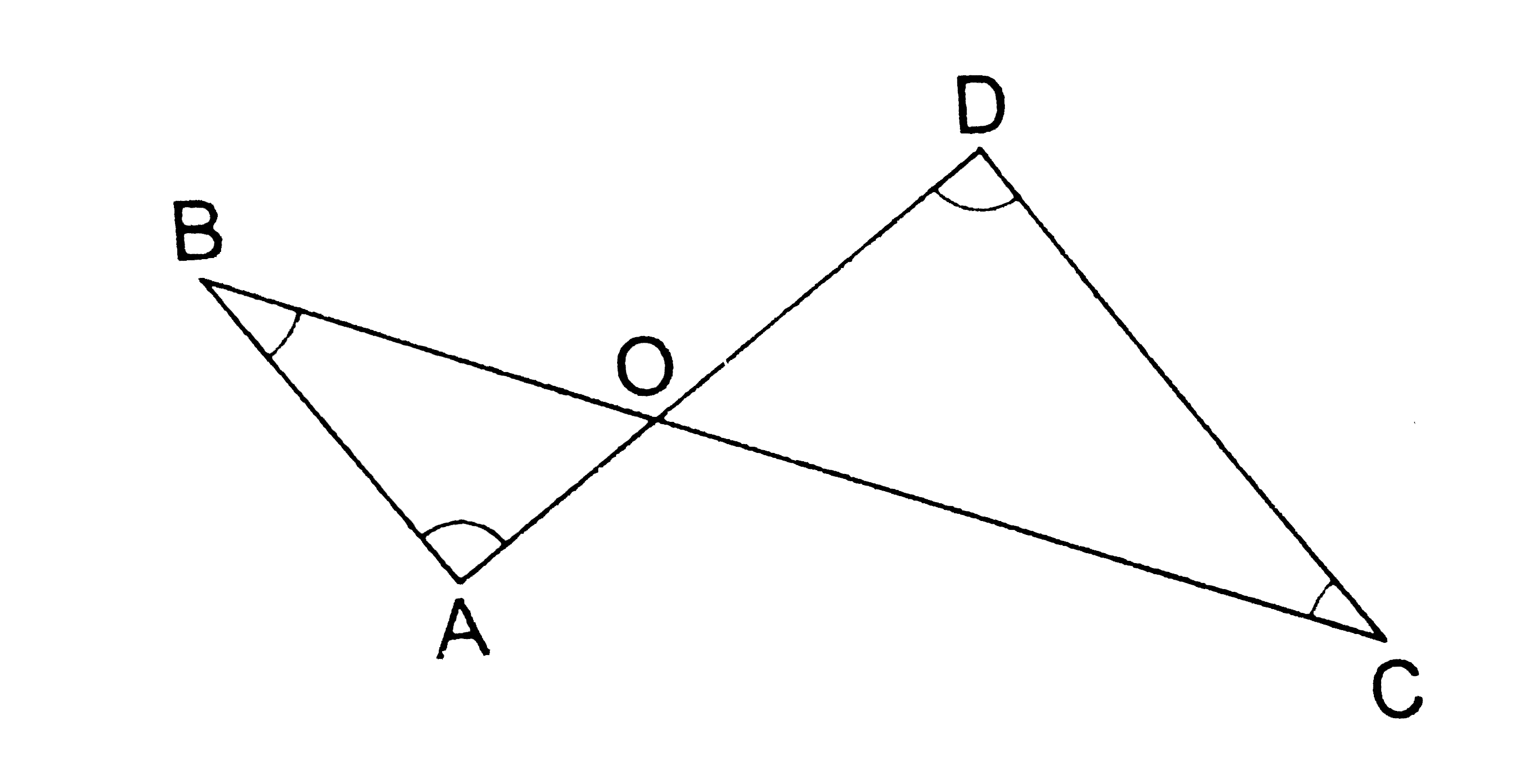
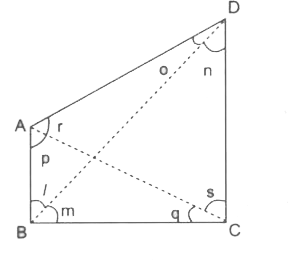
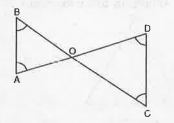
In figure, ∠B<∠A and ∠C<∠D. Show that AD<BC.
To solve the problem, we need to show that if ∠B<∠A and ∠C<∠D, then AD<BC. Here’s a step-by-step solution:
Step 1: Understand the Angles and Sides
Given:
- ∠B<∠A
- ∠C<∠D
From the properties of triangles, we know that the side opposite a larger angle is longer than the side opposite a smaller angle.
