Explain the extraction of iron from haematite.
Text Solution
Haematite ore Fe2O3, contains silica (SiO2), alumina (Al2O3) and phosphates as impurity or gangue. Coke is used for the reduction of ore.
To remove acidic gangue (SiO2) a basic flux CaO is used which is obtained from time stone CaCO3.
(1) Roasting: The concentrated ore is heated strongly in a limited current of air, during which moisture is removed and the impurities are oxidised.
S+O2Δ−−→SO2↑⏐⏐,2As+3O2→As0O3↑⏐⏐
P4+5O2→2P2O5↑.
FeO present in the ore is oxidised to Fe2O3.
4FeO+O2→2Fe2O3
(2) Reduction (or smelting) : The roasted or calcined ore is then reduced by heating in a blast furnace.
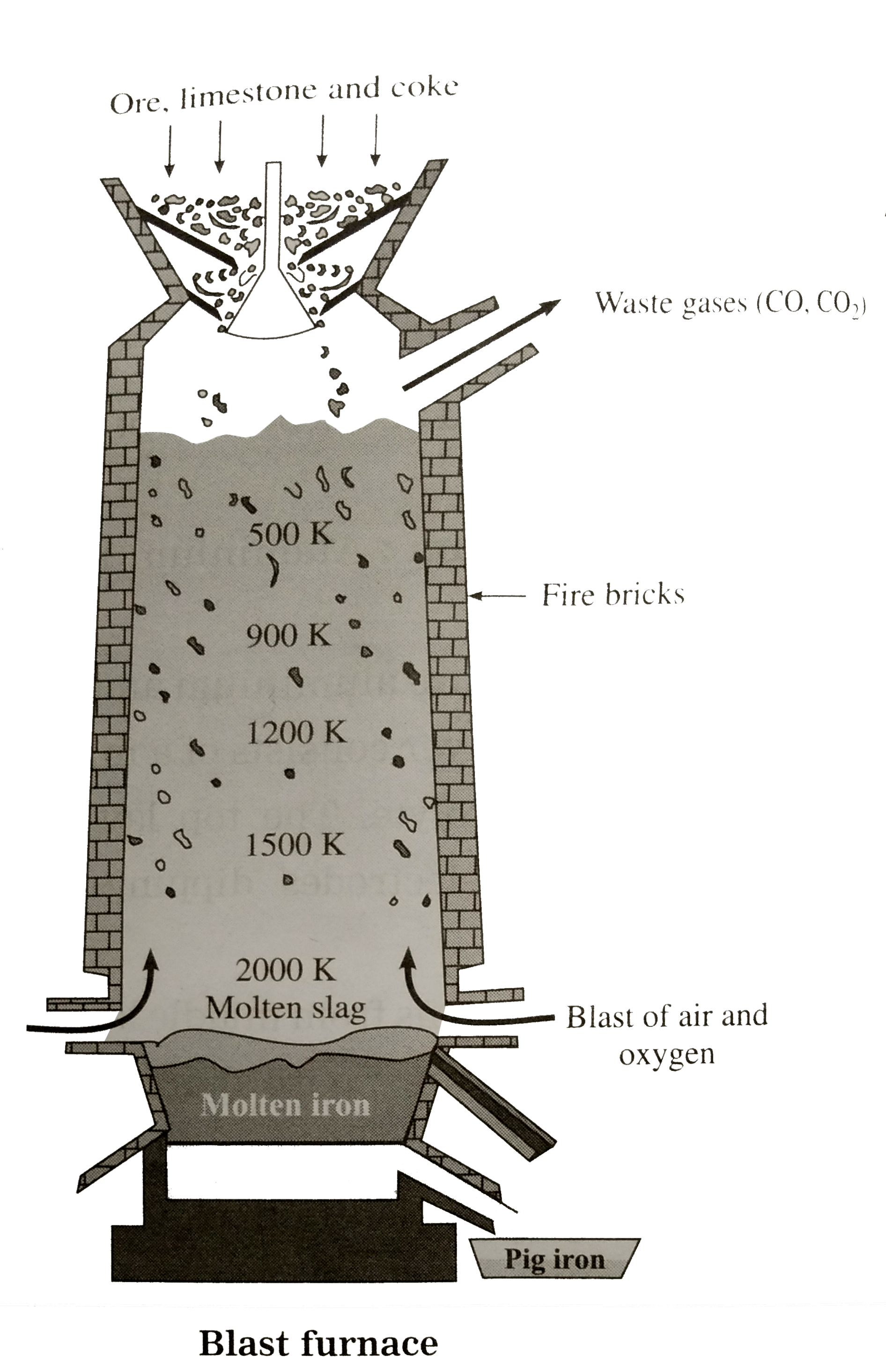
Blast furnace has three parts (i) the hearth, (ii) the bosh and (iii) the stack.
