Assertion (A) : Frenkel defects are shown by AgX.
Reason (R ) : Ag⊕ ions have small size.
If both (A) and (R) are correct, and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
If both (A) and (R) are correct, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
If (A) is correct, but (R) is incorrect.
If both (A) is incorrect but (R) is correct.
The correct Answer is:A
Step by step video, text & image solution for Assertion (A) : Frenkel defects are shown by AgX. Reason (R ) : Ag^(o+) ions have small size. by Chemistry experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 12 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023Topper's Solved these Questions
- SOLID STATEBook:CENGAGE CHEMISTRYChapter:SOLID STATEExercise:Exercises (Interger)
Explore 9 Videos
- SOLID STATEBook:CENGAGE CHEMISTRYChapter:SOLID STATEExercise:Exercises (Fill In The Blanks)
Explore 15 Videos
- SOLID STATEBook:CENGAGE CHEMISTRYChapter:SOLID STATEExercise:Exercises (Single Correct)
Explore 72 Videos
- REDUCTION AND OXIDATION REACTION OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDSBook:CENGAGE CHEMISTRYChapter:REDUCTION AND OXIDATION REACTION OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDSExercise:SUBJECTIVE TYPE
Explore 3 Videos
- SOLUTIONSBook:CENGAGE CHEMISTRYChapter:SOLUTIONSExercise:Ex 2.3 (Objective)
Explore 9 Videos
Similar Questions
If a solid A⊕Bɵ having ZnS Structure is heated so that the ions along two of the axis passing throgh the face centre particles are lost and bivalent ion (Z) enters herre to maintain the electrical neutrality, so that the new formula unit becomes AxByCc, report the value of x+y+c.
View SolutionAlthough amorphous solids do not posses the long range order of crystals, they do have ……… just as liquids do.
View SolutionA crystal is made up of particals X, Y, and Z. X froms f packing. Y occupies all octahedral voids of X and Z occupies all tetrahedral voids of X. If all the particles along one body diagonal are removed. Then the fromula of the crystal would be
View SolutionWrite the statements of the products (A),(B),(C),(D), and (E) in the following scheme.
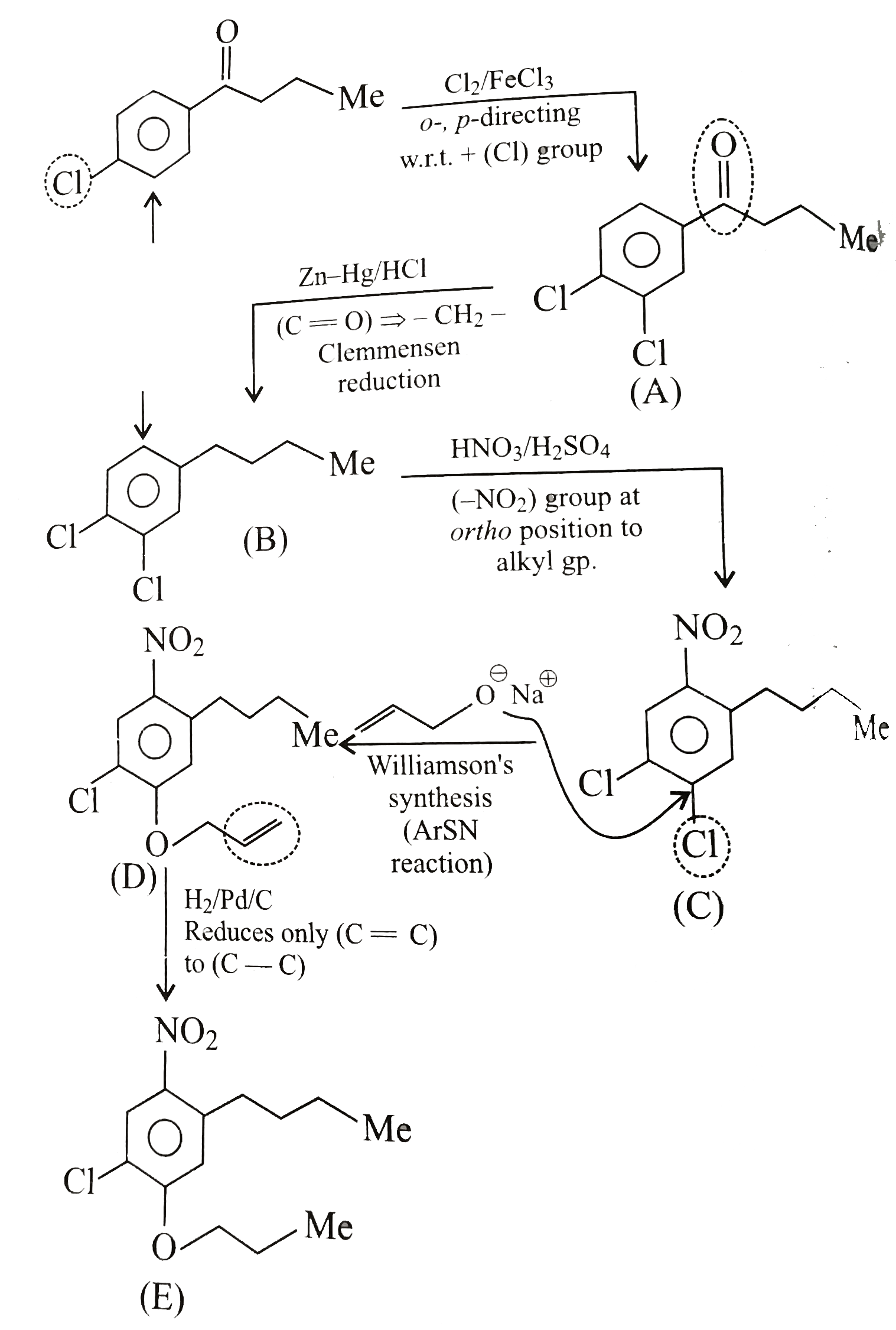
View SolutionWhat should be the boiling point of 1.0molal aqueous KCl solution (assuming complete dissociation of KCl) if KH2Ob is 0.52Km−1?
View SolutionAssertion : In AgCI crystal, frenkel defect can be observed
Reason:Ag+ is a small sized cation
View SolutionAssertion (A) Due to Frenkel defect there is no effect on density of a solid. Reason (R) Ions shift from lattice sites to interstitial sites in Frenkel defect.
View SolutionAssertion (A) : Frenkel defects are shown by AgX.
Reason (R ) : Ag⊕ ions have small size.
View SolutionAssertion (A) : Frenkel defects are shown by AgX.
Reason (R ) : Ag⊕ ions have small size.
View SolutionAssertion : Due to Frenkel defect, density of the crystalline solid decreases. Reason : In Frenkel defect, cation or anion leaves the crystal.
View SolutionAssertion (A) Both Frenkel and Schottky defects are stoichiometric defects. Reason (R ) Both defects change the density of the crystalline solid.
View SolutionAssert : due to Frenkel defect, density of the crystalline solid decrases. Reason : in Frenkel defect cation and anion leaves the crystal.
View SolutionAssertion : Frenkel defects is exhibited by alkali halides Reason : Alkali ions have small size.
View SolutionFrenkel defect is shown by crystals having ...... coordination number
View SolutionAssertion : due to Frenkel defect, density of the crystalline solid decreases. Reason : in Frenkel defect cation and anion leaves the crystal.
View SolutionAssertion : In Frenkel defect, density of the crystalline solid does not change.
Reason : In Frenkel defect, no cation or anion leaves the crystal.
View Solution