Step 2: Relate Angles to Their Opposite Sides
From ∠B<∠A:
- The side opposite ∠B is AO.
- The side opposite ∠A is BO.
- Therefore, we can conclude that:
AO<BO
From ∠C<∠D:
- The side opposite ∠C is OD.
- The side opposite ∠D is OC.
- Therefore, we can conclude that:
OD<OC
Step 3: Combine the Inequalities
Now we have two inequalities:
1. AO<BO
2. OD<OC
Step 4: Add the Inequalities
By adding the two inequalities:
AO+OD<BO+OC
Step 5: Substitute the Sides
Now, we can substitute:
- AO+OD is equal to AD
- BO+OC is equal to BC
Thus, we can rewrite the inequality as:
AD<BC
Conclusion
We have shown that if ∠B<∠A and ∠C<∠D, then AD<BC.
Given:
- ∠B<∠A
- ∠C<∠D
From ∠B<∠A:
- The side opposite ∠B is AO.
- The side opposite ∠A is BO.
- Therefore, we can conclude that:
AO<BO
- The side opposite ∠C is OD.
- The side opposite ∠D is OC.
- Therefore, we can conclude that:
OD<OC
Now we have two inequalities:
1. AO<BO
2. OD<OC
By adding the two inequalities:
AO+OD<BO+OC
Now, we can substitute:
- AO+OD is equal to AD
- BO+OC is equal to BC
AD<BC
We have shown that if ∠B<∠A and ∠C<∠D, then AD<BC.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- TRIANGLESBook:NAGEEN PRAKASHAN ENGLISHChapter:TRIANGLESExercise:Problems From NCERT/exemplar
Explore 5 Videos
- TRIANGLESBook:NAGEEN PRAKASHAN ENGLISHChapter:TRIANGLESExercise:Exercise 7a
Explore 35 Videos
- SURFACE AREA AND VOLUMEBook:NAGEEN PRAKASHAN ENGLISHChapter:SURFACE AREA AND VOLUMEExercise:Revision Exercise (long Answer Questions)
Explore 10 Videos
Similar Questions
If 3 sides of a triangle are 35 cm, 16 cm and 12 cm, then which type of triangle is this ?
View SolutionWhich of the following pairs of triangles are congruent ? Also state the condition of congruency in each case :

