lf z=ilog(2−√3), then cosz=
−1
−1/2
1
2
The correct Answer is:D
To solve the problem where z=ilog(2−√3) and we need to find cosz, we can follow these steps:
1. Identify the expression for z:
z=ilog(2−√3)
2. Use Euler's formula:
Recall that Euler's formula states:
eiz=cos(z)+isin(z)
From this, we can express cos(z) as:
cos(z)=eiz+e−iz2
3. Calculate eiz:
Substitute z into the expression:
eiz=ei(ilog(2−√3))=e−log(2−√3)
Using the property of logarithms, we have:
e−log(a)=1a
Therefore:
eiz=12−√3
4. Calculate e−iz:
Similarly, we find e−iz:
e−iz=e−(−ilog(2−√3))=eilog(2−√3)=2−√3
5. Combine the results:
Now we can substitute eiz and e−iz back into the formula for cos(z):
cos(z)=eiz+e−iz2=12−√3+(2−√3)2
6. Simplify the expression:
To simplify 12−√3+(2−√3), we first rationalize 12−√3:
12−√3⋅2+√32+√3=2+√3(2−√3)(2+√3)=2+√34−3=2+√3
Thus:
cos(z)=(2+√3)+(2−√3)2=42=2
7. Final result:
Therefore, the value of cos(z) is:
cos(z)=2
z=ilog(2−√3)
Recall that Euler's formula states:
eiz=cos(z)+isin(z)
From this, we can express cos(z) as:
cos(z)=eiz+e−iz2
Substitute z into the expression:
eiz=ei(ilog(2−√3))=e−log(2−√3)
Using the property of logarithms, we have:
e−log(a)=1a
Therefore:
eiz=12−√3
Similarly, we find e−iz:
e−iz=e−(−ilog(2−√3))=eilog(2−√3)=2−√3
Now we can substitute eiz and e−iz back into the formula for cos(z):
cos(z)=eiz+e−iz2=12−√3+(2−√3)2
To simplify 12−√3+(2−√3), we first rationalize 12−√3:
12−√3⋅2+√32+√3=2+√3(2−√3)(2+√3)=2+√34−3=2+√3
Thus:
cos(z)=(2+√3)+(2−√3)2=42=2
Therefore, the value of cos(z) is:
cos(z)=2
Topper's Solved these Questions
- COMPLEX NUMBERSBook:CENGAGE ENGLISHChapter:COMPLEX NUMBERSExercise:MULTIPLE CORRECT ANSWERS TYPE
Explore 49 Videos
- COMPLEX NUMBERSBook:CENGAGE ENGLISHChapter:COMPLEX NUMBERSExercise:LINKED COMPREHENSION TYPE
Explore 36 Videos
- COMPLEX NUMBERSBook:CENGAGE ENGLISHChapter:COMPLEX NUMBERSExercise:EXERCISE3.11
Explore 6 Videos
- CIRCLESBook:CENGAGE ENGLISHChapter:CIRCLESExercise:Comprehension Type
Explore 8 Videos
- CONIC SECTIONSBook:CENGAGE ENGLISHChapter:CONIC SECTIONSExercise:All Questions
Explore 101 Videos
Similar Questions
If z=ω,ω2whereω is a non-real complex cube root of unity, are two vertices of an equilateral triangle in the Argand plane, then the third vertex may be represented by z=1 b. z=0 c. z=−2 d. z=−1
View SolutionConsider the complex number z=1−isinθ1+icosθ.
The value of θ for which z is purely real are
View SolutionIf α is complex fifth root of unity and (1+α+α2+α3)2005=p+qα+rα2+sα3 (where p,q,r,s are real), then find the value of p+q+r+s.
