State and explain Hess's law of constant heat summation.
Video Solution
Text Solution
Hess's law of constant heat summation : The law states that the change in enthalpy for a reaction is the same whether the reaction takes place in one step or a series of steps.
The Hess's law is a direct consequence of the fact that the enthalpy is a state function and so the enthalpy change depends only on the initial and final states of the system and not on the path by which the reaction takes place.
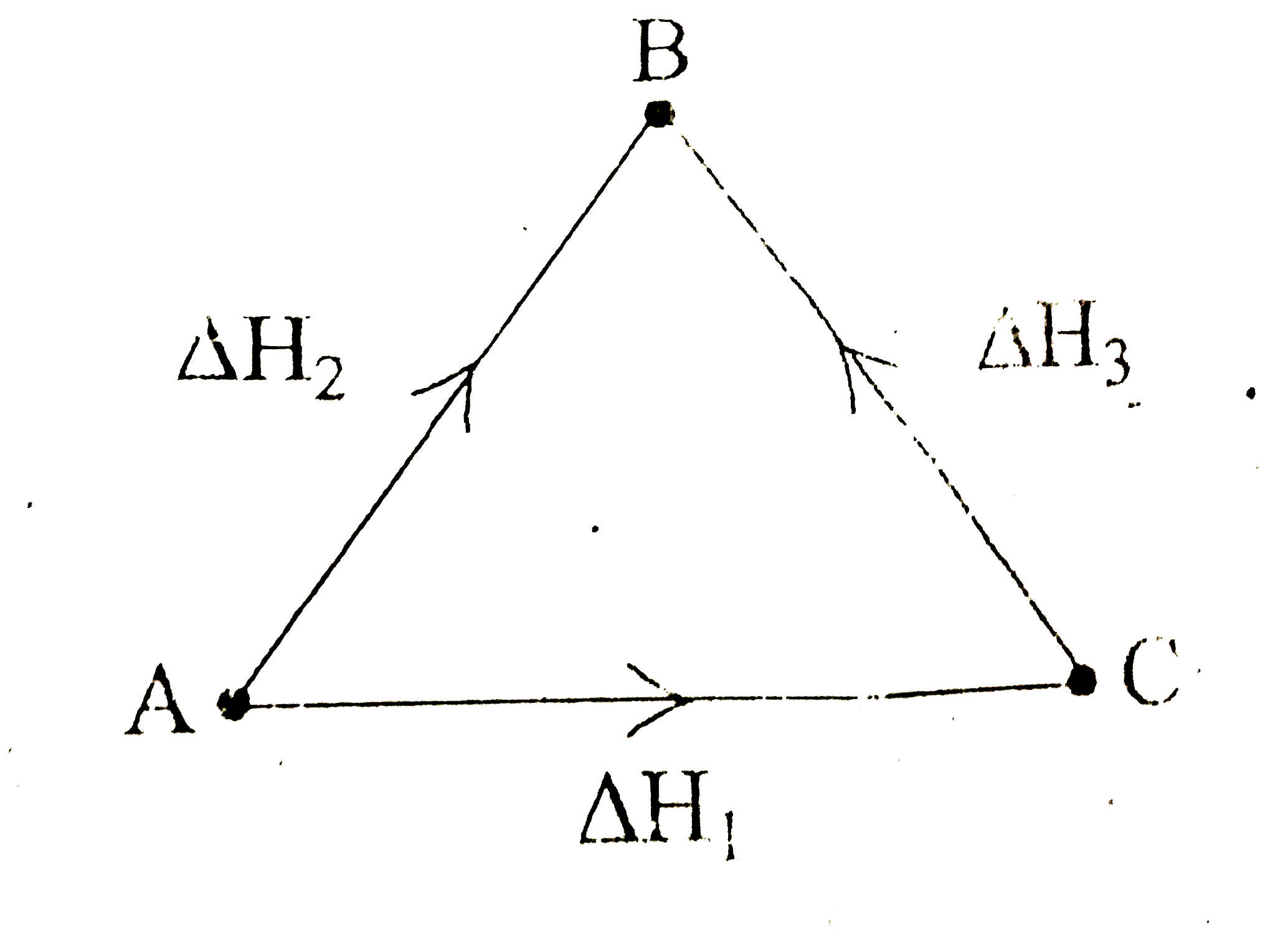
Example :
A→C,ΔH∘=ΔH1
Directly in a single step.
Reaction can also take place in two steps.
Step I. A→B,ΔH∘=ΔH2Step II. B→C,ΔH∘=ΔH3¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯Overall A→C,ΔH∘=ΔH2+ΔH3
According to Hess's law,
ΔH1=ΔH2+ΔH3
|
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
Hess's law of constant heat summation is bases on
AE=mc2BConservation of massCFirst law of thermodynamicsDNone of the aboveHess's law of constant heat summation is bases on
AE=mc2BE=hvCFirst law of thermodynamicsDConservation of mass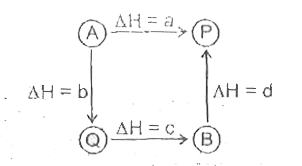
On the basis of Hess's law of constant heat summation, choose the correct relation:Ab=a−cd+cBc=a−b+dCd=a+b+cDa−c=b+d