(iv) In ΔABC and ΔDEF,AB=EF,BC=DF and ∠B=∠F
(v) In ΔABC and ΔPQR,AB=QR,AC=PR and ∠B=∠R
(vi) In ΔABC and ΔPQR,∠A=∠P,AC=PR and AB=PQ
(vi) In ΔABC and ΔPQR,AB=QR,∠A=∠Q and AC=QP.
View SolutionHow many cubic metres of earth must be dug out to sink a well 14 m deep and having a radius of 4 m. If the earth taken out is spread over a plot of dimension (25m×16m). What is the height of the plateform so formed?
View SolutionIn figure, ∠B<∠A and ∠C<∠D. Show that AD<BC.
View SolutionIn a triangle ABC, ∠A<∠B,∠B>∠C and ∠A=2∠C, prove that AC>BC>AB.
View SolutionIn the given figre, ∠B<∠Aand∠C<∠D. Show that AD<BC.
View Solutionआकृति ∠B<∠A और ∠C<∠D है दर्शाइए की AD<BC है

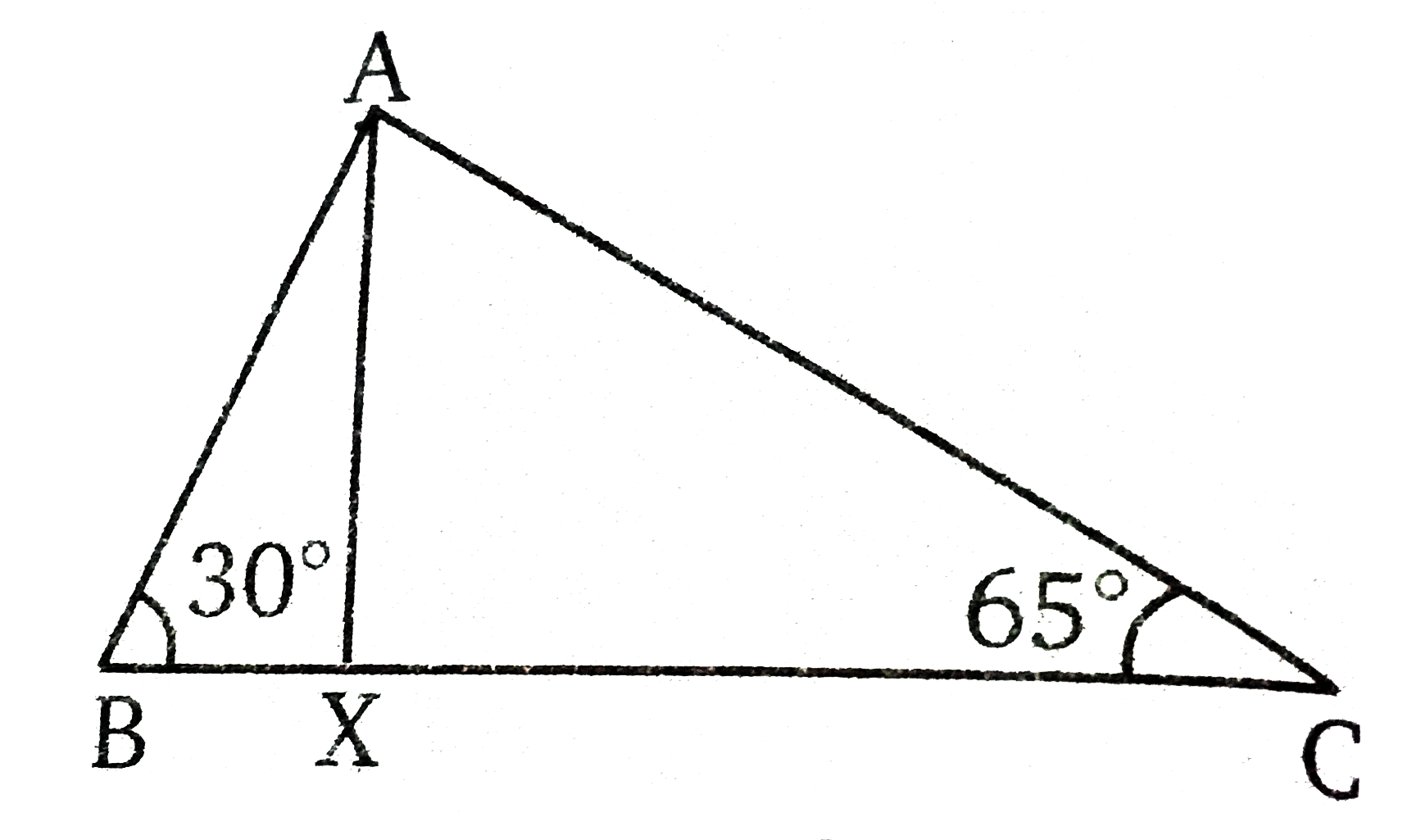
View Solutionसंलग्न चित्र में, ΔABC में, ∠B=30∘, ∠C=65∘ तथा ∠A का समद्विभाजक BC पर X में मिलता है। दिखाइये कि CX<AX<BX
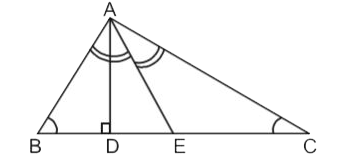
View SolutionIn the figure AE is the bisector of ∠A,AD⊥BC . Show that 2(∠ADE−∠EAC)=∠B+∠C
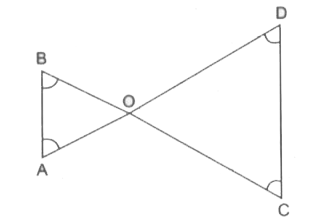
View SolutionIn the given figure, ∠B<∠A and ∠C<∠D. Show that AD<BC.
View SolutionAB and CD are respectively the smallest and longest sides of a quadrilateral ABCD. Show that ∠A<∠C and ∠B>∠D.
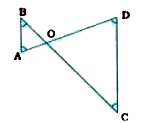
View SolutionIn the given figure, ∠B<∠A and ∠C<∠D. Show that AD < BC.
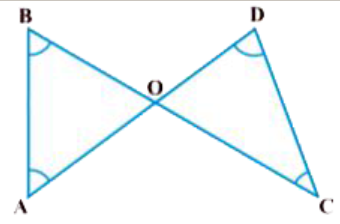
View Solutionआकृति में,∠B<∠A और ∠D>∠C, है तो :
View SolutionIn Fig.
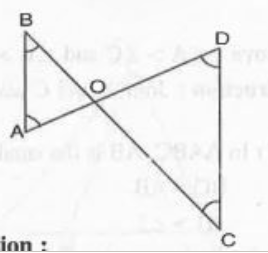 , ∠B<∠A and ∠C<∠D. Show that AD<BC.
, ∠B<∠A and ∠C<∠D. Show that AD<BC.
View SolutionIn fig.
 , ∠B<∠A and ∠C<∠D then relation between AD and BC is :
, ∠B<∠A and ∠C<∠D then relation between AD and BC is :
View Solution