View Solution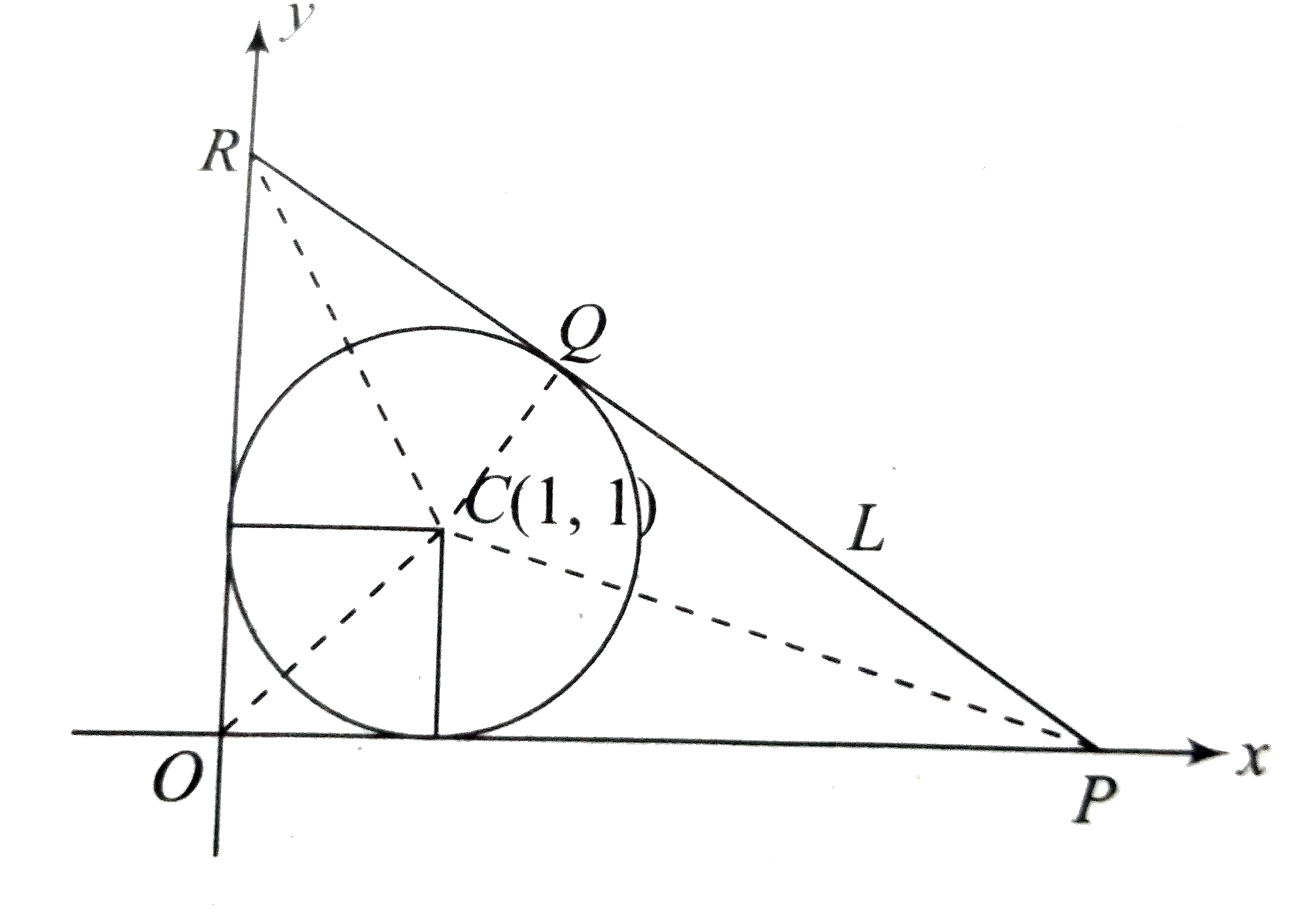
In the diagram as shown, a circle is drawn with centre C(1,1) and radius 1 and a line L. The line L is tangent to the circle at Q. Further L meets the y-axis at R and the x-axis at P in such a way that the angle OPQ equals θ where 0<θ<π2.
Area of triangle OPR when θ=π/4 is
View SolutionGiven that A(1,1) and B(2,−3) are two points and D is a point on AB produced such that AD=3AB. Find the coordinates of D.
View SolutionIf z=[(√32)+i2]5+[(√32)−i2]5 , then Re(z)=0 b. Im(z)=0 c. Re(z)>0 d. Re(z)>0,Im(z)<0
View SolutionWhat is locus of z if ∣∣ ∣∣z−1−sin−1(1√3)∣∣ ∣∣+∣∣ ∣∣z+cos−1(1√3)−π2∣∣ ∣∣=1?
View SolutionIf z=(√2−√−3), find Re(z), Im(z), ¯zand|z|.
View SolutionIf z=iloge(2−√3),wherei=√−1 then the cos z is equal to
View SolutionIf ∣∣∣z=2z∣∣∣ = 2. show that the greatest and least value of |z| are √3+1and√3 - 1 respectively.
View Solutionयदि z=ilog(2−√3), तब cos z=
View Solution∣∣∣z−2z∣∣∣=2, எனில் |z| -ன் மீச்சிறு மற்றும் மீப்பெருமதிப்புகள் √3+1 மற்றும் √3−1 என நிறுவுக.
View Solutionযদি x=2, y=3 z=6 হয় তবে, 3√x√y+√z−4√y√z+√x+√z√x+√y-এর মান হিসাব করে লেখো।
View Solutionयदि z=ilog(2−√3), तब cos z=
View SolutionAssertion (A) : If z = ilog (2−√3) then cos z= 2
Reason (R) : coshθ=eiθ+eiθ2
View SolutionIf z=iloge(2−√3),wherei=√−1 then the cos z is equal to
View Solution
