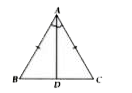
In the adjoining figure, ΔABC is an isosceles triangle in which AB = AC. Side CP is parallel to AB and AP is the bisector of exterior angle CAD of Δ ABC. Prove that ∠PAC=∠BCAand□ABCP is a parallelogram.
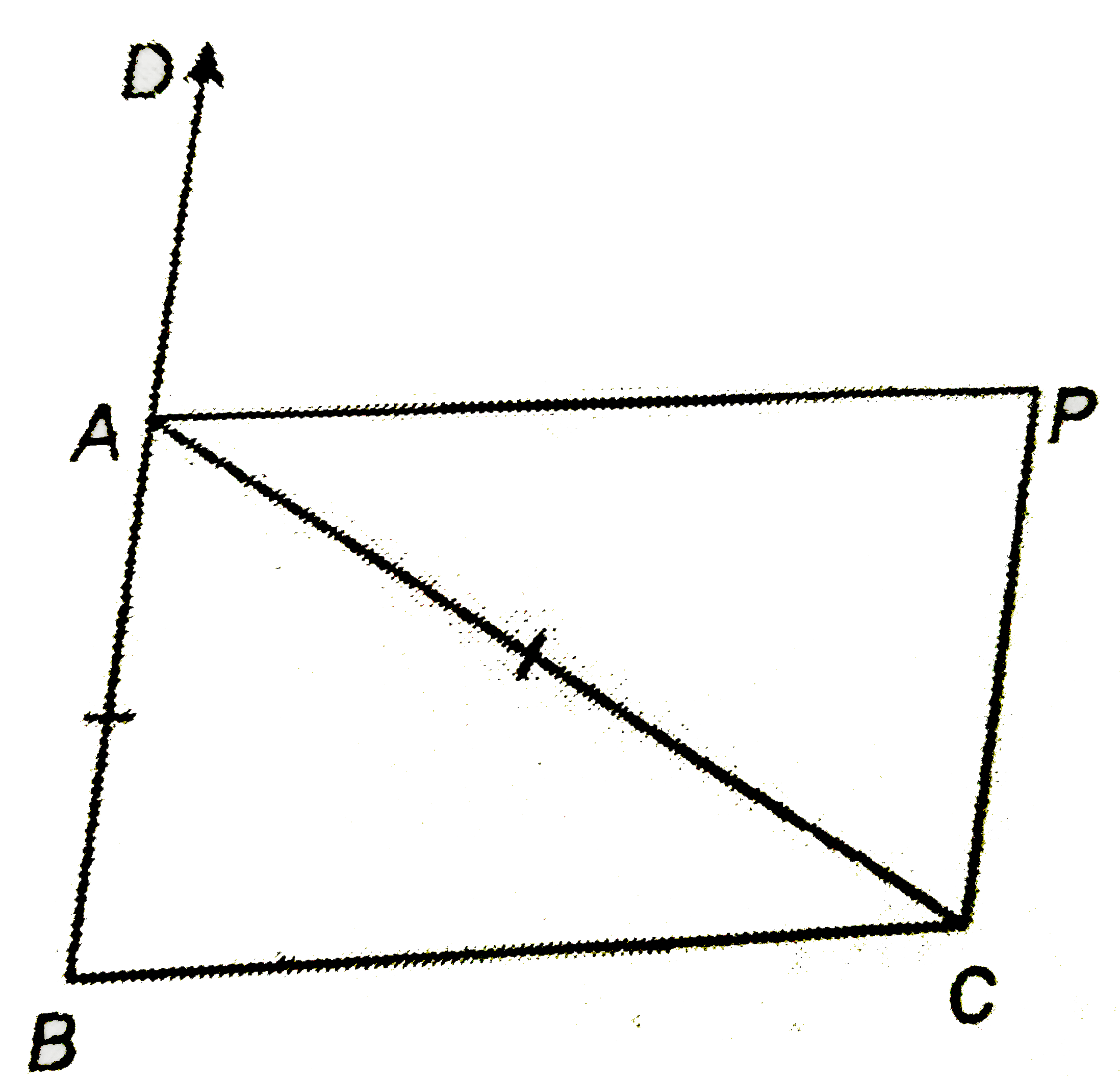
Step by step video, text & image solution for In the adjoining figure, DeltaABC is an isosceles triangle in which AB = AC. Side CP is parallel to AB and AP is the bisector of exterior angle CAD of Delta ABC. Prove that anglePAC=angleBCAand squareABCP is a parallelogram. by Maths experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 9 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
In the adjoining figure, ABC is an isosceles triangle in which AB = AC. If E and F be the midpoints of AC and AB respectively, then
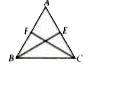 ABE = CFB∠BFC=∠CEBCBF = CEDAll of these
ABE = CFB∠BFC=∠CEBCBF = CEDAll of theseIn the adjoining figure, ABC is an isosceles triangle in which AB=AC. If E and F be the midpoints of AC and AB respectively, then
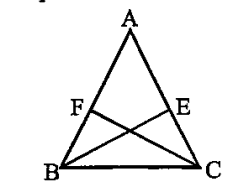 ABE=CFB∠BFC=∠CEBCBF=CEDAll of these
ABE=CFB∠BFC=∠CEBCBF=CEDAll of these
In the adjoining figure, ΔABC is an isosceles triangle in which AB = AC and AD is the bisector of ∠A. Prove that:
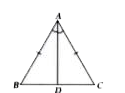
∠B=∠C
View SolutionIn the adjoining figure, ΔABC is an isosceles triangle in which AB = AC. If BM⊥ACandCN⊥AB, prove that:
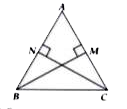
BM = CN
View SolutionIn the adjoining figure, ΔABC is an isosceles triangle in which AB = AC and AD is the bisector of ∠A. Prove that:
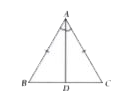
ΔADB≅ΔADC
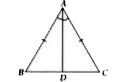
View SolutionIn the adjoining figure, ΔABC is an isosceles triangle in which AB = AC and AD is a median.
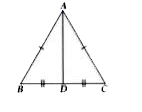 Prove that:
Prove that:
ΔADB≅ΔADC
View SolutionIn the adjoining figure, ΔABC is an isosceles triangle in which AB = AC and AD is a median.
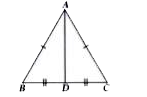 Prove that:
Prove that:
∠BAD=∠CAD
View SolutionIn the figure, ABC is an isosceles triangle in which AB = AC and LM is parallel to BC. If ∠A=50∘ find ∠LMC.
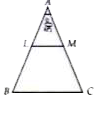
View Solution