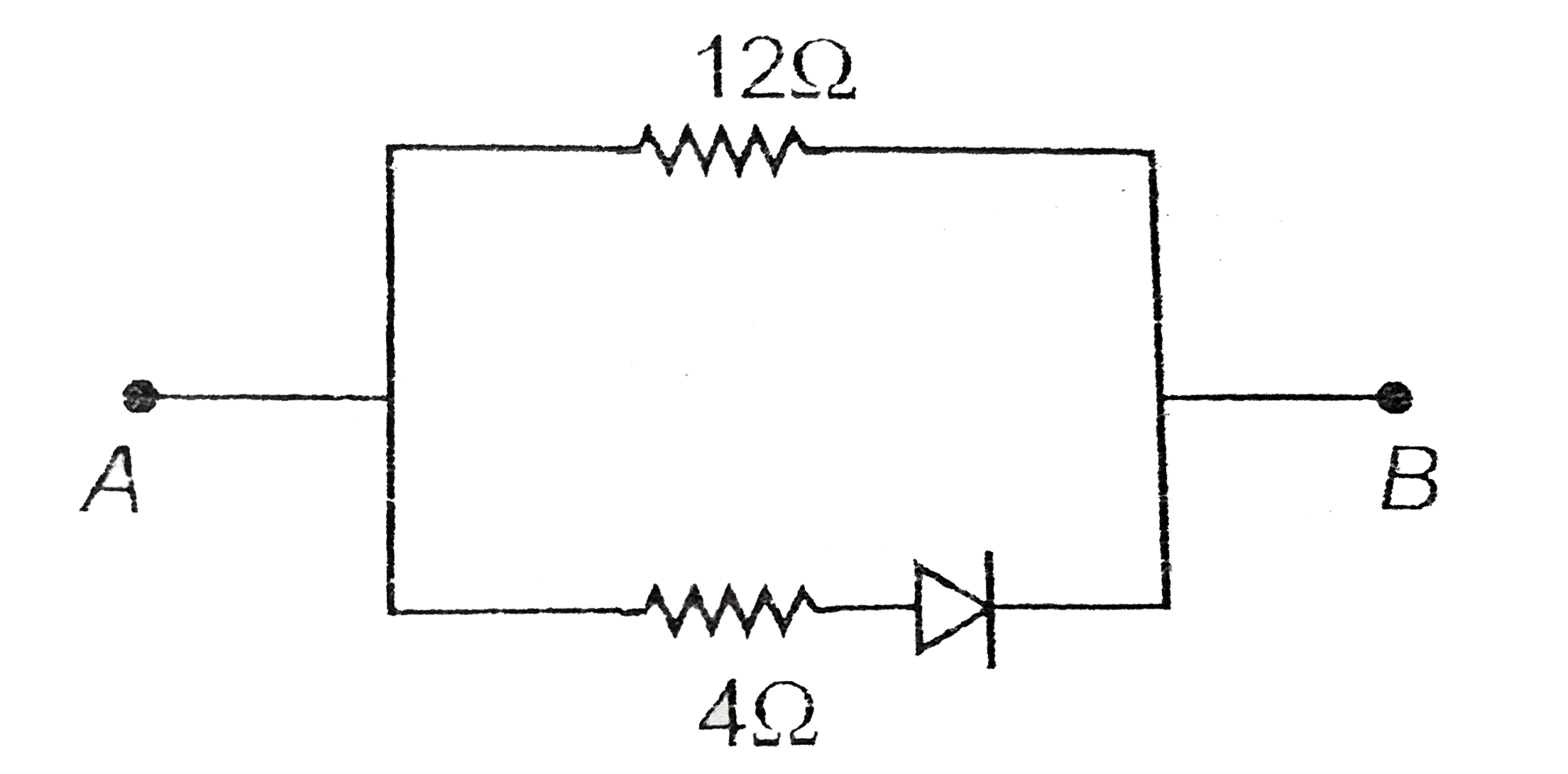
View SolutionFind the equivalent resistance of the network shown in the figure between the points A and B if
(i) VA>VB (ii) VA<VB
View Solutionदर्शाये गये आरेख में बिन्दुओ A तथा B के बीच विभवांतर (VA−VB) होगा :
