When source and detector are stationary but the wind is blowing at speed vW, the apparent wavelength λ' on the wind side is related to actual wavelength λ by [take speed of sound is air as v]
λ'=λ
λ'=vWvλ
λ'=vW+vvλ
λ'=vv−vWλ
The correct Answer is:C
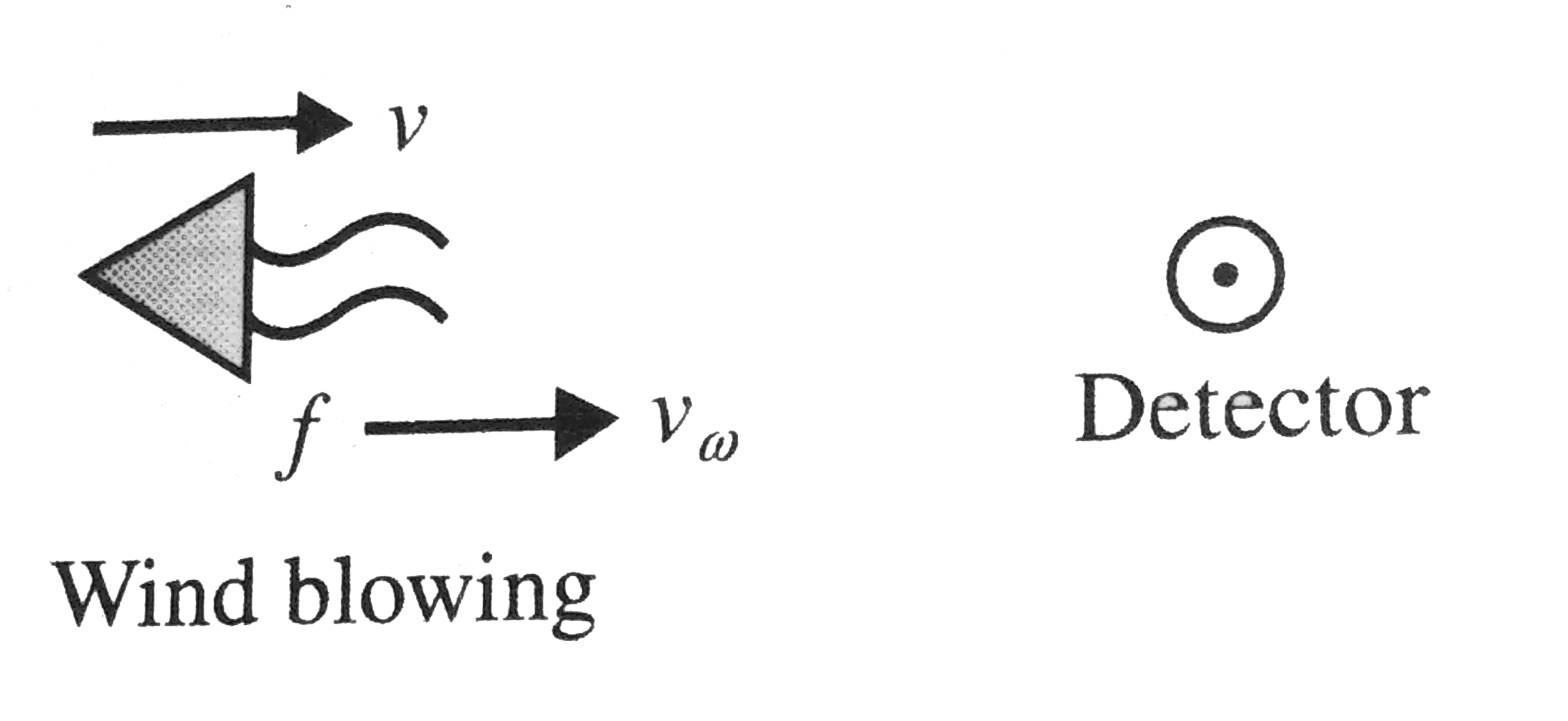
λ'=v+vωf=v+vωvλ
Topper's Solved these Questions
- SOUND WAVES AND DOPPLER EFFECTBook:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:SOUND WAVES AND DOPPLER EFFECTExercise:Multiple Correct
Explore 44 Videos
- SOUND WAVES AND DOPPLER EFFECTBook:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:SOUND WAVES AND DOPPLER EFFECTExercise:Assertion-Reasoning
Explore 24 Videos
- SOUND WAVES AND DOPPLER EFFECTBook:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:SOUND WAVES AND DOPPLER EFFECTExercise:Subjective
Explore 56 Videos
- RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2Book:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2Exercise:Interger
Explore 2 Videos
- SUPERPOSITION AND STANDING WAVESBook:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:SUPERPOSITION AND STANDING WAVESExercise:Comprehension Type
Explore 5 Videos
Similar Questions
Which of the following statements are incorrect?
