A solid metallic sphere of radius a is surrounded by a conducting spherical shell of radius b(b>a). The solid sphere is given a charge Q. A student measures the potential at the surface of the solid sphere as V and the potential at the surface of spherical shell as Vb. After taking these readings, he decides . to put charge of −4Q on the shell. He then noted the readings of the potential of solid sphere and the shell and found that the potential difference is △V .
He then connected the outer spherical shell to the earth by a conducting wire and found that the charge on the outer surface of the shell as He then decides to remove the earthing connection from the shell and earthed the inner solid sphere. Connecting the inner sphere with the earth he observes the charge on the solid sphere as q2. He then wanted to check what happens if the two are connected by the conducting wire. So he removed the earthing connection and connected a conducting wire between the solid sphere and the spherical shelll. After the connections were made he found the charge on the outer shell as q3.
q2 is
Q
Q(ab)
−4Q
zero
The correct Answer is:B
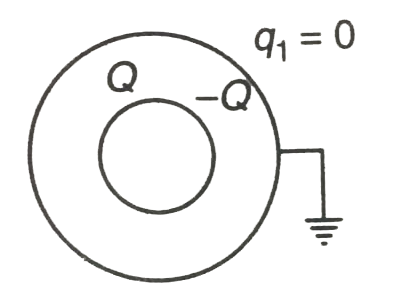
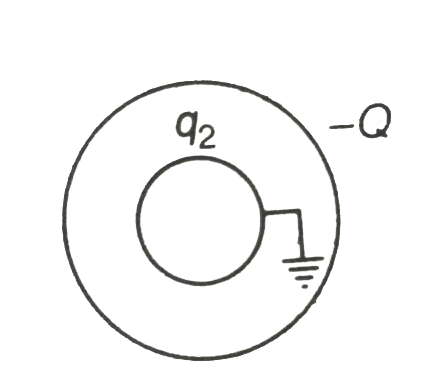
Vinner=0 when solid sphere is earthed
∵kq2a−kQb=0
∵q2=Q(ab)
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
A hollow metal sphere of radius 5 cm is charged such that the potential on its surface is 10 V. What is the potential at the centre of the sphere?
View SolutionA hollow metal sphere of radius 10 cm is charged such that the potential on its surface is 5 V. What is the potential at the centre of the sphere?
View Solution
Knowledge Check
A solid metallic sphere of radius a is surrounded by a conducting spherical shell of radius b(b>a). The solid sphere is given a charge Q. A student measures the potential at the surface of the solid sphere as V and the potential at the surface of spherical shell as Vb. After taking these readings, he decides . to put charge of −4Q on the shell. He then noted the readings of the potential of solid sphere and the shell and found that the potential difference is △V .
He then connected the outer spherical shell to the earth by a conducting wire and found that the charge on the outer surface of the shell as He then decides to remove the earthing connection from the shell and earthed the inner solid sphere. Connecting the inner sphere with the earth he observes the charge on the solid sphere as q2. He then wanted to check what happens if the two are connected by the conducting wire. So he removed the earthing connection and connected a conducting wire between the solid sphere and the spherical shelll. After the connections were made he found the charge on the outer shell as q3.
