For the reaction: aA+bB→cC+dD
Rate =dxdt=−1ad[A]dt=−1bd[B]dt=1cd[C]dt=1dd[D]dt
In the following reaction,
xA→yB
log.[−d[A]dt]=log.[d[B]dt]+0.3
where negative isgn indicates rate of disappearance of the reactant. Thus, x:y is:
A
1:2
B
2:1
C
3:1
D
3:10
Video Solution
Text Solution
The correct Answer is:B
xA→yB
−d[A]xdt=1yd[B]dt
log.(−d[A]dt)=log.d[B]dt+log.xy
∴log.(xy)=0.3
∴xy=2
or x:y=2:1
|
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
For the reaction: aA+bB→cC+dD
Rate =dxdt=−1ad[A]dt=−1bd[B]dt=1cd[C]dt=1dd[D]dt
A reaction follows the given concentration-time graph. The rate for this reaction at 20s will be
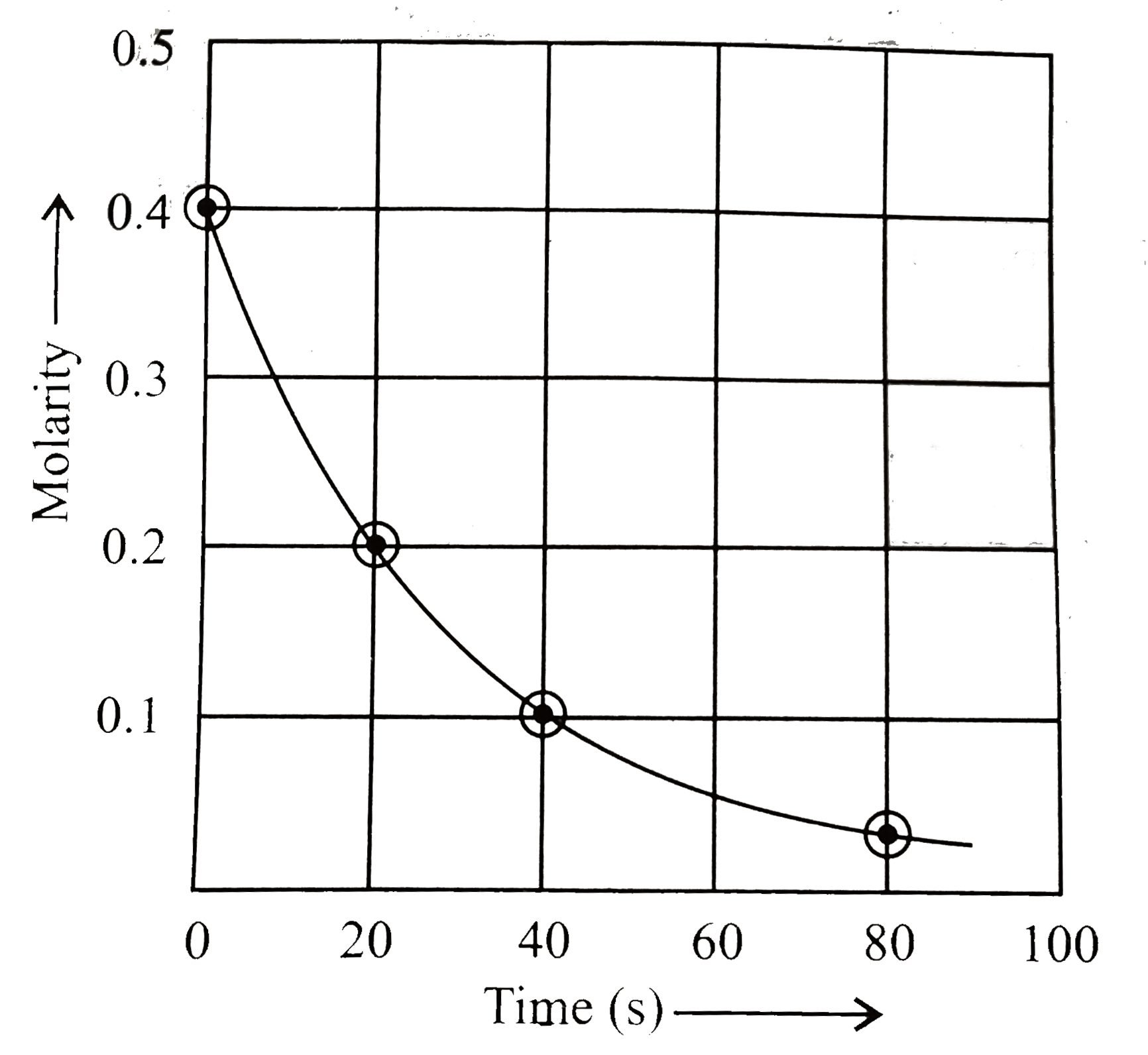 A4×10−3Ms−1B1×10−2Ms−1C2×10−2Ms−1D7×10−3Ms−1
A4×10−3Ms−1B1×10−2Ms−1C2×10−2Ms−1D7×10−3Ms−1For the reaction: aA+bB→cC+dD
Rate =dxdt=−1ad[A]dt=−1bd[B]dt=1cd[C]dt=1dd[D]dt
The rate of formation of SO3 in the following reaction 2SO2+O2→2SO3 is 100g−1min. Hence the rate of disappearance of O2 isA2g−1minB20g−1minC200g−1minD50g−1minIn the reaction xA→yB,log{−d[A]dt}=log{+d[B]dt}+0.3 Then, x:y is
A2:1B1:2C3:1D3:10
For a reaction of the type Aa+bB→products
(−)d[A]dt is equal to
(A) −d[B]dt
(B) −bdd[B]dt
(C) −ab×d[B]dt
(D) −ba×d[B]dt
View SolutionIn the following reaction, xA→yB
log10[−d[A]dt]=log10[d([B])dt]+0.3010 ‘A’ and ‘B’ respectively can be:
View SolutionFor the reaction: aA+bB→cC+dD
Rate =dxdt=−1ad[A]dt=−1bd[B]dt=1cd[C]dt=1dd[D]dt
For reaction 3BrOɵ→BrOɵ3+2Brɵ, the value of rate constant at 80∘C in the rate law for −d[BrOɵ]dt was found to be 0.054Lmol−1s−1. The rate constant (k) for the reaction in terms of d[BrOɵ3]dt is
View SolutionThe rate of the reation is expressed in different way as followed :
−1m.d[A]dt=+1nd[B]dt=−1pd[C]dt=+1qd[D]dt
The reaction is
View Solutionअभिक्रिया xA→yB में, log{−d[A]dt}=log{+d[B]dt}+0.3तब, x : y है:
View Solution
