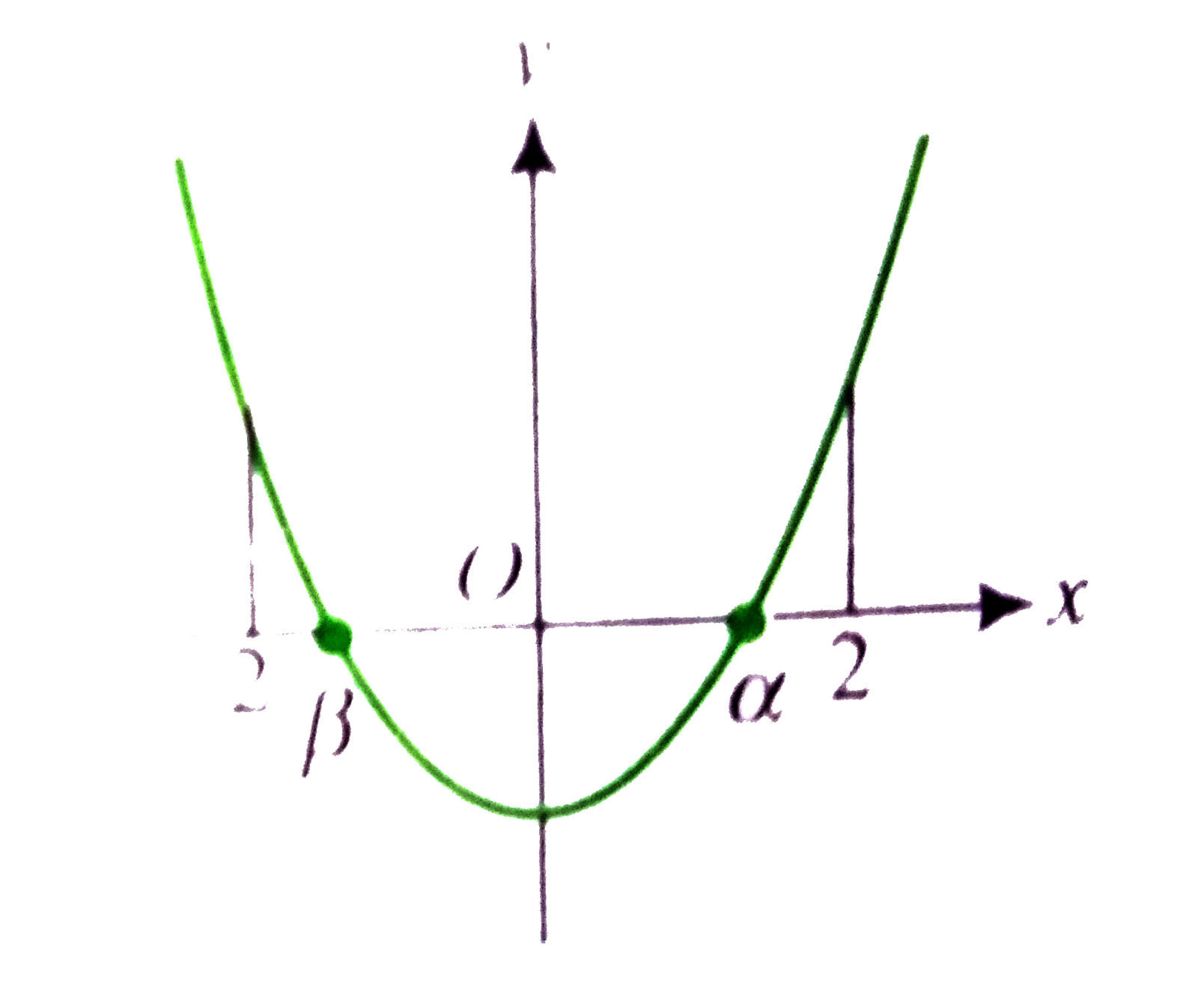
Consider a quadratic equation ax2+bx+c=0 having roots α,β. If 4a+2b+c>0,a−b+c<0and4a−2b+C>0 then |[α]+[β]| can be {where [] is greatest integer}
−2
−1
0
1
The correct Answer is:1,2,3
Form the given conditions we have following possible graph of y=f(x) Form the graph.