Potential difference (△CV) measured by the student between the inner solid shere and outer shell after putting a charge −4Q isAVa−3VbB3(Va−Vb)CVaDVa−VbA uniform metal sphere of radius a and mass M is surrounded by a thin uniform spherical shell of equal mass and redius 4a. The centre of the shell falls on the surface of the iner sphere
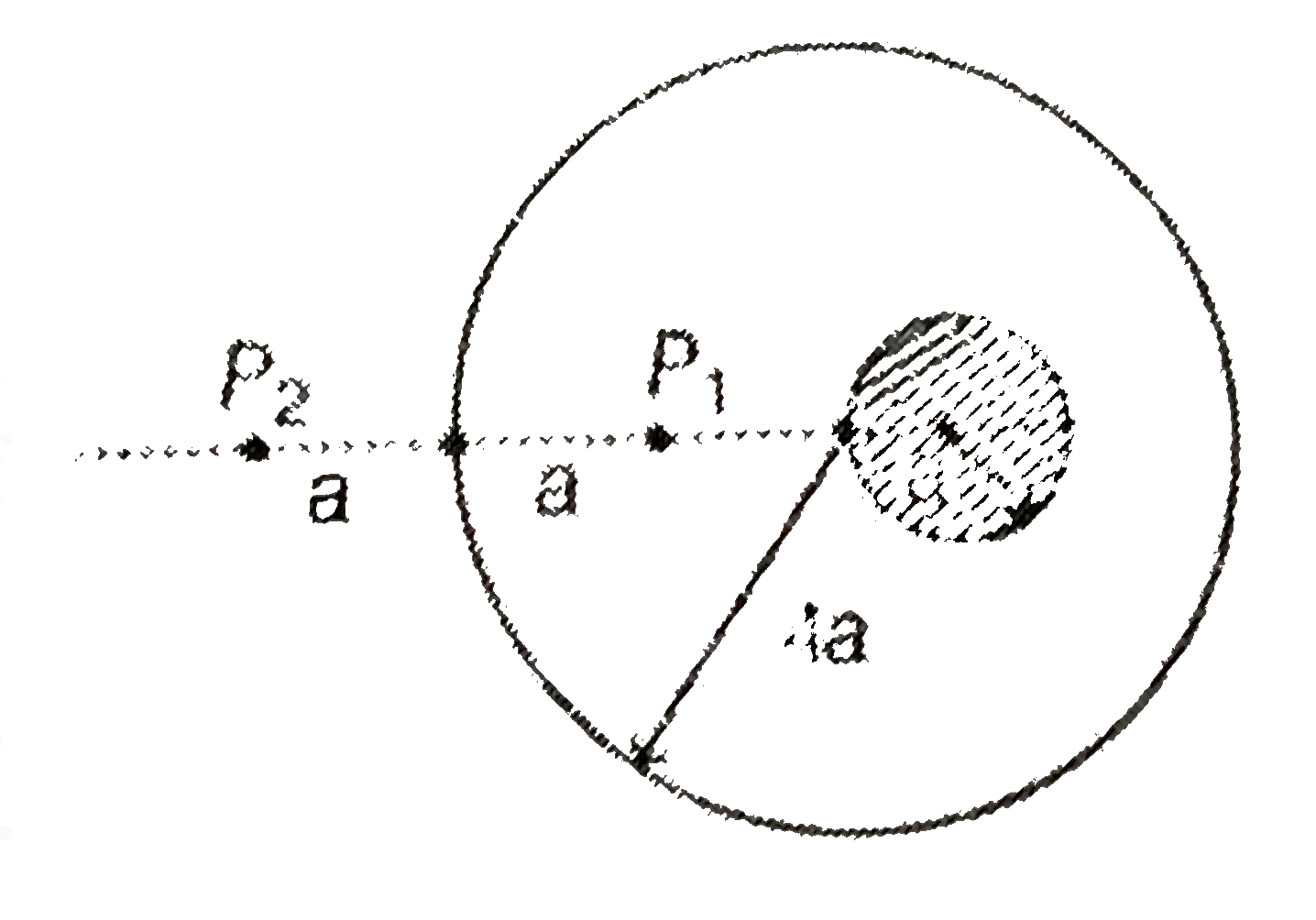 AThe gravitational field intensity at P1 is GM16a2BThe gravitational field intensity at P2 is 61GM900a2CThe gravitational potential at P1=0DThe gravitational potential at P2=0
AThe gravitational field intensity at P1 is GM16a2BThe gravitational field intensity at P2 is 61GM900a2CThe gravitational potential at P1=0DThe gravitational potential at P2=0A solid metal sphere of radius 50 cm carries a charge 25×10−10C. The electrostatic potential at the surface of the sphere will be
A25 VB15 VC35 VD45 V
A hollow metal sphere of radius 6 cm is charged such that the potential on its surface is 12 V.What is the potential at the centre of the sphere?