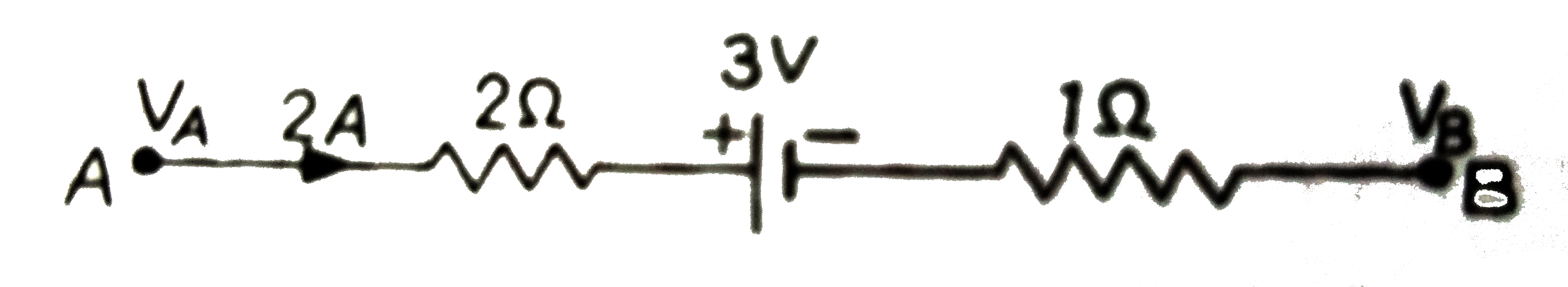
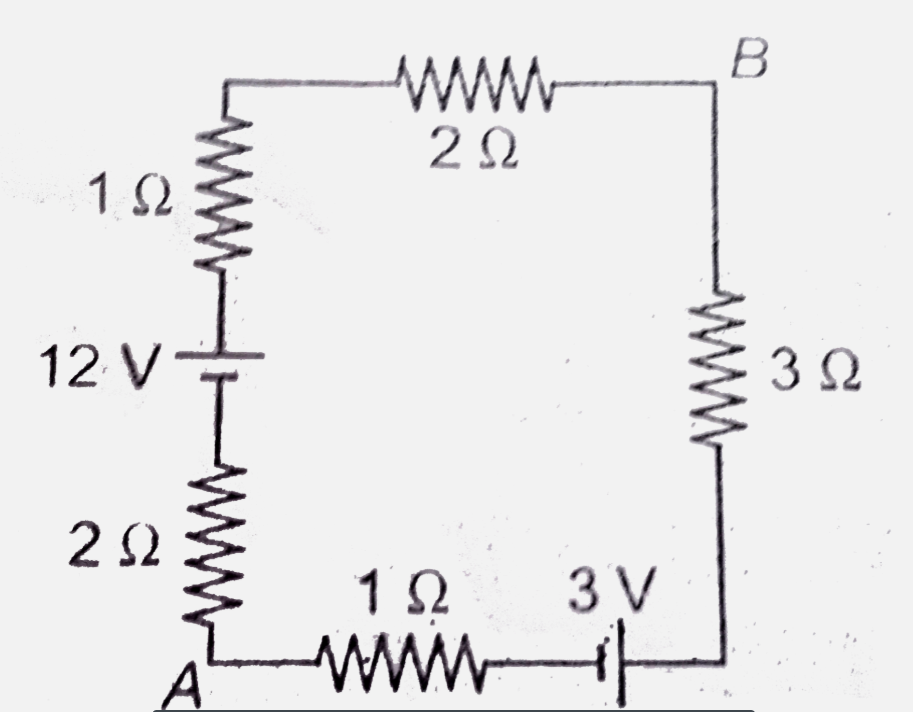
View SolutionPotential difference VB−VA in the network shown is
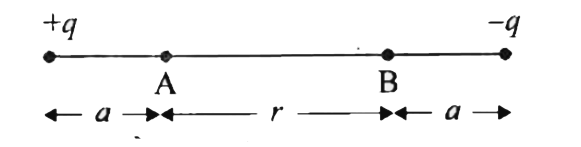
View Solutionदो आवेशों +q तथा –q चित्रानुसार व्यवस्थि)त हैं। A तथा B बिंदुओं पर विभव क्रमशः VA तथा VB हैं तब VA−VB ज्ञात कीजिए।
