Complete Solutions to NCERT EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS WITH ANSWERS, HINTS AND SOLUTIONS (MULTIPLE QUESTIONS-I) of chapter ELECTROCHEMISTRY of Class 12 book with complete answers and questions
| Class 12 | CHEMISTRY |
| Chapter | ELECTROCHEMISTRY |
| PRADEEP | NCERT EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS WITH ANSWERS, HINTS AND SOLUTIONS (MULTIPLE QUESTIONS-I) |
| Number Of Questions | 39 |
| Academic Year | 2023-24 |
Which cell will measure standard electrode potential of copper electrode?
View SolutionElectrode potential for `Mg` electrode varies according to the equation
`E_(Mg^(2+)|Mg)=E_(Mg^(2+)|Mg)^(ϴ) -(0.059)/2 "log" 1/([Mg^(2+)])`
The graph of `E_(Mg^(2+)|Mg) vs log [Mg^(2+)]` is
View SolutionWhich of the following statement is correct?
View SolutionThe difference between the electrode potentials of two electrons when no current is drawn through the cell is called:
View SolutionWhich of the following statement is not correct about an inert electrode in a cell?
View SolutionAn electrochemical cell an behave like an electrolytic cell when
View SolutionWhich of the statements about solution of electrolytes is not correct?
View SolutionUsing the data given below:
`E_(Cr_(2)O_(7)^(2-)|Cr^(3+))^(@)=1.33V E_(Cl_(2)|Cl^(-))^(@)=1.36V`
`E_(MnO_(4)^(-)|Mn^(2+))^(@)=1.51V E_(Cr^(3+)|Cr)=-0.74V`
Mark the strongest reducing agent.
View SolutionFind out which of the following is the strongest oxidizing agent.
View SolutionFind out in which option the order of reducing power is correct.
View SolutionUse the data given in Q.8 and find out the most stable ion in its reduced form.
View SolutionFind out the most stable oxidised species.
View SolutionThe quantity of charge required to obtain one mole of aluminium from `Al_(2)0_(3)` is
View SolutionThe cell constant of a conductivity cell
View SolutionWhile charging the lead storage battery:
View Solution`wedge^(@)m[NH_(4)OH]` is equal to ____
View SolutionIn the electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride solution which of the hall cell reaction will occur at anode?
View SolutionCan absolute electrode potential of an electrode be measured?
View SolutionCan `E_("cell")^(@)` or `Delta_(r)G^(@)` for cell reaction ever be equal to zero?
View SolutionUnder what condition is `E_("cell")^(@)=0` or `Delta_(r)G=0`?
View SolutionWhat does the negative sign in the expression `E_(Zn^(2+)//Zn)^(@)=-0.76V` mean?
View SolutionAqueous copper sulphate solution and aqueous silver nitrate solution are electrolysed by 1 ampere current for 10 minutes in separate electrolytic cells. Will the mass of copper and silver deposited on the cathode be same of different? Explain your answer.
View SolutionDepict the galvanic cell in which the cell reaction is
`Cu+2Ag^(+)rarr2Ag+Cu^(2+)`
View SolutionValue of standard electrode potential for the oxidation of `Cl^(-)` ions is more positive than that of water, even then in the electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride, why is `Cl^(-)` oxidsied at anode instead of water?
View SolutionWhat is electrode potential?
View SolutionConsider the following diagram in which an electrochemical cell is coupled to an electrolytic cell. What will be the polarity of electrodes 'A' and 'B' in the electrolytic cell?
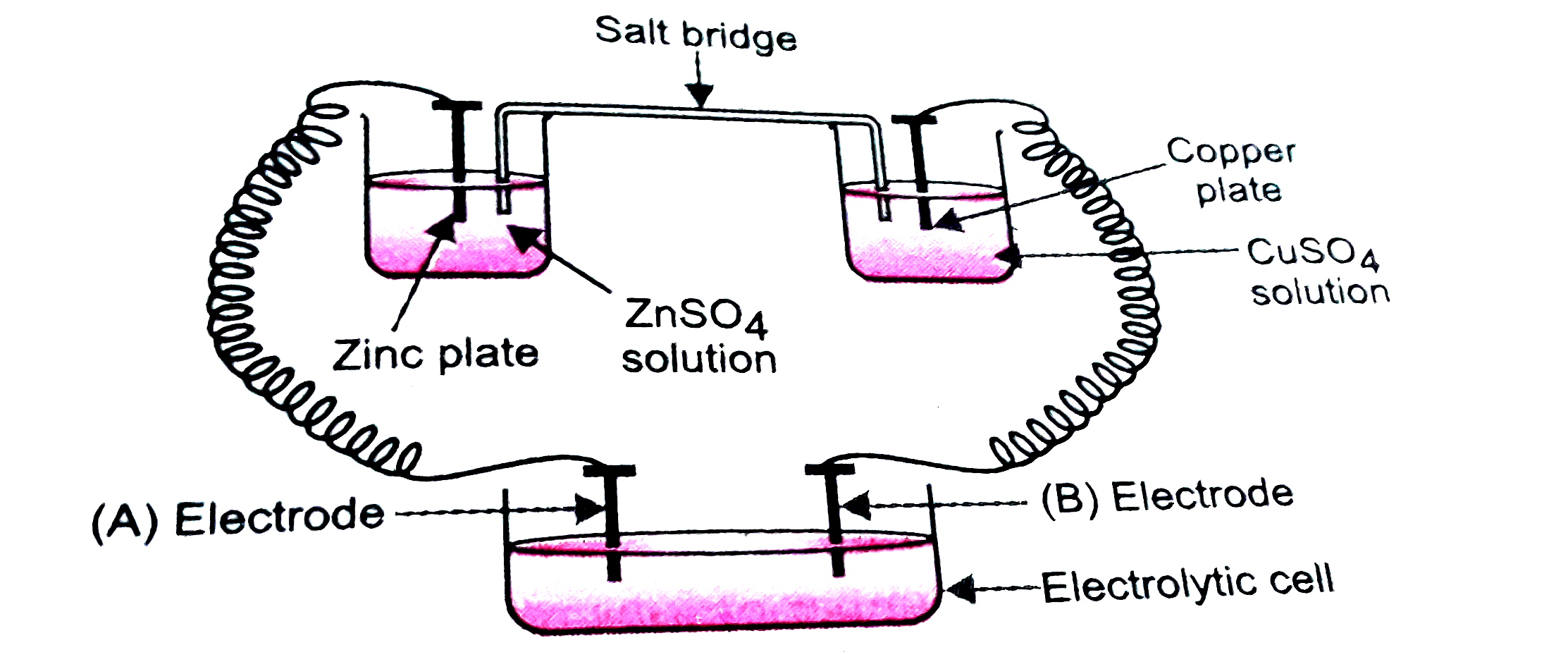
View SolutionWhy is alternating current used for measuring resistance of an electrolytic solution ?
