Let f:[2,∞)→{1,∞) defined by f(x)=2x4−4x3andg:[π2,π]→A defined by g(x)=sinx+4sinx−2 be two invertible functions, then
The set "A" equals to
[-5,-2]
[2,5]
[-5,2]
[-3,-2]
The correct Answer is:a
Step by step video solution for Let f :[2,oo)to {1,oo) defined by f (x)=2^(x ^(4)-4x ^(3))and g : [(pi)/(2), pi] to A defined by g (x) = (sin x+4)/(sin x-2) be two invertible functions, then The set "A" equals to by Maths experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 12 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023Topper's Solved these Questions
- FUNCTIONSBook:ARIHANT MATHS ENGLISHChapter:FUNCTIONSExercise:Exercise (Matching Type Questions)
Explore 2 Videos
- FUNCTIONSBook:ARIHANT MATHS ENGLISHChapter:FUNCTIONSExercise:FUNCTION EXERCISE 5: Matching Type Questions
Explore 2 Videos
- FUNCTIONSBook:ARIHANT MATHS ENGLISHChapter:FUNCTIONSExercise:Exercise (Statement I And Ii Type Questions)
Explore 11 Videos
- ESSENTIAL MATHEMATICAL TOOLS Book:ARIHANT MATHS ENGLISHChapter:ESSENTIAL MATHEMATICAL TOOLS Exercise:Exercise (Single Integer Answer Type Questions)
Explore 3 Videos
- GRAPHICAL TRANSFORMATIONSBook:ARIHANT MATHS ENGLISHChapter:GRAPHICAL TRANSFORMATIONSExercise:Exercise (Questions Asked In Previous 13 Years Exam)
Explore 10 Videos
Similar Questions
Match the statements of Column I with values of Column II.
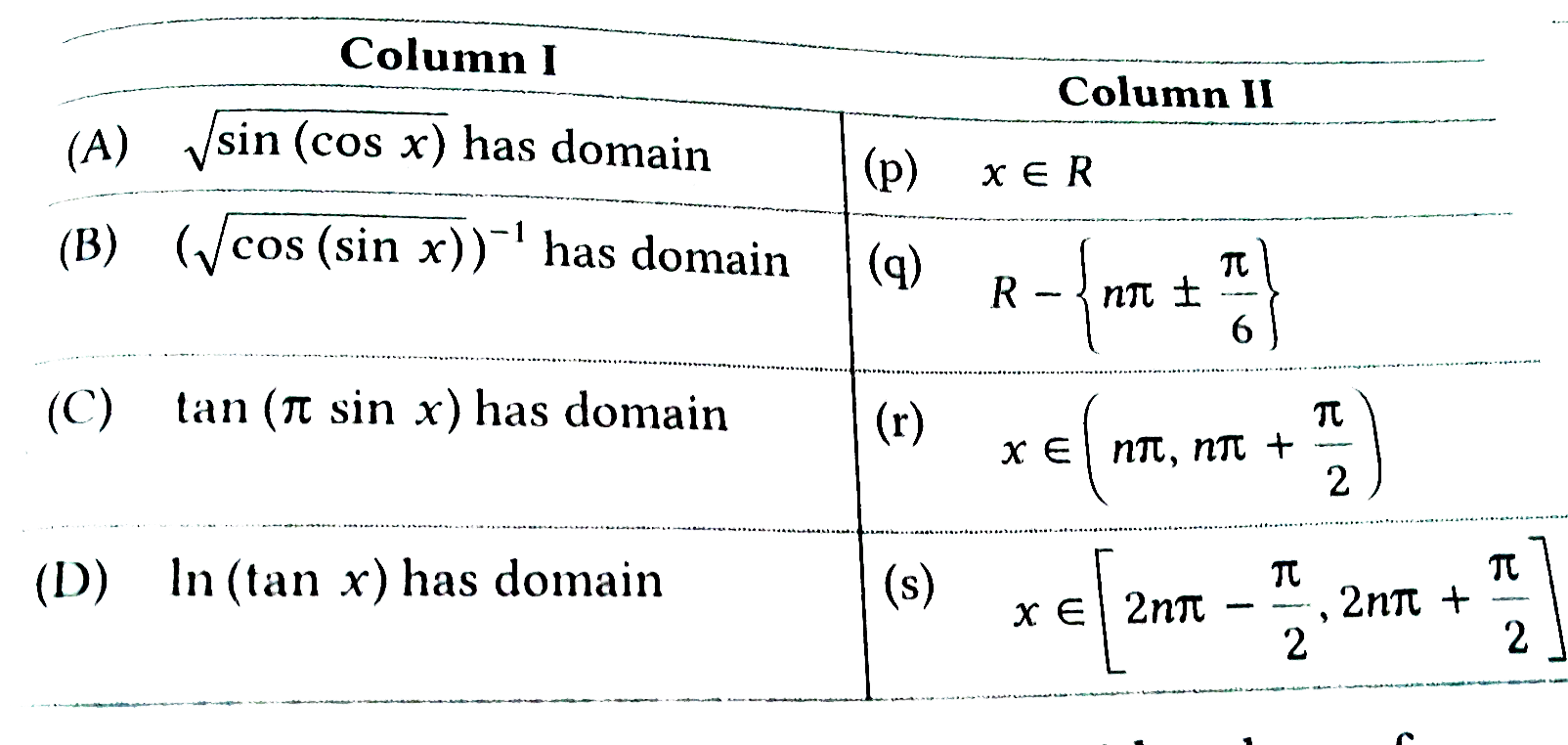
View SolutionMatch the statements of Column I with values of Column II.