View SolutionFind V_(A)-V_(B)
View SolutionPotential difference VA−VB in the network shown in
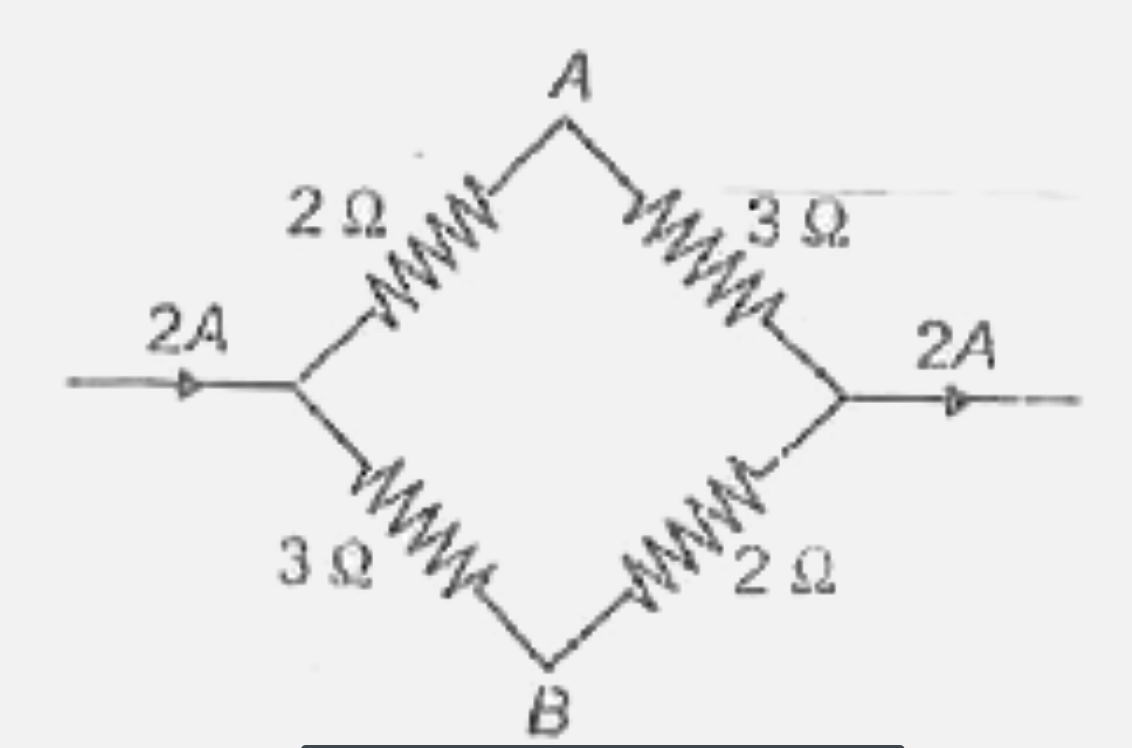
View SolutionVA,VB,VC, ज्ञात कीजिए तथा यदि VA=VC हो तो आवश्यक शर्त क्या होगी।
View Solution

