How does a transition metal ion acquire a colour?
Text Solution
(1) The transition metal ions has have incompelety filled (n-1) d-orbitlas.
(2) d-orbitals are degenerte orbitals, i.e., all five suborbitals of d-orbitals namely dxy,dyz,dx2−y2,dz2 have nearly equal energy in a free metal ions.
(3) In compounds , in the pressnce of anions or complexing ligands, degenergy is lost and these five degenerate d-orbitals splits into two groups as follows.
(i) One group of d-orbitals have lower energy and consists of three orbitals namely dxydxy and dxy .They are called t2g orbitals .
(ii) The second group of d-orbitals have higher energy and consist two orbitals dx2−y2 and dz2 and they are called eg orbitals.
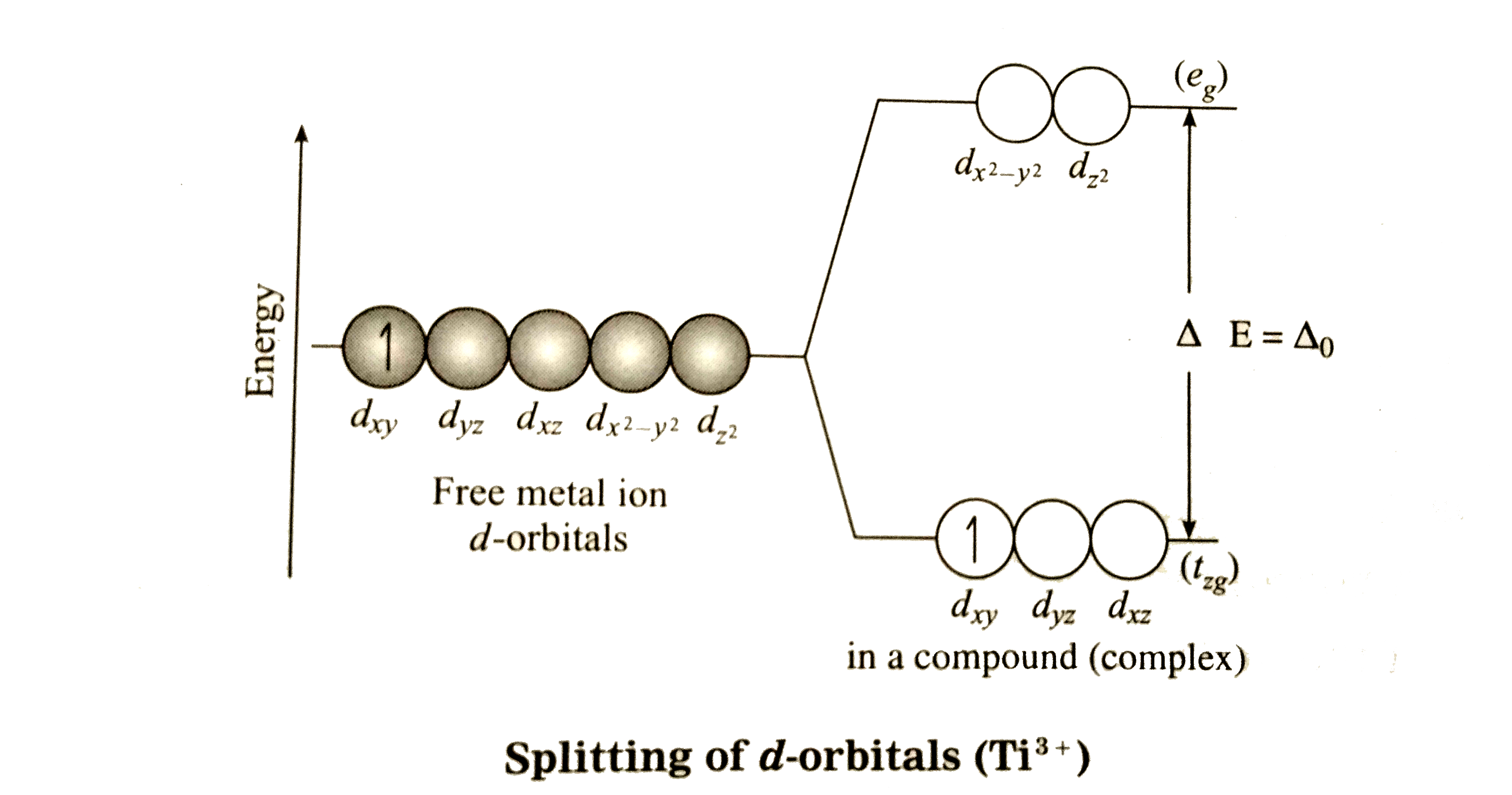
(4) They energy differenec ΔE between these two sets of d-orbitals is called crystal be field splitting energy (CFSE).
(5) ΔE has very small value equal to the energy of electromagnetic radiation in the visible region (ΔEhu=hcλ)
(6) There ariese a transition of one or more unpaired electrons form t2g orbitals to eg orbitals due to the absorption of radiation in the visible region.
(7) When the electron d-orbitals (t2g) it transmits the light that is complementary in colour to colour of radiation absorbed. This imparts a characteristic colour to the compound or a metal ion.
For example in the figure the transition of one elecrons (3d1) in the complex [Ti(H2O)6]3+ is shown.
|
Similar Questions
The colour of transition metal ions is due to
View SolutionExplain why transition metal ions are usually coloured.
View SolutionTransition metal ions are generally coloured. Why?
View SolutionTransitional metal ions shows colour due to
View SolutionThe colour of the transition metal ions is due to
View SolutionThe colour of transition metal ion is attributed to:
View SolutionThe colour of the transition metal ions is//are due to:
View Solutionthe colour of the transition metal or its ion is due to
View Solution