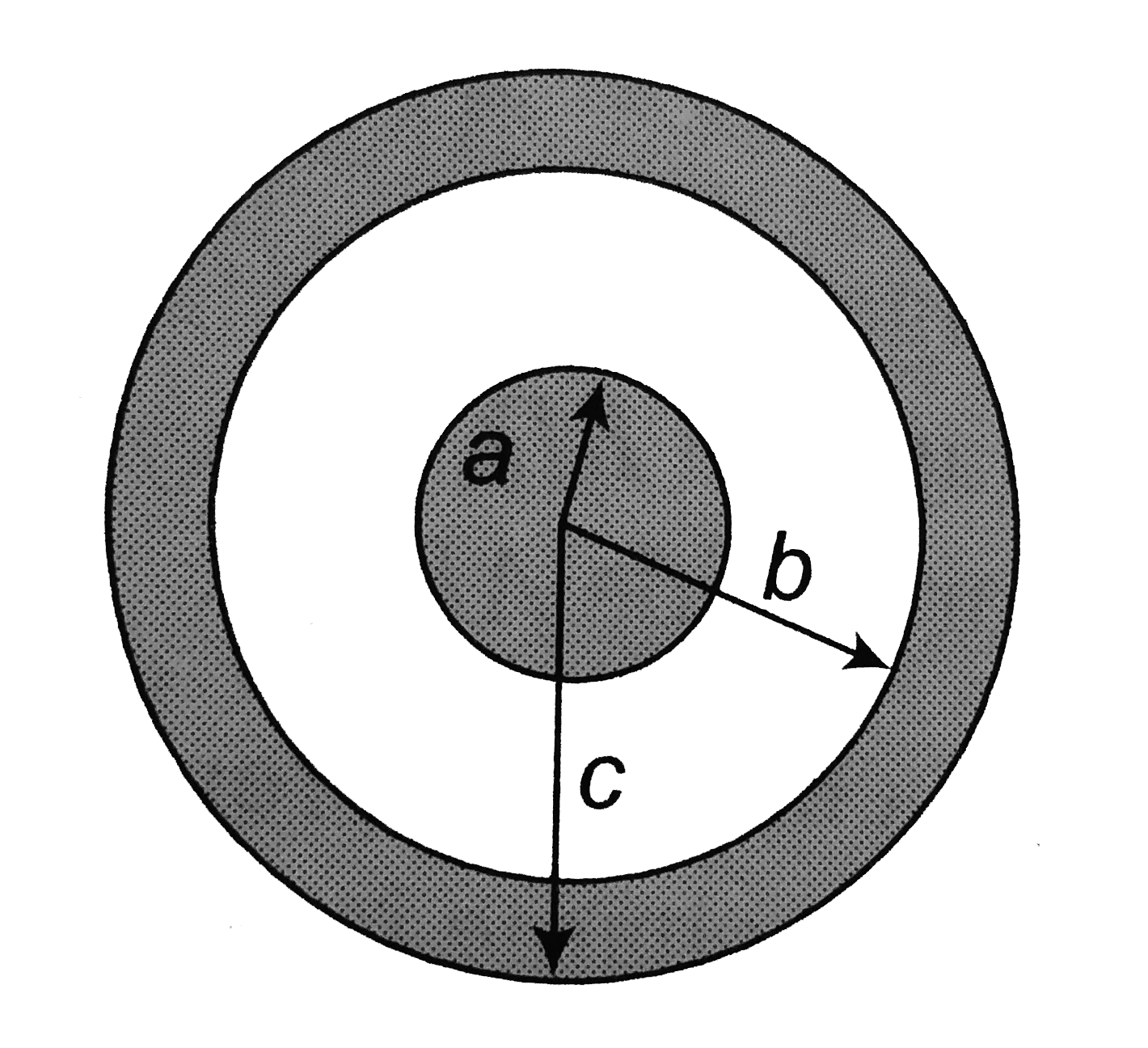
View SolutionA solid conducting sphere of radius a has a net positive charge 2Q. A conducting spherical shell of inner radius b and outer radius c is concentric with the solid sphere and has a net charge −Q. The surface charge density on the inner and outer surfaces of the spherical shell will be
View SolutionA metal sphere of radius 'a' is having charge +Q. Now it is connected by a conducting wire concentric spherical shell of radius '2a'. Then the potential at the surface of outer shell is

Here, K=14πε0
View SolutionA hollow metal sphere of radius 5cm is charged so that the potential on its surface is 10V. The potential at the centre of the sphere is
View SolutionA solid sphere of radius a and mass m is surrounded by cocentric spherical shell of thickness 2a and mass 2m the gravitational field at a distance 3a from their centres is
View Solution

