If nsinx=logex has exactly 1 root, then find the possible value of n(n∈N).
nsinx=logex
⇒sinx=logexn
For exactly one root, the graph of y=sinx must intersect the graph of y=logexn exactly once.
Maximum value of sin x is 1.
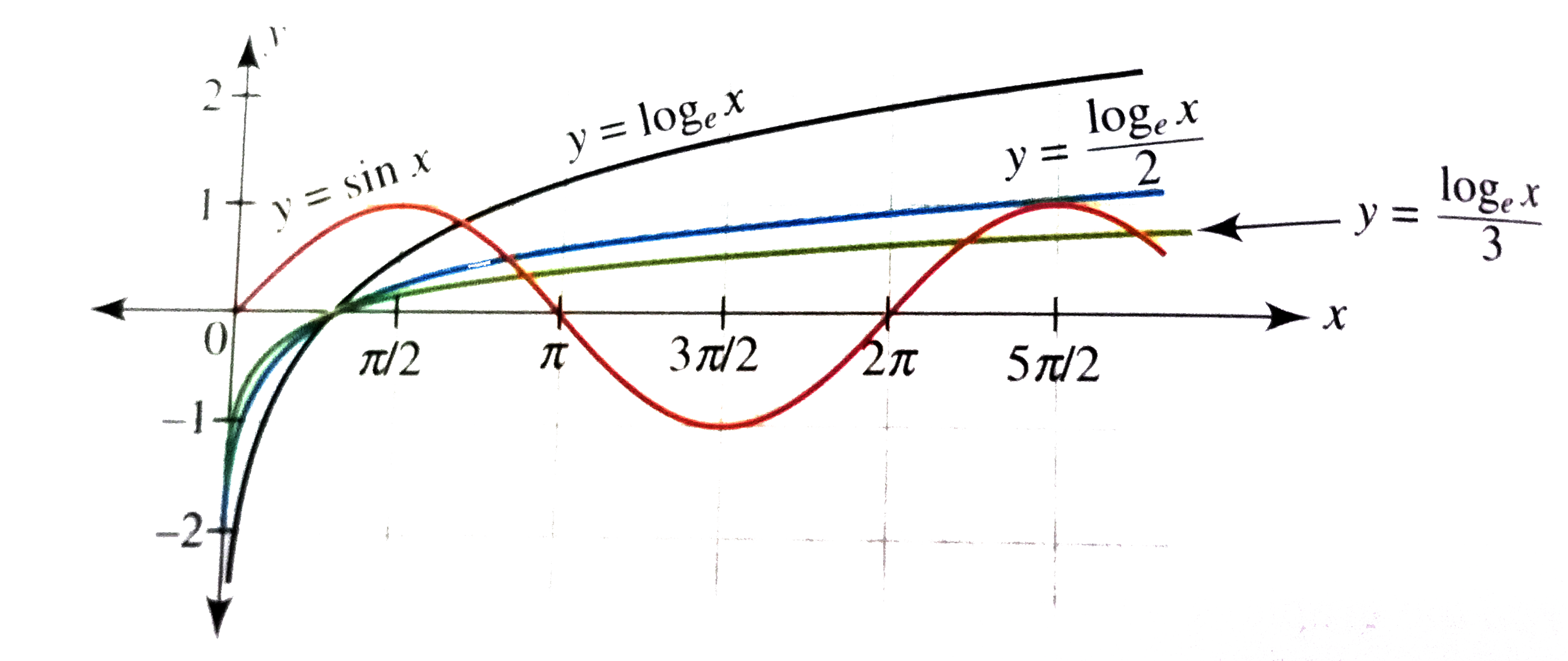
For n=1,sinx=logex
Graphs of y=sinxandy=logex intersect only once as shown in the following figure. For x=e,logee=1, hence after x=e,y=logex never meets y=sinx.
For n=2,letlogex2=1∴logex=2orx=e2<5π/2
Hence the graph of y=logex2 meets y=sinx only once.
But for n=3andlogex3=1,x=e2>5π/2 hence the graph of y=logex3 meet the graph of y=sinx more than once.
So for exactlly one root of the equation sinx=logexn,n=1or2.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- GRAPHICAL TRANSFORMATIONSBook:CENGAGEChapter:GRAPHICAL TRANSFORMATIONSExercise:Exercise
Explore 22 Videos
- GRAPH OF INVERSE TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONSBook:CENGAGEChapter:GRAPH OF INVERSE TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONSExercise:Exercise
Explore 18 Videos
- GRAPHS OF POLYNOMIAL AND RATIONAL FUNCTIONSBook:CENGAGEChapter:GRAPHS OF POLYNOMIAL AND RATIONAL FUNCTIONSExercise:Exercise
Explore 13 Videos
Similar Questions
Draw the graph of y=tan−1x−cot−1x.
View SolutionDraw the graph of y=tan−1x+cot−1x
View SolutionDraw the graph of y=(x−1)(x2−x+1).
View SolutionFind the possible values of p such that the equation px2=(log)ex has exactly one solution.
View SolutionIf exactly one root of the equation x^(2)-2kx+k^(2)-1=0 satisfies the inequality log_(sqrt(3))(2-x)<=0 then find sum of all possible integral values of k
View SolutionEvaluate limn→∞1n2(logen−loge(n−1))+n.
View SolutionIf loge(logex−logey)=ex2y(1−logex), then find the value of y'(e).
View SolutionEquation xn−1=0,n>1,n∈N, has roots 1,a1,a2,...,an−1,. The value of (1−a1)(1−a2)...(1−an−1), is
View Solution∫xn[logex+1]dx का मान ज्ञात कीजिए |
View SolutionGiven
x2−8x+64=0 has equal roots
logma+logna=logm+na
ex−y=(exey)
If x, y in R |x + y| = |x – y| then xy = 1 Find which two are correct in the above
View SolutionEvaluate ∫1xl(x)l2(x)....ln(x) dx
where ln(x)=logeloge.......Loge(x ) (n times)
View SolutionIf nsinx=logex has exactly 1 root, then find the possible value of n(n∈N).
View SolutionEvaluate limn→∞1n2(logen−loge(n+1))+n.
View SolutionIf loge(logex−logey)=ex2y(1−logex), then find the value of y'(e).
View SolutionIf loge(logex−logey)=ex2y(1−logex), then find the value of y'(e).
View Solution