The roasted ore in mixed with coke and limestone in the approximate ratio of 12 : 5: 3. A blast of hot air at about 1000 K is blown from downwards to upwards by layers arrangement. There are three zones of temperature in which three main chemical reactions take place.
(i) Zone of combustion : The hot air blown from the bottom of the furnace oxidises coke to CO which is an exothermic reaction, due to which the temperature of the furnace rises.
C+12O2→COΔH=−220KJ
The hot gases with CO rise up in the furnace and heat the chare coming down. CO acts as a fuel as well as a reducing agent.
(ii) Zone of reduction : At about 900K, CO reduces Fe2O3 to spongy (or poropus) iron.
Fe2O3+3CO→2Fe+3CO2
Carbon also reduces partially Fe2O3 to Fe.
Fe2O3+3C→2Fe+3CO
Zone of slag formation : At 1200 K limestone, CaCO3 in the charge, decomposes and forms a basic flux CaO which further reacts at 1500K with gangue (SiO2,Al2O3) and forms a slag of CaSiO3 and Ca3AlO3 which is removed from the bottom.
(iv) Zone of fusion : The impurities in ore like MnO2 and Ca3(PO4) are reduced to Mn and P while SiO2 is reduced to Si. The spongy iron moving down in the furance melts in the fusion zone and dissolved the impurities like C, Si, Mn, phosphorus and sulphure. The molten iron collects at the bottom of furnace. The lighter slag floats on the molten iron and prevents its oxidation.
The molten iron is removed and cooled in moulds. It is called pig iron or cast iron. It contains about 4% carbon.
|
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
The chief ores of iron are haemalite (Fe2O3) , magnetite (Fe3O4) , limonite (FeO(OH)) and siderite (FeCO3).In the extraction of iron , oxides ores of iron, after concentration through calcination/roasting in reverberatory furnace are mixed with lime stone and coke and fed into a blast furnace. Here, the oxide is reduced to the metal.
Which of the following is obtained as a slag in the extraction of iron from haematite ore ?AFeSiO3BCaSiO3CCaCO3DMgSiO3The slag formed in the blast furnace during the extraction of iron from haematite is
ACa3(PO4)2BCaSiO3CFeSiO3DMnSiO3The reaction(s) which (do) not occur in the reduction zone in the extraction of iron from haematite ore is(are):
AFe2O3+CO→2FeO+CO2BFeO+CO→Fe+CO2CFe2O3+3C→2Fe+3CODCaO+SiO2→CaSiO3
The reaction (s) which does (do) not occur in the reduction zone in the extraction of iron from haematite ore is (are)
View SolutionThe main reaction occuring in blast furnace during the extraction of iron form haematite is
View SolutionIn the extraction of iron from haematitie, the charge used is haematite, coke and lime stone in the following weight ration
View SolutionThe flux used in the extraction of iron from Haematite in te blast furnace is [EAM(ENG)2014]
View SolutionCalcination silicate(slag) formed in the slag formation zone in extraction of iron from haematite ore:
View Solution