[α]=0or1,[β]=−2or−1
∴[α]+[β] can be −1,0,−2
Topper's Solved these Questions
- THEORY OF EQUATIONSBOOK - CENGAGE PUBLICATIONCHAPTER - THEORY OF EQUATIONSEXERCISE - Linked Comprechension Type
37 Videos
- THEORY OF EQUATIONSBOOK - CENGAGE PUBLICATIONCHAPTER - THEORY OF EQUATIONSEXERCISE - MATRIX MATCH TYPE
6 Videos
- THEORY OF EQUATIONSBOOK - CENGAGE PUBLICATIONCHAPTER - THEORY OF EQUATIONSEXERCISE - Single Correct Answer Type : Exercise
89 Videos
- STRAIGHT LINESBOOK - CENGAGE PUBLICATIONCHAPTER - STRAIGHT LINESEXERCISE - ARCHIVES (NUMERICAL VALUE TYPE)
1 Video
- THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRYBOOK - CENGAGE PUBLICATIONCHAPTER - THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRYEXERCISE - All Questions
291 Videos
Similar Questions
Consider an unknow polynomial which divided by (x−3) and (x−4) leaves remainder 2 and 1, respectively. Let R(x) be the remainder when this polynomial is divided by (x−3)(x−4).
If equations R(x)=x2+ax+1 has two distint real roots, then exhaustive values of a are.
View SolutionMatch the following for the equation x2+a|x|+1=0 where, a is a parameter.

View SolutionThe value of expression x4−8x3+18x2−8x+2 when x=2+√3
View SolutionFor a point P in the plane, let d1(P)andd2(P) be the distances of the point P from the lines x−y=0andx+y=0 respectively. The area of the region R consisting of all points P lying in the first quadrant of the plane and satisfying 2≤d1(P)+d2(P)≤4, is
View SolutionFind the angle between the line whose direction cosines are given by l+m+n=0andl2+m2−n2=0.
View SolutionIf αandβ are roots of the quadratic equation ax2+bx+c=0 and a+b+c>0,a−b+c>0&c<0,then[α]+[β] is equal to (where [.] denotes the greatest integer function) 10 b. −3 c. −1 d. 0
View SolutionIf alpha and beta(alpha
View SolutionIf alpha,beta are the roots of the equation ax^(2)+bx+c=0 such that beta
View SolutionIf alpha and beta ( alpha
View SolutionConsider a quadratic equation ax^(2)+bx+c=0 having roots alpha,beta. If 4a+2b+c>0,a-b+c then [[alpha]+[beta]| can be { where [] is greatest integer }
View SolutionLet αandβ be the roots of the quadratic equation ax2+bx+c=0,c≠0, then form the quadratic equation whose roots are 1−ααand1−ββ.
View SolutionLet a, b, c ∈ R and α,β are the real roots of the equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 and if a + b + c < 0, a – b + c < 0 and c > 0 then [α]+[β] is equal to (where [.] denotes the greatest integer function.)
View SolutionIf α,β are the roots of ax2+bx+c=0, αβ=3 and a, b, c are in A.P., then α+β =
View SolutionConsider a quadratic equation ax2+bx+c=0 having roots α,β. If 4a+2b+c>0,a−b+c<0and4a−2b+C>0 then |[α]+[β]| can be {where [] is greatest integer}
View Solutionα,β are roots of quadratic equation ax2+bx+c=0. Then (α+β)=______ a)−ba b)ba c)−ca d)ca
View SolutionLet a, b and c bereal numbers such that 4a+2b+c=0 and ab > 0. Then the quadratic equation ax2+bx+c=0 has
View Solution