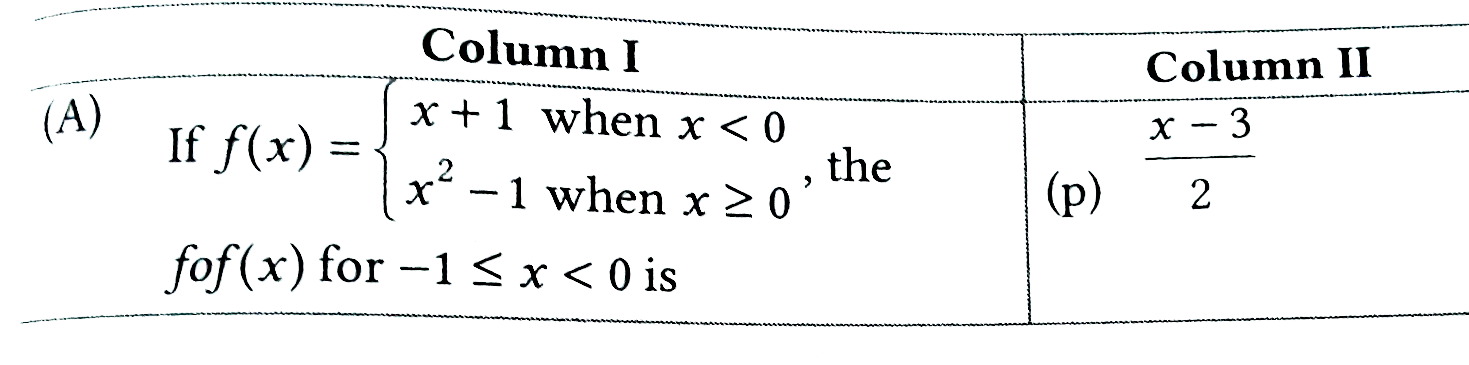

View SolutionStatement I The function f(x) =xsinx and f'(x)=xcosx+sinx are both non-periodic.
Statement II The derivative of differentiable functions (non-periodic) is non-periodic funciton.
View SolutionThe number of solutions of the equation |x−1|−|2x−5|=2x
View SolutionFind the number of solutions of the equation x21−|x−2|=1, graphically.
View SolutionLet g(x)=f(x)sinx,wheref(x) is a twice differentiable function on (−∞,∞) such that f(−π)=1. The value of ∣∣g−π∣∣ equals __________
View SolutionLet f and g be two differential functions such that f(x)=g'(1)sin x+(g''(2)-1)xg(x)=x^(2)-f'((pi)/(2))x+f''((-pi)/(2))
View SolutionLet f:(2,∞)→X be defined by f(x)=4x−x2. Then f is invertible, if X=
View SolutionLet f:(−∞,2]→(−∞,4] be a function defined by f(x)=4x−x2. Then, f−1(x) is
View SolutionLet f:[2,∞)→[1,∞) defined by f(x)=2x4−4x2 and g:[π2,π]→A defined by g(x)=sinx+4sinx−2 be two invertible functions.
The domain of f−1g−1(x) is
View SolutionLet f:[2,∞)→{1,∞) defined by f(x)=2x4−4x3andg:[π2,π]→A defined by g(x)=sinx+4sinx−2 be two invertible functions, then
f−1(x) is equal to
View SolutionLet f:[2,∞)→{1,∞) defined by f(x)=2x4−4x3andg:[π2,π]→A defined by g(x)=sinx+4sinx−2 be two invertible functions, then
The set "A" equals to
View SolutionIf f is a function defined as f(x)=x2−x+5,f:(12,∞)→(194,∞), and g(x) is its inverse function, then g'(7) is equal to
View SolutionLet f:[2,∞)→X be defined by f(x)=4x−x2. Then, f is invertible if X =
View SolutionLet f:[2,∞)→{1,∞) defined by f(x)=2x4−4x3andg:[π2,π]→A defined by g(x)=sinx+4sinx−2 be two invertible functions, then
f−1(x) is equal to
View SolutionLet f:(−∞,2]→(−∞,4] be a function defined by f(x)=4x−x2. Then, f−1(x) is
View Solution