View SolutionA galvanic cell has electrical potential of 1.1 V . If an opposing potential of 1.1 V is applied to this cell, what will happen to the cell reaction and current flowing through the cell ?
View SolutionHow will the pH of brine (aq NaCl solution) be affected when it is electrolysed.
View SolutionUnlike dry cell, the mercury cell has a constant cell has a constant cell potential throughout its useful life, why?
View SolutionSolutions of two electrolytes A and B are diluted. The `Lambda_(m)` of 'B' increases 1.5 times while that of A increases 25 times. Which of the two is a strong electrolyte? Justify your answer.
View SolutionWhen acidulated water (dil. `H_(2)SO_(4)` solution) is electrolysed, with pH of the solution be affected? Justify your answer.
View SolutionIn an aqueous solution how does specific conductivity of electrolytes change with additon of water?
View SolutionWhich reference electrode is used to measure the electrode potnetial of other electrodes?
View SolutionConsider a cell given below.
`Cu|Cu^(2+)|Cl^(-)|Cl_(2).Pt`
Write the reactions that occur at anode and cathode.
View SolutionWrite the Nernst equation for the cell reaction in the Daniel cell. How will the `E_("cell")` be affected when concentration of `Zn^(+)` ions is increased?
View SolutionWhat advantage do the fuel cells have over primary and secondary batteries?
View SolutionWrite the cell reaction of a lead storage battery when it is discharged. How does the density of the electrolyte change when the battery is discharged?
View SolutionWhy on dilution the `Lambda_(m)` of `CH_(3)COOH` increases drastically, while that of `CH_(3)COONa` increases gradually?
View Solution
NCERT EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS WITH ANSWERS, HINTS AND SOLUTIONS (MULTIPLE QUESTIONS-I) questions and complete solutions for chapter ELECTROCHEMISTRY of PRADEEP CHEMISTRY (HINGLISH) of Class 12
All Exercises from PRADEEP Class 12 CHEMISTRY ELECTROCHEMISTRY
- ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS(LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS)
- ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS(SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS)
- ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS(VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS)
- Advanced Problem For Competitions
- CONCEPTUAL QUESTIONS
- Curiosity Question
- HIGHER ORDER THINKING SKILLS
- HIGHER ORDER THINKING SKILLS (HOTS PROBLEMS)
- IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR BOARD EXAMINATION
- NCERT EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS WITH ANSWERS, HINTS AND SOLUTIONS (ASSERTION AND REASON TYPE QUESTIONS)
- NCERT EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS WITH ANSWERS, HINTS AND SOLUTIONS (LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS)
- NCERT EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS WITH ANSWERS, HINTS AND SOLUTIONS (MATCHING TYPE QUESTIONS)
- NCERT EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS WITH ANSWERS, HINTS AND SOLUTIONS (MULTIPLE QUESTIONS-I)
- NCERT EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS WITH ANSWERS, HINTS AND SOLUTIONS (MULTIPLE QUESTIONS-II)
- NCERT EXERCISES
- NCERT QUESTIONS AND EXERCISES WITH ANSWER
- Problem
- Problem for Practice
- Sample Problem
- TEST YOUR GRIP (FILL IN THE BLANKS)
- TEST YOUR GRIP (MUTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION)
- VALUE BASED QUESTIONS WITH ANWER (Assertion-Reason Type Question Type-I)
- VALUE BASED QUESTIONS WITH ANWER (Assertion-Reason Type Question Type-IO)
- VALUE BASED QUESTIONS WITH ANWER (Integer Type Question)
- VALUE BASED QUESTIONS WITH ANWER (Matching Type Question)
- VALUE BASED QUESTIONS WITH ANWER (Matrix-Type Questions)
- VALUE BASED QUESTIONS WITH ANWER (Multiple Choice Questions-I)
- VALUE BASED QUESTIONS WITH ANWER (Multiple Choice Questions-II)
- VALUE BASED QUESTIONS WITH ANWER (Multiple Choice Questions-III Based on the given Passage/Comprehension)