The sum of the first n terms of an A.P. is 4n2+2n . Find the nth term of this A.P.
The correct Answer is:8n-2
Step by step video, text & image solution for The sum of the first n terms of an A.P. is 4n^2+2n . Find the n t h term of this A.P. by Maths experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 10 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023Topper's Solved these Questions
- ARITHMETIC PROGRESSIONS Book:VK GLOBAL PUBLICATIONChapter:ARITHMETIC PROGRESSIONS Exercise:PROFICIENCY EXERCISE ( SHORT ANSWER QUESTION II)
Explore 39 Videos
- ARITHMETIC PROGRESSIONS Book:VK GLOBAL PUBLICATIONChapter:ARITHMETIC PROGRESSIONS Exercise:PROFICIENCY EXERCISE ( LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS )
Explore 21 Videos
- ARITHMETIC PROGRESSIONS Book:VK GLOBAL PUBLICATIONChapter:ARITHMETIC PROGRESSIONS Exercise:PROFICIENCY EXERCISE (VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS )
Explore 12 Videos
- AREAS RELATED TO CIRCLESBook:VK GLOBAL PUBLICATIONChapter:AREAS RELATED TO CIRCLESExercise:Self -Assessment Test
Explore 11 Videos
- CIRCLES Book:VK GLOBAL PUBLICATIONChapter:CIRCLES Exercise:SELF - ASSESSMENT TEST
Explore 11 Videos
Similar Questions
Find the 41st term of an AP whose 13th term is 79 and 26th term is 157.
View SolutionFind the sum of the integers between 100 and 200 that are
(i) divisible by 9. (ii) not divisible by 9.
View SolutionFind the common difference of an AP in which a25−a12=−52.
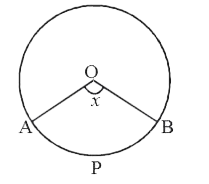
View SolutionIn fig., O is the centre of a circle. The area of sector OAPB is 518 of the area of the circle. Find x.
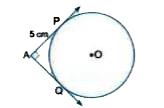
View SolutionIn Fig . pair of tangents AP and AQ drawn from an external point A to a circle with centre O are perpendicular to each other and length of each tangent is 5 cm. Find the radius of the circle.
View SolutionThe sum of first n terms of an A.P. is 3n2+4n . Find the 25th term of this A.P.
View SolutionThe sum of the first n terms of an A.P. is 3n2+6n . Find the nth term of this A.P.
View SolutionThe sum of the first n terms of an A.P. is 4n2+2n . Find the nth term of this A.P.
View SolutionIf the nth term of an A.P. is 2n+1 , then the sum of first n terms of the A.P. is n(n−2) (b) n(n+2) (c) n(n+1) (d) n(n−1)
View SolutionIf the sum of first n terms of an A.P. is given by S=3n^(2)+4n. Determine the A.P. and the n^(th) term.
View SolutionIf the sum of the first 2n terms of the A.P.2,5,8,…, is equal to the sum of the first n terms of the A.P.57,59,61,…, then n equals
View Solutionएक A.P. के प्रथम nपदों का योग Sn=(2n2+5n) हैं , तो A.P. का n वाँ पद ज्ञात कीजिए ।
View SolutionIf the sum of first 2n terms of the A.P. 2, 5, 8,…. Is equal to the sum of the first n terms of the A.P. 57, 59, 61,… then find n.
View SolutionIf Sn the sum of first n terms of an A.P. is given by Sn=3n2−4n, find the nth term.
View SolutionIf the nth term of an A.P is 2n−1 then sum to n terms of that A.P. is ........... .
View SolutionIf the sum of the first 2n terms of the A.P. 2,5,8, "……….." is equal to the sum of the first n terms of the A.P. 57,59,61, "…………" then n equals :
View Solution