View SolutionStatement I: A tuning fork is considered as a source of an acoustic wave of a single frequency as marked on its body. Statement II: The tuning fork cannot produce any of its harmonics due to its special nature of construction.
View SolutionIn a car race sound signals emitted by two cars are detected by the detector on the straight track at the end point of the race. Frequency observer is 330 Hz and 360 Hz and the original frequency is 300 Hz of both cars. Race ends with the separation of 100 m between the cars. Assume both cars move with constant velocity and velocity of sound is 330ms. Find the time taken by wining car.
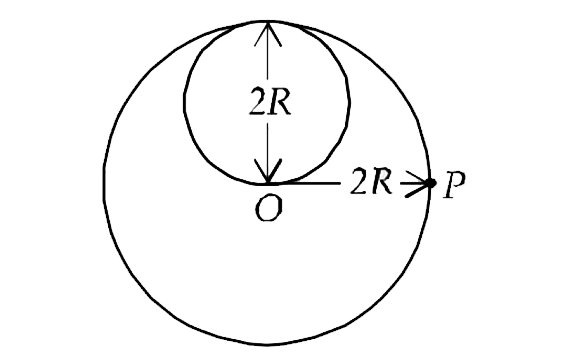
View SolutionA lamina is made by removing a small disc of diameter 2R from a bigger disc of uniform mass density and radius 2R, as shown in the figure. The moment of inertia of this lamina about axes passing though O and P is IOandIP respectively. Both these axes are perpendicular to the plane of the lamina. The ratio IPIO is
View SolutionA string of length L, fixed at its both ends is vibrating in its 1st overtone mode. Consider two elements of the string of the same small length at positions l1=0.2Landl2=0.45L from one end.
If K1andK2 are their respective maximum kinetic energies,then
View SolutionA stationary source emits sound of frequency
υ=1200Hz. If a wind blows at the speed of 0.1c deduce (i) the percentage change in the wavelength and (ii) the change in the frequency for a stationary observer on the wind side of the source. What happens when there is no wind, but the observer moves at speed 0.1c towards the source?
View SolutionAn observer moves towards a stationary source of sound with a speed (15)th of the speed of sound. The wavelength and frequency of the source emitted are λ and f, respectively. The apparent frequency and wavelength recorded by the observer are, respectively.
View SolutionWhen source and detector are stationary but the wind is blowing at speed v_W , the apparent wavelength lamda' on the wind side is related to actual wavelength lamda by [take speed of sound is air as v]
View SolutionA stationary source emits sound of frequency 1200 Hz. If would blows at the speed of 0.1 v. deduce (a) The change in the frequency for a stationary observer on the wind side of the source (b) Report the calculations for the case when there is no wind but the observer moves at 0.1 v speed towards the source (Given : velocity of sound = v)
View SolutionA sound source emits waves of frequency f0 and wavelength λ0 in still air. When there is a wind blowing with speed u from left to right what will be wavelength of sound to the right of the source and to the left of the source.
View SolutionIn the case of sound waves, wind a blowing from source to reciver with speed U_(W) . Both source and receiver are stationary.If lambda_(0) is the original wavelength with no wind and V is speed of sound in air then wavelength as received is given by :
View SolutionA source of sound S having frequency f. Wind is blowing from source to observer O with velocity u. If speed of sound with respect to air is C, the wavelength of sound detected by O is :
View SolutionAn observer is approaching with a speed v , towards a stationary source emitting sound waves of wavelength lambda_0 . The wavelength shift detected by the observer is ( Take c= speed of sound )
View SolutionWhen source and detector are stationary, but the wind is blowing at speed Vw, the apparent wavelength λ1 on the wind side is related to the actual wavelength λ by (speed of sound is V):
View SolutionOne person moves towards a stationary source of sound with a speed (1)/(5) times the speed of sound. Sound emitted from the source has wavelength lamda and frequency f. Frequency and wavelength of sound heard by this person are respectively ......
View SolutionWhen source and detector are stationary but the wind is blowing at speed vW, the apparent wavelength λ' on the wind side is related to actual wavelength λ by [take speed of sound is air as v]
View Solution
