Let z1 and z2 be two distinct complex numbers and z=(1−t)z1+tz2, for some real number t with 0<t<1 and i=√−1. If arg(w) denotes the principal argument of a non-zero compolex number w, then
|z−z1|+|z−z2|=|z1−z2|
(z−z1)=(z−z2)
∣∣∣z−z1¯z−¯z1z2−z1¯z2−¯z1∣∣∣=0
arg(z−z1)=arg(z2−z1)
The correct Answer is:A, C, D
Given z≡(1−t)z1+tz2
⇒z=(1−t)z1+tz2(1−t)+t
⇒z divides the line segment joining z1 and z2 in ratio (1-t):t internally as 0<t<1
⇒z,z1andz2 are collinear.
⇒arg(z−z1)=arg(z2−z)

⇒∣∣∣z−z1¯z−¯z1z2−z1¯z2−¯z1∣∣∣=0
AP+PB=AB
⇒|z−z1|+|z−z2|=|z1−z2|
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
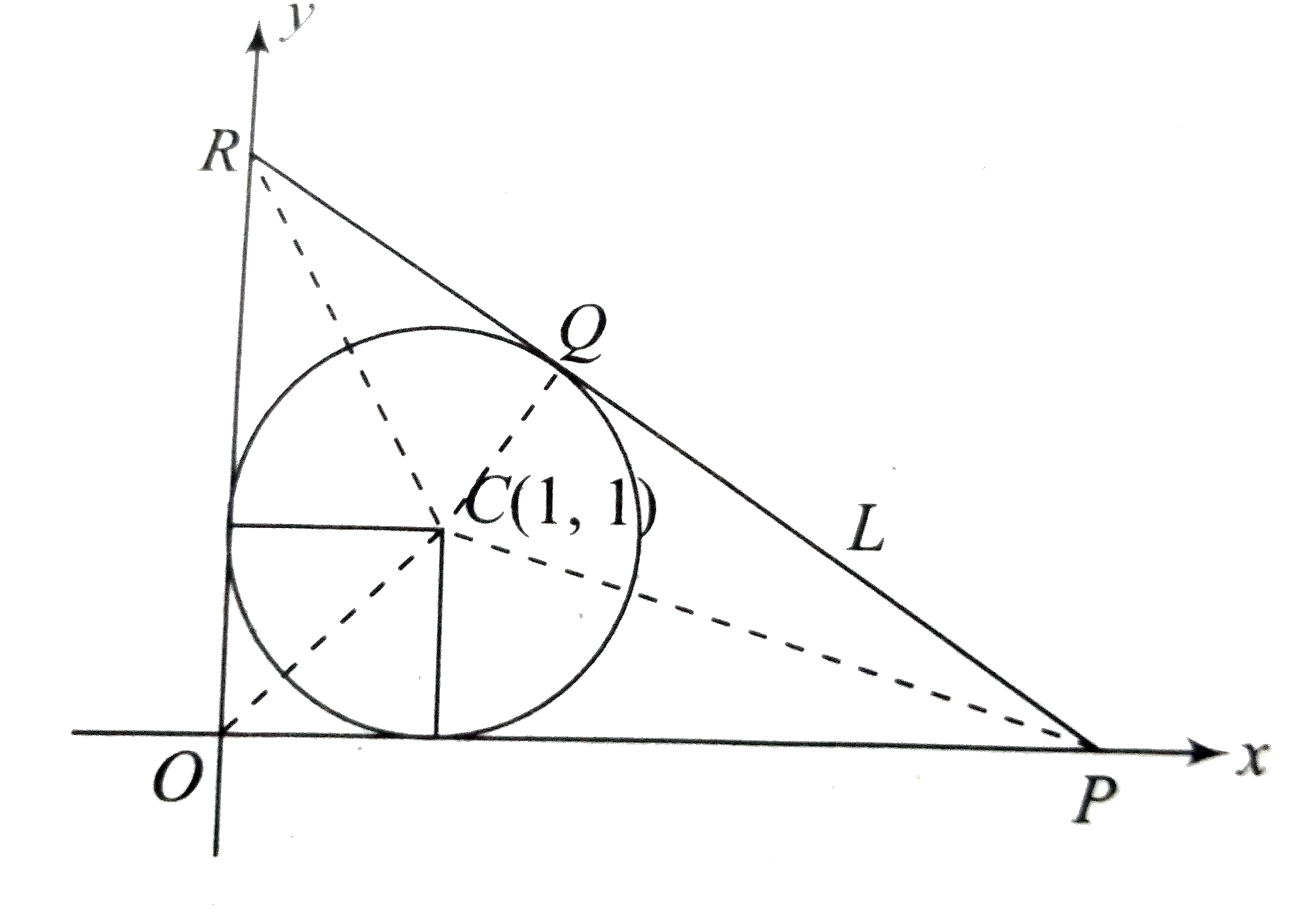
In the diagram as shown, a circle is drawn with centre C(1,1) and radius 1 and a line L. The line L is tangent to the circle at Q. Further L meets the y-axis at R and the x-axis at P in such a way that the angle OPQ equals θ where 0<θ<π2.
Area of triangle OPR when θ=π/4 is
View Solutionमाना कि z1 तथा z2 दो भिन्न सम्मिश्र संख्याऐं हैं तथा किसी वास्तविक संख्या t जहां 0<t<1, के लिए z=(1−t)z1+tz2 है। यदि किसी शून्येत्तर सम्मिश्र संख्या w के लिए Arg(w),w के प्रमुख कोणांक को दर्शाता है तो
View Solutionz1,z2 are two complex numbers with |z1−z2|< k. If the complex number z satisfies the condition |z1−z2|+|z−z2|= k , then z lies on
View SolutionIf z1 and z2 are two non-zero complex numbers such that |z1+z2|=|z1|+|z2|, then arg.z1−arg.z2 equals :
View SolutionLet z1 and z2 be two distinct complex numbers and let z=(1−t)z1+tz2 for some real number t with 0<t<1. If Arg(w) denotes the principal argument of a non zero complex number w, then
View Solutionमाना कि z1 तथा z2 दो भिन्न सम्मिश्र संख्याऐं हैं तथा किसी वास्तविक संख्या t जहां 0<t<1, के लिए z=(1−t)z1+tz2 है। यदि किसी शून्येत्तर सम्मिश्र संख्या w के लिए Arg(w),w के प्रमुख कोणांक को दर्शाता है तो
View SolutionLet z1 and z2 be two distinct complex numbers and z=(1−t)z1+tz2, for some real number t with 0<t<1 and i=√−1. If arg(w) denotes the principal argument of a non-zero compolex number w, then
View SolutionLet z1 and z2 be two distinct complex numbers and let z=(1−t)z1+tz2 for some real number t with 0<t<1. If Arg(w) denotes the principal argument of a non-zero complex number w, then
View Solution
